What is Business Intelligence (BI) Testing?
|
|
Business Intelligence (BI) testing refers to the process of testing the functionality, performance, and security of BI applications, especially the flow of data between different sources into a BI system and its transformation, storage, and reporting. Testing makes sure that the BI system provides precise, trustworthy, and practical insights on huge amounts of data. BI testing is very important in assisting organizations to make decisions based on data.

With the intricacies of managing large volumes of data, numerous systems, and different reporting levels, BI testing guarantees that companies can have confidence in the information on which they base their decisions. It entails testing data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) and verifying reports, dashboards, and performance measures.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
What is Business Intelligence Testing?
Business Intelligence (BI) testing is the process of testing the functionality and performance of BI systems to ensure that data is properly gathered, transformed, integrated, and presented in reports, dashboards, or analytics tools. BI testing aims to ensure that the information utilized in the decision-making process is accurate, valid, and prepared to be consumed by the end-users. BI systems are usually associated with complicated procedures like data mining out of different sources, converting it into a format that can be used, and loading it into data warehouses or BI systems to be reported. BI testing is used to verify that every step in this pipeline works as intended.
Why is BI Testing Important?
BI (Business Intelligence) testing is essential to verify the quality of data processing and rendering components. It confirms the reliability of any insights provided by BI tools, helping organizations to make strategic decisions. BI testing also acts as a guardrail to keep businesses from making bad decisions, breaking compliance, and losing potential revenue. It ensures the accuracy of data integration, compliance, and performance.
- Data Accuracy for Decision-Making: BI testing is used to verify that the data that has been extracted, transformed, and loaded into the system is accurate and consistent.
- Data Integration Validation: BI testing confirms that data across different sources flows well through the ETL process and into the data warehouse or reporting system.
- Compliance and Regulations: BI testing will help ensure that the BI system complies with compliance or regulations (including industry-specific regulations, data privacy regulations (like GDPR or HIPAA), or financial reporting regulations) and avoids legal risks, fines, and reputational losses. Read: AI Compliance for Software.
- Performance Assurance: BI testing involves performance testing to determine whether the system is capable of processing large amounts of data and producing results in a timely fashion.
- Preventing Revenue Loss: It is used to make sure that the system provides real-time and accurate data, which enables businesses to make fast and strategic decisions.
Key Components of BI Testing
BI testing contains several critical elements that function together to promote a true, reliable, and effective business intelligence application. It is split into components, each targeting a particular part of the data lifecycle. Starting from validating source data and ETL processes, through to testing the final output in production databases, as well as more static lower environments.
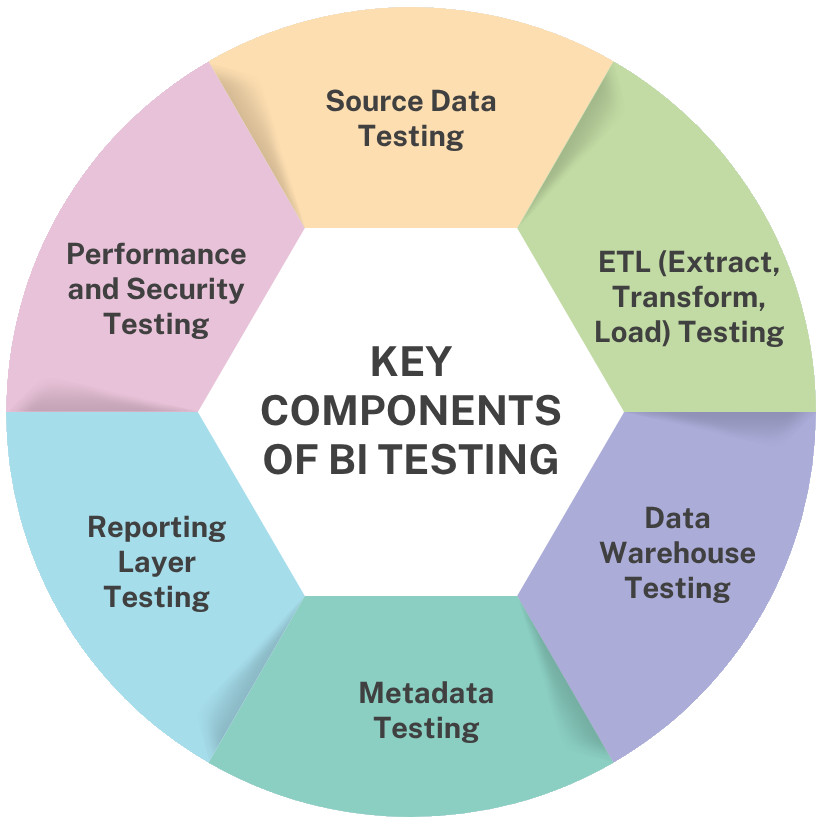
Source Data Testing
Source data testing is concerned with ensuring the accuracy, completeness, and quality of data prior to its entry into the BI system. This is done by verifying raw data across various sources (databases, APIs, or external systems) to verify that it is of the necessary quality and complies with business rules. Any problems with the source data may cause inconsistencies in the future of the ETL process or reports. Key aspects of this testing include:
- Verifying data formats, completeness, and consistency.
- Making sure that there are no errors and duplicates in the data.
- Verifying the absence, wrong, or old data entries.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Testing
ETL testing is the process of testing the ETL process, which is used to extract data from different sources, convert it into a format needed, and load it into a target system (e.g., a data warehouse or BI platform). BI testing is used to verify that data transformations (aggregations, filters, or business rules) are properly implemented, and that the data is loaded into the destination without loss or corruption. Key areas of ETL testing are:
- Extraction: Ensuring that data is properly pulled out of the source systems.
- Transformation: Making sure that data transformations are correct and fulfill business needs.
- Loading: Ensuring that the data is loaded correctly into the destination system (e.g., data warehouse) without errors or duplication.
In practice, ETL testing can be automated using intelligent test automation tools. For instance, these tools can automate validation of data extraction, transformation logic, and loading processes by comparing values from source and destination systems — all through simple natural language commands. This reduces human error and ensures that data transformations adhere to business rules consistently. Read about Why Do LLMs Need ETL Testing?
Data Warehouse Testing
It is concerned with the quality and accuracy of the data that is loaded into the data warehouse and whether the data warehouse is performing as intended. The testing ensures that the data that has been loaded into the warehouse during the ETL process is in the expected format and can be accessed correctly to be analysed or reported. Key areas of data warehouse testing are:
- Ensuring that data is consistent and available.
- Maintaining the integrity of the data warehouse.
- Testing data retrieval mechanisms (queries, reports) for accuracy and performance.
Metadata Testing
Metadata is the descriptive information that gives context to the real data in the system (field names, data types, and table relationships). Metadata testing is used to verify that the metadata within the BI system is correct and reflects the business rules and the underlying data. Key aspects of metadata testing are:
- Ensuring that metadata descriptions are consistent with the real data structure.
- Making sure that data relationships (e.g., foreign key constraints) are correct.
- Ensuring that modifications in the metadata (including schema changes) do not cause the system to crash.
Reporting Layer Testing
Reporting layer testing is the process of ensuring the accuracy, functionality, and performance of reports, dashboards, and analytics generated by the BI system. This testing is done to make sure that the right data is displayed to the end-users in a comprehensible format. The reports must align with the business needs and give actionable information. Essential features of reporting layer testing are:
- Ensuring that reports and dashboards show correct data.
- Making sure that calculations and aggregations are accurate.
- Testing the user interface (UI) to make sure that it is user-friendly and the reports are responsive.
- Validating drill-down capabilities and interactive features in dashboards.
Testing report accuracy and dashboard functionality manually can be time-consuming. With tools like testRigor, testers can verify visual components, data accuracy, and interactive dashboard elements without scripting. testRigor can validate that reports display the correct metrics, respond to filters, and remain stable across browser and device combinations.
Performance and Security Testing
Performance and security testing are done to make sure that the BI system works effectively in various circumstances and that sensitive information is not exposed to unauthorized access. Key areas of performance and security testing are:
- Performance Testing: Ensuring that the BI system is capable of processing large amounts of data, responding to complex queries in a short period of time, and performing at peak loads. Read more here: What is Performance Testing: Types and Examples.
- Security Testing: This is to ensure that there are access controls, data encryption, and other security measures that are implemented to ensure that data is not accessed or breached by unauthorized individuals.
While load and security testing often rely on specialized tools, testRigor can complement these by automating regression checks to ensure that security updates, role permissions, and data encryption validations remain intact after system updates.
BI Testing Process
The BI testing process outlines the structured approach used to validate the accuracy, performance, and reliability of Business Intelligence systems. It ensures that every stage — from requirement analysis to final sign-off is systematically tested to deliver trustworthy and high-quality data for decision-making.
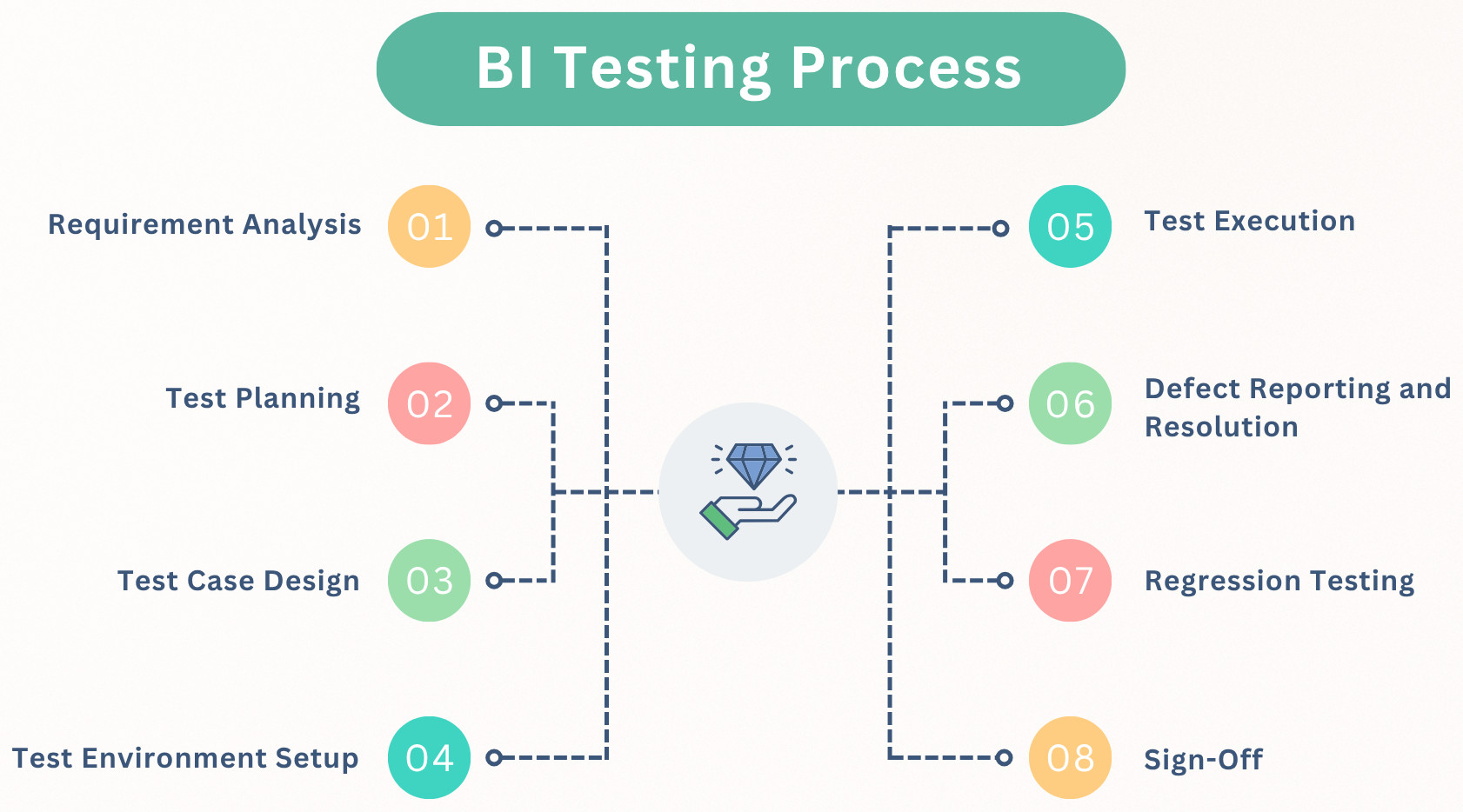
Requirement Analysis
The first and most important step in the BI testing process is requirement analysis. During this phase, the testing team works with the business stakeholders, data analysts, and developers to understand the business requirements, data flow, and reporting requirements.
Key Activities:
- Business Rules: The business logic governing data processing, transformations, and reporting.
- Data Sources Review: The review of the source systems, their structure, and the type of data extracted.
- Testing Scope: Decide what should be tested in the BI system, such as ETL processes, data warehouses, reports, or security.
This phase aims to ensure that all the business requirements are captured and well understood, which will inform the next testing phases. Read about Requirement Traceability Matrix RTM: Is it Still Relevant?
Test Planning
Test planning is the process of developing a detailed plan that includes the overall strategy, scope, objectives, resources, timeline, and deliverables of BI testing. It establishes clear expectations of what is to be tested, the manner in which testing will be done, and the success criteria.
Key Activities:
- Defining Test Objectives: Establishing the objective of each test (e.g., checking data accuracy, performance, or report accuracy).
- Resource Identification: The resources needed to conduct the testing process are identified, such as the testing tools, team members, and infrastructure.
- Planning Testing Processes: Developing a plan of various testing steps and allocating tasks.
A properly designed test plan facilitates the testing process and makes sure that every required area of the BI system is properly covered. Read about Test Planning – a Complete Guide.
Test Case Design
Test case design is the process of developing elaborate test cases according to the business requirements and the anticipated system behaviour. These test cases specify the conditions, inputs, expected results, and pass/fail criteria of each test scenario.
Key Activities:
- Developing Test Scenarios: Determining the important scenarios to test, including data extraction, transformation logic, and reporting accuracy.
- Defining Input Data: The test data needed to run the test cases must reflect real-world conditions.
- Expected Results: Determining the expected results to confirm whether the system is operating properly, e.g., proper calculations, data formatting, or performance standards.
Proper test case design will guarantee comprehensive testing and adequate coverage of both functional and non-functional areas of the BI system. Read: All-Inclusive Guide to Test Case Creation in testRigor.
Test Environment Setup
Test environment setup entails the preparation of the required infrastructure and systems to run the BI tests. This can involve the installation of test databases, BI tools, servers, and other resources required to recreate the production environment.
Key Activities:
- Replicating Production Environment: It is important to ensure that the test environment is similar to the production environment to replicate the real-world conditions.
- Setting up Tools: BI tools, test automation frameworks, and performance monitoring tools.
- Loading Test Data: Preparation and loading of appropriate test data to test the BI system in various situations.
An adequately set-up test environment is critical in ensuring that tests yield valid and meaningful results. Read more: What is a Test Environment?: A Quick-Start Guide.
Test Execution
The stage of test execution is the stage of actual testing. Test cases are run, and the results are documented to determine any defects or problems in the BI system. During test execution, automation platforms can execute BI test cases across multiple layers, from data validation to report rendering using natural language test steps. This ensures faster test cycles and reduces dependency on technical scripting skills.
Key Activities:
- Running Test Cases: Running the predefined test cases and recording test results (pass/fail).
- Monitoring System Behaviour: Observing system performance, data flows, and report generation.
- Documenting Results: Recording the results of every test case and comparing the actual results with the expected results.
The execution of the tests assists in revealing functional, performance, and security problems that must be resolved prior to the deployment of the BI system.
Defect Reporting and Resolution
Defect reporting and resolution is the process of detecting, recording, and monitoring defects detected during the execution of tests. Any problems (e.g., wrong data, system failures, or performance bottlenecks) are recorded, examined, and ranked to be resolved.
Key Activities:
- Reporting Defects: Documenting problems identified during testing with specifics (e.g., severity, reproduction steps, and screenshots).
- Cooperation with Development: Cooperation with developers to correct the defects and retest after they are corrected.
- Prioritizing Defects: Ranking defects by their seriousness and system impact.
This stage will make sure that the defects are corrected promptly and that the system is up to the standards before proceeding. Read more about Test Reports – Everything You Need to Get Started.
Regression Testing
Regression testing is done after defects are fixed or after the BI system is improved. This is aimed at making sure that new changes or fixes have not adversely affected the existing functionality. Regression testing in BI environments can be automated efficiently using testRigor. Its AI-driven automation detects changes in data structures or UI layouts, automatically adapting test scripts to prevent maintenance overhead and ensure continued test reliability after updates.
Key Activities:
- Re-running Past Tests: Re-running previously successful test cases to make sure that no functionality is lost.
- Checking New Features: Ensuring that new features or fixes do not introduce new issues.
- Checking Data Integrity: Ensuring that data flows and reports are functional after updates.
Regression testing is used to make sure that the system is stable and reliable following any changes.
Sign-Off
The last phase of the BI testing process is sign-off, during which the stakeholders officially accept the system as being ready to be deployed or used in production. In this stage, the testing team examines the results of all the testing processes and compiles final reports.
Key Activities:
- Reviewing Test Results: Ensuring that all test cases are executed, defects are corrected, and the system is in compliance with all business requirements.
- Approval: Stakeholder (e.g., business users, project managers) approval to deploy or release.
The sign-off indicates that the BI system has undergone all the required tests and is now prepared to be implemented in production.
Challenges in Business Intelligence Testing
- High Volume of Data: It is difficult to test large volumes of data, particularly in terms of accuracy, performance, and completeness.
- Data Transformation Complexity: BI systems can be characterized by complicated data transformations, and it is hard to test that the data is properly processed and transformed across the system.
- Dynamic Data: The constant dynamism of data may lead to inconsistencies, and it may be hard to test the system reliably because the data under test may change in the process.
- Integration Across Systems: BI systems tend to draw data across various sources, and it may be difficult to ensure that there is smooth integration and proper flow of data between the systems.
Conclusion
Business Intelligence (BI) testing ensures the accuracy, reliability, and performance of BI systems that support data-driven decision-making. It validates each stage of the data lifecycle from extraction and transformation to reporting to guarantee consistent and actionable insights. With automation tools like testRigor, organizations can streamline testing, reduce human error, and maintain continuous quality assurance. Ultimately, BI testing builds trust in analytics, enabling businesses to make confident and informed decisions. It serves as the foundation for ensuring that business strategies are guided by precise, real-time, and meaningful data.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












