Startup Testing: How to Move Fast Without Breaking Everything (Strategies, Tools, and Templates)
|
|
Nowadays, startups are everywhere. Startups are built on speed. This speed encompasses speed of execution, speed of learning, and speed of iteration. Founders are told to “move fast,” “ship early,” and “fail forward” to stay in the competition. In this speedy development and release culture, startup testing is often seen as a luxury, something to be added later, once the product stabilizes or the company grows.
But in reality, this is where most startups fail.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
This article examines how startups can develop intelligent, lightweight, and scalable testing strategies that enable them to move quickly without compromising quality.
What is Startup Testing?
Startup testing is the methodology to validate a business idea, product, or feature with real users early and often.
It uses methods like hypothesis testing, beta testing, and Minimum Viable Product (MVP) testing to identify flaws, collect feedback, and confirm product-market fit before significant resources are utilized. This saves founders time and money while building user trust. It is crucial for startups to make data-driven decisions, reduce risk, and ensure their offering genuinely solves a problem for customers.

Key Goals of Startup Testing
- Validate Assumptions: A startup is always founded with an idea in mind. So before building on the guesses, confirm if your idea truly meets a market need.
- Save Resources: Design flaws and bugs are easier and cheaper to fix when found early. So save resources and cost by catching them early.
- Gain User Insights: Understand users’ attitudes toward the product by analyzing what they value, how they interact with it, and what is missing.
- Build Trust: Deliver a quality product that meets user expectations, fostering loyalty.
- Achieve Product-Market Fit: Consider the market feedback and iterate quickly to find the right product that fits the market.
Why It’s Critical for Startups
- Data-driven Decisions: This is one of the primary reasons why testing is important for startups. It enables the startups to challenge their hypotheses and theories in a controlled environment. Using testing, startups can gather concrete data that can refute or support their assumptions instead of solely relying on intuition or past experiences. This way, startups can make more informed and data-driven decisions and reduce expensive errors and overlooked opportunities.
- Improvement and Optimization: With testing, startups can identify areas that require improvement and optimization. It is necessary to determine what resonates with the target audience by comparing different versions of a product, marketing campaign, or user experience. Startups can gather these insights by testing and using them to refine and enhance various business aspects, from product development to customer acquisition and retention strategies. By improving and optimizing regularly, startups can achieve better performance and growth.
- Risk Mitigation: Yet another area tied to startups. There are various risks associated with a startup that should be avoided or mitigated before investing heavily in a product and its associated market campaigns. Testing helps startups assess potential success on a smaller scale. By conducting user testing, market research, or pilot programs, startups can determine potential challenges or issues early on. This way, they can make prior adjustments before committing substantial resources. Startups can thus minimize risks and avoid costly setbacks.
- Continuous Improvement: Startups remain agile and adaptable in the face of rapidly changing market conditions, consumer preferences, and technological innovations by regularly conducting tests and experiments. Testing fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within a startup. Teams constantly seek out new ways to enhance customer experience, drive better results, and improve the overall quality of the product. This is vital for the startup to stay in the competition and be relevant in the marketplace.
Core Principles for Startup Testing
- Pragmatic Prioritization: Testers should consider the crucial systems, such as payments, user trust, and so on, with the highest priority. They can allow faster iteration in low-risk features.
- Early and Frequent Validation: Validate startup ideas with users before coding, by using usability tests and prototypes, ensuring you build something people want.
- Strong Foundation: The Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is not disposable; instead, build a solid, intentional architecture to avoid future technical debt.
- Focus on Learning: In addition to measuring outputs like lines of code or features shipped, measure learning and business outcomes (e.g., user retention) too.
- Smart Automation: Automate builds and key tests to catch issues quickly without heavy manual QA by implementing continuous integration (CI) with tools like Jenkins.
Why Testing Is Especially Hard for Startups?
It is given that testing in startups is fundamentally different from testing in large enterprises.
- Constant Change Is the Norm: Startups do not have stable requirements as features evolve frequently. Customer feedback, investor input, or market pressure can also shift product direction. For this reason, traditional test plans and rigid test cases cannot keep up with these changing requirements.
- Limited Resources: In their early stages, most startups do not have dedicated QA teams. Thus, testing responsibilities often fall on developers, product managers, or founders themselves. At the same time, time, budget, and tooling are constrained.
- Speed Is a Survival Requirement: Startups need to compete with well-funded establishments and other agile startups. For this reason, slow shipping can be fatal. Missing a launch/release window or delaying a feature can lead to loss of customers or an entire market opportunity.
- Early Mistakes Are Amplified: In the initial stages of startups, a single critical bug can destroy the user’s trust. Startups don’t have brand loyalty to fall back on like large companies. Moreover, users are unforgiving, and negative experiences spread quickly.
All these reasons and constraints create a contradiction: There are fewer resources for testing, but startups need testing more than established companies.
The Myth: “We’ll Add Testing Later”
Postponing the testing “later” is one of the most common startup mistakes. Although the logic “build fast now, stabilize later” sounds sensible, it rarely works.
- Technical Debt Adds Up: Without testing, there is a lot of untested code, and it becomes harder to change safely. Read: How to Manage Technical Debt Effectively?
- Slower Development: Teams spend more time firefighting than developing and building products.
- Fear of Change Sets In: Developers become reluctant to refactor because they are in no position to know what might break.
- Rewriting is Inevitable: Incremental improvements are rare; instead, teams resort to costly rewrites.
Generally, skipping testing early results in slower development later.
Testing Strategy for Startups
As a startup, it’s extremely important to validate your ideas, gather data, and optimize your strategies to ensure success. There are several essential test strategies/methods that startups can use to achieve these goals, as summarized here:
A/B Testing
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a powerful testing method for startups to compare two versions of a product, marketing campaign, or user experience. For example, a startup can test two different email subject lines to determine which one leads to a higher open rate. Similarly, testing two landing page designs of a website can reveal which one results in more conversions. With A/B testing, startups can make data-driven decisions and continuously optimize their efforts.
Multivariate Testing
This is an advanced form of A/B testing, using which startups can evaluate multiple variables simultaneously. Multivariate testing is especially useful when there are several website elements, such as images, headlines, and call-to-action buttons, that can be combined in various ways. Startups can test these different combinations to identify the optimal mix of elements that drives the best results.
MVP Testing
MVP testing is the process of launching a basic version of a product with core features to a target audience. MVP testing aims to gather real-world feedback, validate the core idea, and learn if people will pay for the product, and guides further development efficiently by minimizing risk and wasted resources. Key MVP testing methods include beta testing, user interviews, surveys, and analyzing usage patterns. All these methods focus on the build-measure-learn feedback loop to achieve product-market fit.
Usability Testing
Usability testing is an essential method for startups to assess the ease and intuitiveness of a product or service. Startups can observe users as they interact with a product or navigate a website, gathering valuable feedback on their experience and pinpointing areas for improvement. By testing product usability, startups can create user-friendly products and experiences that meet customer needs and expectations.
Market Research
Startups can use market research to gain insights into customer preferences, market trends, and competitive landscapes. It is a broad category of testing methods that includes surveys, focus groups, interviews, and observational studies. With thorough market research, startups can validate product ideas, identify target audiences, and develop effective marketing strategies.
Customer Surveys
Customer surveys are a specific type of market research involving direct questions to customers for feedback on products, services, or experiences. Surveys are distributed through various channels, including email, social media, or in-person interactions. Startups can gather valuable insights into customer satisfaction, preferences, and pain points. The information gathered can then be utilized to improve product and customer service strategies.
For best results with maximum chances of success, startups should employ a combination of these essential testing methods. These testing methods help startups make informed decisions, optimize their strategies, and thrive in today’s competitive business landscape.
Lean Startup Methodology
The lean startup methodology is a scientific approach to building businesses through the Build-Measure-Learn loop by rapidly testing ideas with customers. Popularized by Eric Ries, many of the methods discussed in the previous sections fall under the umbrella of the Lean Startup methodology.
This is a continuous process that focuses on validated learning and iteration to minimize waste and reduce market risk. It helps avoid the costly mistake of building something nobody wants. In this methodology, instead of extensive upfront planning, emphasis is on creating a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) to quickly gather customer feedback that provides real-world data and not assumptions. This ensures the product meets actual market requirements.
The Lean Startup Methodology Cycle
The methodology cycle consists of the following steps:
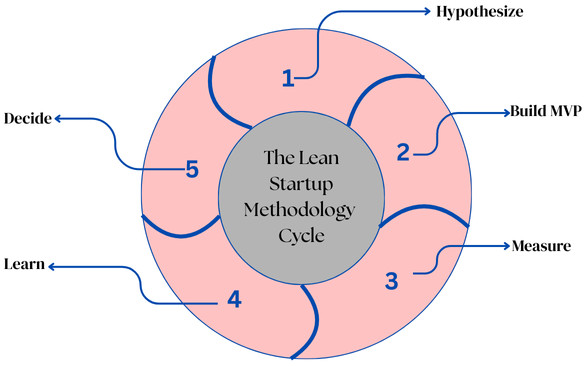
- Hypothesize: Generate a business hypothesis (e.g., “Customers want feature XXX”).
- Build MVP: Create the smallest possible product (prototype) to test the hypothesis developed in step 1.
- Measure: Release the MVP and collect actual data on how customers interact with it.
- Learn: Analyze the data for the viability and correctness of the hypothesis.
- Decide: Repeat the cycle by pivoting to a new hypothesis or persevering with the current one.
Key Benefits of the Lean Startup Methodology
- Reduces Risk: The lean startup methodology minimizes wasted time and money on unwanted products.
- Faster Time-to-Market: It helps functional products reach customers quickly.
- Customer-Centric: The methodology ensures the product genuinely solves customer problems.
- Adaptable: The lean startup methodology allows for quick adjustments to market changes.
Risk-Based Testing for Startups
When testing a startup product, not all parts are equally important. Risk-based testing helps teams focus their efforts where failures would hurt the most. Risk-based testing involves performing testing by separating the testing areas into high-risk and low-risk areas.
Identifying High-Risk Areas
- What features of the startup product directly impact revenue?
- What paths or sequences are used most frequently by users?
- What kind of failures would cause data loss or security issues?
- What integrations are critical (payments, auth, APIs)?
- Checkout and payment flows
- User sign-up and login
- Core workflows that define the product’s value
- Data integrity and permissions
Accepting Imperfection Elsewhere
Low-risk features like internal dashboards, experimental UI tweaks, or rarely used settings can be considered for lighter testing.
Such a selective criterion ensures that the testing is aligned with startup priorities.
Shift Left: Testing Early and Often
Shift left testing is one of the most powerful ways startups can test faster.
- Developers write and run tests as part of their development process.
- Bugs are treated as feedback, not as a reason to blame others.
- Testing is not a separate phase but is embedded in the workflow.
This doesn’t mean developers are QA experts, but it means that the quality is a shared responsibility among QA and developers.
Shift left testing helps to catch bugs early in the development cycle, saving the cost of fixing bugs at a later stage.
Test Automation for Startups
Although manual testing is required for startups because humans are excellent at exploring the product, it alone does not scale in a fast-moving startup. Automation is essential for propelling the product faster into the market. However, it must be used wisely.
- They try to automate everything at once.
- Developers write brittle tests tied to implementation details.
- They choose tools that require heavy maintenance.
This results in flaky tests that slow teams down, rather than helping them.
- End-to-end testing approach for critical user journeys.
- API testing for core business logic
- Smoke testing to assess basic system health
CI/CD Testing for Startups
Modern startups rely heavily on continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD). It should be ensured that testing fits seamlessly into this pipeline.
- Execute automatically on every commit or pull request.
- Provide results within minutes.
- Fail clearly and loudly when code breaks.
Slow test execution makes developers reluctant to run them, undermining trust in the system.
When tests pass, teams should feel confident deploying, thus enabling frequent releases.
Using AI for Better Startup Testing
When you need speed and intelligence, using automation powered by AI can be the solution. With AI-based testing tools, you can simplify test creation, execution, and maintenance. However, not all tools in the market can give you reliable performance. But if you opt for a tool like testRigor, you’re bound to get assured success in your QA endeavors.
testRigor is an AI-powered test automation tool. Its agentic testing abilities let you write automation tests in simple English, which is very convenient for a startup environment where the teams tend to be smaller, and team members may not possess the technical proficiency to write code. You can test across various platforms (web, mobile, desktop, mainframes) and browsers with this single solution. Automate all kinds of scenarios, even ones involving AI-based features like LLMs and chatbots. Cover different types of testing like UI testing, regression testing, functional testing, mobile and desktop testing, accessibility testing, and even API testing.
You can integrate testRigor with your existing QA ecosystem (CI/CD and test management tools) and ensure continuous testing. testRigor can reduce your test maintenance woes to a bare minimum through its intelligent AI engines that adjust test scripts even when there are small changes in the application’s UI.
Conclusion
- Focusing on high-risk areas
- Shifting testing left
- Using automation strategically
- Embracing a quality-first culture
Startups can build innovative products that can become successful. In essence, moving fast without breaking is not about testing more but about testing smarter.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












