What are AI Guardrails?
|
|
Artificial Intelligence has crossed the chasm from being primarily a research pursuit to becoming a key ingredient of the operational infrastructures for businesses across every sector, enabling automation and decision-making at scale as well as large-scale personalization. Being both probabilistic and generative: that makes it very powerful, but also very unpredictable. Flexibility that makes it possible to be creative and insightful also permits you to hallucinate, act by accident, or cause harm in a way that more rigid software never could.
That’s where AI guardrails come in, acting as the bumpers and brakes that steer AI back into alignment with ethical, regulatory, and business expectations. As a highway guardrail stops cars from careening off the road, these controls prevent AI from producing false, unsafe, or noncompliant outputs. By no means stifling innovation, guardrails allow companies to confidently roll out AI in even the most high-risk areas like healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and customer experience.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
Understanding AI Guardrails
AI guardrails describe the structures, constraints, guidelines, and mechanisms that support safe and responsible operationalization of artificial intelligence systems. They are guardrails: a form of protective barrier that plays the same role as the physical guardrails on a highway, keeping AI from veering onto dangerous ground or engaging in unintended behavior. These guardrails may be technical, organizational, or ethical – even legal and social. They may exist during:
- Data preparation
- Model training
- System deployment
- Real-time AI execution
- User interaction
- Post-deployment monitoring
At their core, AI guardrails answer one critical question:
“How do we develop AI systems that behave in a safe and predictable manner, while also aligning with social norms?”
Read: Generative AI in Software Testing
To further understand the concept, imagine a self-driving car. The car is responsible for sensing, analyzing, predicting, and deciding. Without guardrails, it could:
- Break speed limits
- Ignore traffic rules
- Misinterpret signs
- Endanger pedestrians
- Make chaotic or unpredictable choices
But with guardrails, you have speed limiters, rule-based limitations, safety rules of operation, outside observation, and fail-safe mechanisms. With all these features, the car works safely and predictably.
It’s the same for AI that powers software, business operations, or digital products. The more autonomous an AI system is, the more guardrails it requires.
Read: What are AI Hallucinations? How to Test?
Why AI Guardrails Are a Critical Requirement Today
Artificial intelligence is no longer a technology bound to the labs. It’s ingrained everywhere, like in chatbots, automation platforms, analytics tools, virtual assistants, enterprise systems, testing tools, medical devices, and government applications. With this growth, the complexity and risk surface has exponentially grown.
There are several reasons why we have come to need guardrails:

Read: AI Slop: Are We Ready for It?
Preventing Harmful Or Unsafe Outputs
AI systems are capable of creating biased outcomes, inappropriate content, or dangerous advice by mistake when fed with flawed training data or due to errors in model interpretation. Such malicious outputs potentially could cause real-world harm, misinform users, or reinforce undesirable stereotypes. Guardrails can mitigate some of these risks by filtering potential outputs, acting as a safety-carapace layer, and maintaining models within an acceptable range.
Ensuring Compliance With Laws And Regulations
All the world’s leading global regulations, such as the EU AI Act, GDPR, NIST AI RMF, and ISO/IEC standards, require stringent governance for AI systems. Companies must prove that their AI fulfills the requirements for transparency, fairness, privacy, and accountability. The guardrails serve as the structural underpinning on which to rely, ensuring that staying within the bounds of law is attainable and predictable.
Protecting User Trust And Brand Reputation
Just one incorrect or harmful AI output can suddenly dismantle customer trust and undermine a company’s credibility. Those mistakes also risk drawing regulatory inquiries and presenting long-term public-relations challenges. Guardrails are a way to ensure the AI always acts safely and responsibly.
Maintaining Accountability And Transparency
AI-based decisions need to be explainable, traceable, and auditable in order to measure the accountability of an organization. Guardrails impose documentation, logging, and oversight mechanisms that render AI operations interpretable. That transparency not only builds trust but also lowers risk and supports ethical decision-making.
Aligning AI With Organizational Values
Each business has its own values, ethics, and operational procedures that AI should represent. AI can act beyond these intended borders if it does not have strong guidance. Guardrails are the tools that represent organizational values and transform them into predictable behavior by AI, ensuring consistency across all processes.
Preventing Model Drift And Unintended Evolution
AI models dynamically evolve with time as new data trends and changes in circumstances occur. Without supervision, these transitions may result in subpar or unexpected behavior. The guardrails keep the system on its original target and prevent it from getting off-course at any stage during operations.
In short, guardrails ensure that AI remains safe, compliant, aligned, and controllable, even as it becomes more powerful.
Read: Will AI Replace Testers? Choose Calm Over Panic
Types of AI Guardrails
There are a lot of different kinds of AI guardrails. They work best when applied at several stages of the AI life cycle. We can broadly divide guardrails into the following five types: technical, ethical, procedural, regulatory, and user-level. Each plays a distinct role in maintaining AI quality and integrity.
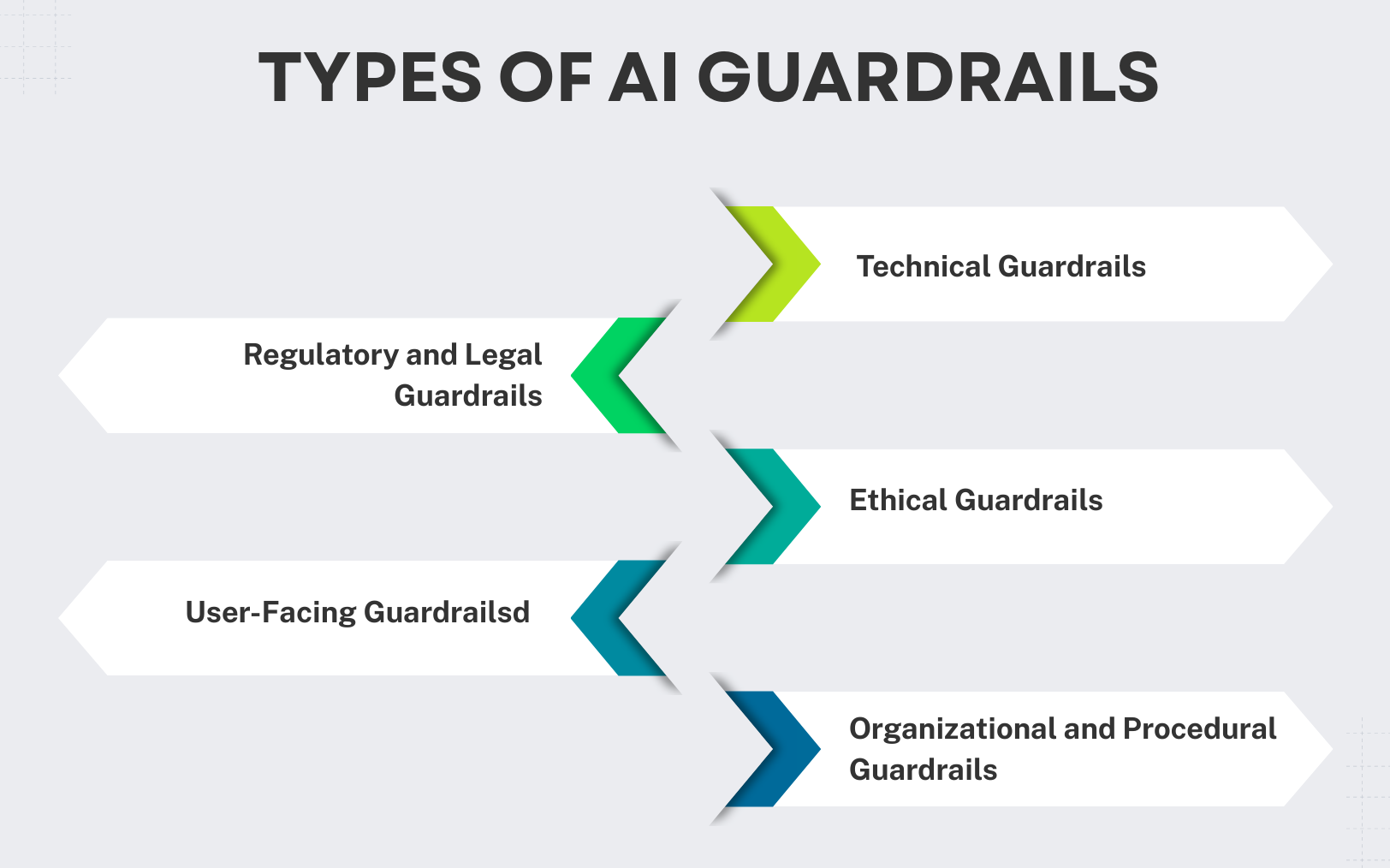
Technical Guardrails
Technical guardrails are programmed into the AI system itself, in the form of rules, algorithms, and monitoring layers that govern its behavior. They help determine what the AI is allowed to say, what data it can connect to, and how it processes responses in real time. These guard rails provide the immediate and essential model of defense, particularly in high-risk environments.
Examples:
- Content filters
- Toxicity detection
- Bias mitigation algorithms
- Prompt filtering and rewriting
- Access control mechanisms
- Real-time model monitoring
- Reinforcement learning safety layers
- Rate limiters
- Red-teaming simulations
Ethical Guardrails
Ethics and guardrails ensure that AI serves societal, moral, and cultural aspirations and does not operate based on just statistical descriptions. Principles they stress are fairness, inclusiveness, transparency, safety, privacy, and accountability. These are the values that underpin technical and organizational decisions about how AI should act responsibly.
Examples:
- Fairness audits
- Bias-reduction guidelines
- Transparency reports
- Privacy-by-design rules
- Ethical review checklists
Organizational and Procedural Guardrails
Organizational guardrails consist of governance structures and formal processes to ensure that AI is done in a responsible manner, from development through deployment into operation. These include human supervision, documentation format, and streamlined approval flows. These guardrails enforce quality, compliance, and control throughout all phases of the AI lifecycle.
Examples:
- Human-in-the-loop validation
- AI ethics committees
- Incident reporting systems
- Data governance rules
- Audit workflows
- Documentation standards
- Rules for model versioning
- Employee training programs
- Approval protocols for new AI features
Regulatory and Legal Guardrails
Regulatory guardrails are issued by governmental authorities and mandate that certain legal standards for safety, privacy, transparency, and automated decision-making are followed. These regulations mandate the need for enterprises to keep their AI systems responsible and compliant. Organizations need to have processes in place that show they are following these laws when it comes to all their AI activities.
Examples:
- Privacy-by-design policies
- Risk classification and reporting
- User consent mechanisms
- Explainability requirements
- Logging and audit trails
User-Facing Guardrails
User-level guardrails define how humans interact with AI by preventing misuse and making clear the boundaries of systems. These guardrails shape how users act through warnings, limitations, and protective user interface elements. They are used to provide safe and predictable interaction between users and an AI system.
Examples:
- User instructions and warnings
- UI constraints
- Feedback mechanisms
- Permission controls
- Rejection of harmful user prompts
- Clear disclaimers
Read: How to Keep Human In The Loop (HITL) During Gen AI Testing?
How AI Guardrails Work?
AI guardrails function through a combination of detection, control, enforcement, and feedback. While AI technologies vary, the principles behind guardrail operation remain consistent. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the core mechanisms.
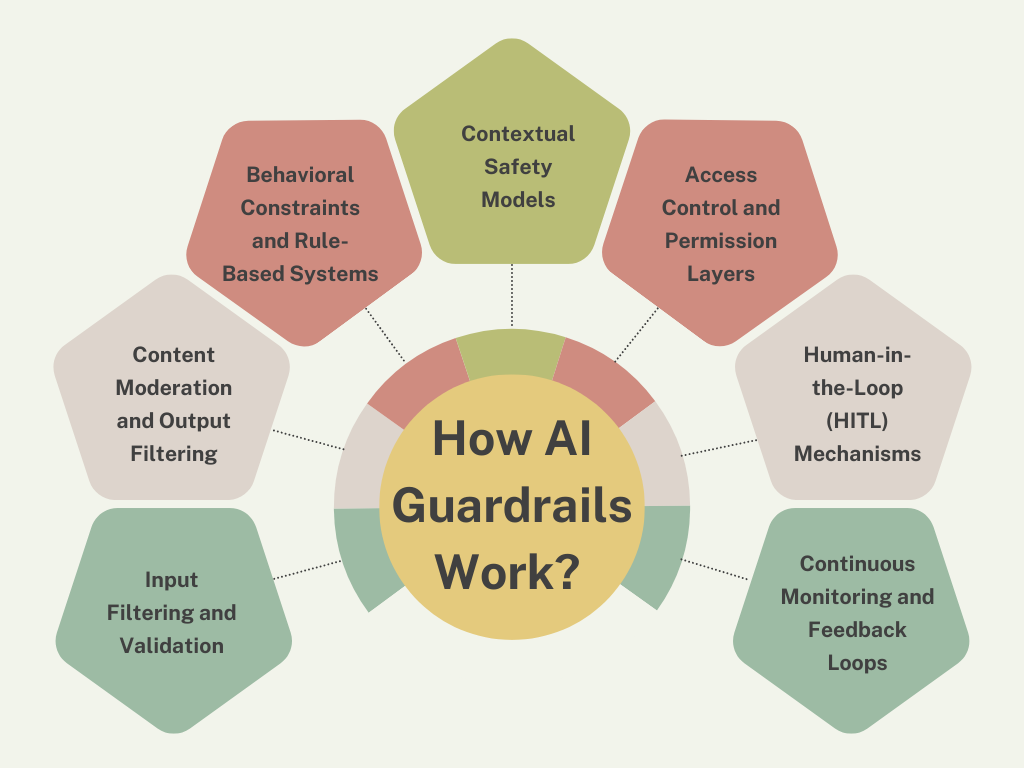
Input Filtering and Validation
Input filtering screens prompt by checking what the AI will process for harmful, malicious, or unlawful intent. It can block unsafe commands, deny misuse, and guide users to more secure alternatives. With the ability to catch threats such as maliciously generated prompts and return a safety message, these guardrails arrest harmful content before it even makes it to the model.
Content Moderation and Output Filtering
After the model generates a response, output guardrails evaluate it for toxicity, misinformation, bias, or inappropriate content. Such filters strip out unsafe language, swap bad words, and steer the AI towards safer choices. It provides an important two-fold protection: input filtering and output moderation, which greatly mitigates the possibility of unsafe outputs for end users.
Behavioral Constraints and Rule-Based Systems
Behavioral constraints are predefined rules that, more or less explicitly, infer how AI should or should not behave in certain situations. “Never diagnose with a medical test,” and “Never post toxic comments.” These statements are enacted through reinforcement learning, fine-tuning, and reward-aligned optimization. These limitations ensure consistent and predictable AI behavior in all interactions.
Contextual Safety Models
Contextual safety models work with the main AI system to figure out what someone wants, find subtle risks, and look at all the interactions as a whole. They help the AI understand conversations on a deeper level, which lets it tell the difference between harmless questions and sensitive topics like self-harm. The AI can give safer, kinder, and more appropriate answers because it knows the context.
Access Control and Permission Layers
Access control guardrails make sure that AI is operating based on the data and tools it has permission to access. These layers enforce the authentication, authorize data sources, and user roles to restrict capability exposure. They moderate access to prevent AI from acting out of bounds or being too powerful in a system.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) Mechanisms
HITL guardrails insert human reviewers into the decision chain for high-risk or high-stakes AI outputs. Humans verify the accuracy and fairness of results produced by systems that are applied in fields such as health care, fraud detection, and hiring. This is a fail-safe to prevent very important decisions from being made only by machines.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback Loops
While this ensures that systems are better monitored, guardrails can adapt as the AI system evolves due to new data, changing environments, or user behavior. These monitors follow errors, drift, compliance lapses, and deleterious outputs to sense emerging risks. Observations of monitoring feed into updates that enhance the safety and quality of AI over time.
Read: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Differences
How do AI guardrails generate value?
AI guardrails deliver value beyond compliance by building customer confidence, defending companies against legal risks, and facilitating responsible AI use. When companies succeed in using guardrails, they show a dedication to acting ethically with their technology that can make it easier for them to hire and keep top employee talent. By building guardrails into enterprise platforms, businesses can deploy and scale AI responsibly while mitigating risks like privacy violations, biased results, hallucinations, and misuse of intellectual property (IP).
A real-world instantiation of value creation is shared by ING, which launched an AI-enabled customer support chatbot that was armed with a bevy of guardrails. These guardrails filtered out sensitive content, prevented risky advice, and ensured each conversation was compliant. The consequence has been that ING was able to deliver safe, reliable customer experiences while staying in compliance and building trust in its AI systems.
Read: Why Gen AI Adoptions are Failing – Stats, Causes, and Solutions
Where AI Guardrails Fail
The most sophisticated guardrails are never perfect, and can fail under complex or unexpected circumstances. These constraints reinforce the importance of not letting one down, with continuous monitoring as well as updates and human control over AI systems.
- Ambiguous user intent: AI doesn’t always know the difference between educational, harmful, or accidental searches and ends up blocking too much – or too little.
- Contextual misunderstanding: Guardrails can occasionally misinterpret benign content as harmful, resulting in overblocking.
- Bias in safety systems: The guardrails themselves could come pre-biased from their training data, enforcing unevenly.
- Over-reliance on filtering: Too much filtering can stifle creativity and diminish the value of AI-led suggestions.
- Adversarial prompt attacks: Experienced users may be able to break through guardrails with veiled instructions, encoded messages, or indirect language.
- Data and model drift: Guardrails are eroded over time as the model gets updated if not regularly maintained.
Read: Generative AI vs. Deterministic Testing: Why Predictability Matters
Designing AI Guardrails: Principles and Best Practices
Implementing robust AI guardrails involves a thoughtful, multilayered approach that revolves around safety, usability, and flexibility. Thoughtful guardrails put AI systems on a stable path to success and establish flexibility in the face of emerging risks and evolving business requirements. By respecting clear principles and a disciplined process of execution, organizations will be able to keep their AI systems safe and matched up with expectations.
Core Principles of Strong AI Guardrails
- Safety first: The top priority here is to not cause harm rather than convenience or speed, so all outputs are and must be safe from harmful or dangerous content.
- Transparency: Users must have visibility into the system’s constraints and security so they can wield AI responsibly with confidence.
- Value alignment: The behavior of AI aligns with the values and normative standards of the organization.
- Adaptability: The AI guardrail should be updated according to new risks, new data patterns, and environmental changes in the system’s operation.
- Layered defenses: A combination of protective measures has to be employed. Having a single guardrail cannot eliminate all risk completely.
- Human judgment: Human oversight is necessary for high-stakes choices so that human expertise remains the ultimate judge of our policies.
A Structured Approach for Building Guardrails
- Understand risks: Companies need to find out what could go wrong and how enclosures can be limited before they build any fences.
- Classify the model: In identifying the risk level of a model, you can define how strict and complex its guardrails should be.
- Define operational boundaries: Transparent boundaries ensure the AI functions only within safe, authorized actions.
- Build multi-layer guardrails: A mixture of input filtering, output filtering, monitoring, and oversight ensures safety adoption.
- Test rigorously: Guardrails must be tested constantly, red-teamed, stressed, and validated to ensure they are working as expected.
- Monitor continuously: Continuously monitoring can identify drift, anomalies, and emerging threats, for adjustments as needed to respond appropriately.
Read: Types of AI and Their Usage
The Future of AI Guardrails
As AI becomes more sophisticated, we’re likely to see guardrails become capable of performing autonomous safety checks and have capabilities such as real-time intent modeling and predictive risk detection. Enterprises will increasingly utilize multi-model guardrail ecosystems, standardized global regulations, and AI systems that monitor and enforce guardrails on other AI systems. This transition will create AI safety as its own field of study, in the same way that cybersecurity emerged many decades ago.
In turn, companies will invest in AI safety teams, governance platforms, predictive risk scoring tools, and industry-standard guardrail frameworks to prevent any bad practices from proliferating. These investments will enable the safe deployment of AI at scale, reducing risk for operations and regulation. Rather than inhibiting innovation, guardrails will pave the way for safe, responsible, and trusted AI expansion.
Read: Integrating AI into DevOps Pipelines: A Practical Guide
Wrapping Up
AI guardrails are not key features; instead, they’re the foundation of AI systems that are safe, reliable, ethical, compliant, and trusted. As AI moves towards greater autonomy and control, it will be necessary to put guardrails around the intelligence in order to transform raw capability into something that can be controlled, predicted, and made compatible with human desires. They will decide whether AI becomes a secure global common good or an unmanaged risk. For any and all organizations, guardrails are not limits but the means of responsible, scalable, and sustainable AI advancement, sheer stabilizing forces that safeguard your organizational balance.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












