React Testing

ReactJS, or React, is an open-source JavaScript library used for building interactive user interfaces and web applications. React is a frontend library that gradually became the most popular web framework. As of 2022, React is the second most used web framework after NodeJS. React was created by Jordan Walke, a Software Engineer at Facebook. His early prototype was called “FaxJS.” In 2017, Facebook introduced React Fiber, a new rendering algorithm that replaced the old rendering algorithm – stack, thus eliminating the slow process of rendering complex animations. React is maintained by Meta (formerly Facebook). The latest version, 18.2.0, was released in 2022. React mainly focuses on the View layer of the application’s MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern.
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- End-to-End Testing
Let’s dive deep into each of them.
Unit Testing
- Snapshot Testing
- DOM Testing
The tool we can use for both methods is called Jest. Support of other libraries like Enzyme or React-testing-library is required for DOM testing. We will cover this further down the line. Now let’s look into Snapshot testing.
Snapshot Testing
When we perform snapshot testing, the test case using the test renderer generates a quick serializable value for the React tree. Then the generated tree is compared with the reference stored for that particular test case. If the comparison matches, the test case passes; else, it’s a failure. Usually, the failure happens in case of an unexpected change or if any new functionality was added. We can perform this using Jest.
Jest
Jest is the most popular unit testing framework used across all JavaScript codebases. Using Jest, we can access the DOM via Jsdom. Jest provides a great iteration speed. Consider a sample test script for the Link component.
import renderer from 'react-test-renderer';
import Link from '../Link';
it('renders correctly', () => {
const tree = renderer
.create(<Link page="http://www.facebook.com">Facebook</Link>)
.toJSON();
expect(tree).toMatchSnapshot();
});
exports[`renders correctly 1`] = `<a
className="normal"
href="http://www.facebook.com"
onMouseEnter={[Function]}
onMouseLeave={[Function]}>Facebook</a>`;
This snapshot will be committed along with the unit test code base and code-reviewed. This snapshot will be taken as a reference for future executions. So the test case fails when there is an unexpected change in the code snippet. Consider if a new functionality has been added, so we need to update the snapshot; that can be done by executing the command – jest --update snapshot. This will regenerate a new snapshot.
DOM / Functional Testing
Snapshot testing captures the whole rendering and compares it with test iterations. In DOM testing, we test the functionality by adding assertions. To achieve that, we need to use other libraries such as Enzyme or React Testing Library.
Enzyme
The Enzyme is an open-source JavaScript library used for react apps. The Enzyme helps to manipulate, simulate, or add assertions to the script to validate the output. Using Enzyme, we can find elements and interact with them.
Jest can be used with any Javascript app, but Enzyme works only with React. Jest can be used without Enzyme, although Enzyme requires a test runner.
import Enzyme, {shallow} from 'enzyme';
import Adapter from 'enzyme-adapter-react-16';
import CheckboxWithLabel from '../CheckboxWithLabel';
Enzyme.configure({adapter: new Adapter()});
it('CheckboxWithLabel changes the text after click', () => {
// Render a checkbox with label in the document
const checkbox = shallow(<CheckboxWithLabel labelOn="On" labelOff="Off" />);
expect(checkbox.text()).toBe('Off');
checkbox.find('input').simulate('change');
expect(checkbox.text()).toBe('On');
});
DOM is more effective when compared to Snapshot testing because it covers more scenarios. Snapshot testing can be considered smoke scenarios for unit testing.
Integration Testing
In integration testing, we check how components work when they are integrated. When we perform unit testing, we mock responses from other components. But when performing integration, mocking is not required. Integration testing for React apps is done by manipulating the component state or DOM in react lifecycle methods.
- Enzyme
- React Testing Library
Since we have already gone through Enzyme, let’s get into more details about react-testing-library.
React Testing Library
RTL is built on top of DOM testing libraries by adding APIS for working with React components. RTL provides an API that returns HTML elements and also has a querying function that queries by text content or HTML data attributes. Even if we use RTL, we need a runner library like Jest or others.
import React from "react";
import { render, screen } from "@testing-library/react";
import user from "@testing-library/user-event";
import { fetchPost as mockFetchPost } from "../api";
import App from "../app";
jest.mock("../api");
test("Can search for a post using its ID", async () => {
const mockPost = {
id: "1",
title: "Post Title",
body: "Post Body",
};
mockFetchPost.mockResolvedValueOnce(mockPost);
render();
expect(screen.getByText(/submit/i)).toBeDisabled();
expect(screen.getByText(/welcome/i)).toBeInTheDocument();
expect(screen.getByText(/search.*post.*id/i)).toBeInTheDocument();
user.type(screen.getByLabelText(/post id/i), mockPost.id);
const submitButton = screen.getByText(/submit/i);
expect(submitButton).toBeEnabled();
user.click(submitButton);
user.click(screen.getByText(/back.*home/i));
await screen.findByText(/welcome/i);
});
End-To-End Testing
- Cypress
- Playwright
- Selenium
- testRigor
Cypress
Cypress is an open-source automation tool in JavaScript. Cypress provides a faster execution time with an easy setup option. Automation scripts are written in JavaScript and use Behavior Driven Development patterns. Scripts are written in the Mocha framework and use Chai as an assertions library. You can only use JavaScript or TypeScript to create tests in Cypress.
describe('login and logout', () => {
it('login', () => {
cy.visit('/');
cy.getByTestId('username').type('user123');
cy.getByTestId('password').type('pass123');
cy.getByTestId('submit').click();
});
it('logout', () => {
cy.getByTestId('home')
.should('exist').then(function (home) {
home.find('[data-cy=logout]').click();
});
cy.url().should('include', '/login');
});
});
Playwright
Playwright helps to execute E2E tests on browsers like Chrome, Edge, Firefox, Opera, and Safari. It’s a platform-independent tool that can work with most operating systems. Playwright has useful features like auto-wait, parallel executions, and trace viewer.
const { test, expect } = require("@playwright/test");
const { default: Input } = require("../src/components/Input");
test("homepage has E2E Testing with Playwright", async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto("http://localhost:3000/");
await page.screenshot({ path: "screenshot/homepage.png" });
await expect(page).toHaveTitle(/React App/);
const getStarted = page.locator("text=Get Started");
await expect(getStarted).toHaveAttribute("href", "http://localhost:3000");
await getStarted.click();
const inputField = await page.locator("id=nameInput");
await inputField.fill("codedamn");
await expect(inputField).toHaveValue("codedamn");
await page.screenshot({ path: "screenshot/inputField.png" });
});
Playwright is based on BDD and supports the Mocha and Jasmine frameworks. We can also perform basic API operations with this tool as well. If there is a request with redirecting URLs, Playwright won’t be able to execute that.
Selenium
Selenium used to be one of the industry’s favorite tools until a few years back. We don’t have to go much into Selenium, as everyone knows about this legacy tool. Many pieces of information and tutorials are available online about it. But its vast, complex structure and subpar test running speed and stability made the companies move out, looking for some lightweight tools.
testRigor
Most of the tools we discussed here for E2E automation require programming knowledge. When it comes to testRigor, the key differentiators from any other solution on the market are no-code, speed and ease of test creation, and virtually obliterated test maintenance.
click "Sign in"
enter "jacob" into "Username"
enter "jacobs-secure-password" into "Password"
click "Verify me"
check that sms to "+12345678902" is delivered and matches regex "Code\:\d\d\d\d" and save it as "sms"
extract value by regex "(?<=Code\:)[0-9]{4}" from "sms" and save it as "confirmationCode"
enter saved value "confirmationCode" into "code"
click "Continue to Login"
check that page contains text "Welcome, Jacob!"
You may need clarification about whether the above is a manual test case or an automation script. Since testRigor is independent of the programming language, all scripts are written in plain English (unless using Regex or building API testing). The most significant benefits here are the absence of implementation details and allowing anyone on the team to build automated tests and increase test coverage.
- You don’t need to use any element locators in testRigor. So while selecting an element based on how an actual user would describe it, testRigor’s integrated AI captures multiple locators for that element. The test will still pass even if one of the locators changes – which is exactly what we want for an end-to-end test from a customer’s perspective.
- testRigor is a cloud-hosted tool, so there is no need to put effort into setting up the tool and infrastructure. Once logged into the account, users can start creating scripts immediately.
- testRigor supports cross-browser testing, API automation, desktop, mobile, visual, load testing, etc. It aims to be the only tool for functional end-to-end testing you will ever need. You can read more about key features of testRigor here.
Time and effort are significant factors affecting the company’s profit. Using any tool that requires time and effort to set up and debug may be reconsidered as the market shift is currently more towards a “first to market” strategy.
How to do End-to-end Testing with testRigor
Let us take the example of an e-commerce website that sells plants and other gardening needs. We will create end-to-end test cases in testRigor using plain English test steps.
Step 1: Log in to your testRigor app with your credentials.
Step 2: Set up the test suite for the website testing by providing the information below:
- Test Suite Name: Provide a relevant and self-explanatory name.
- Type of testing: Select from the following options: Desktop Web Testing, Mobile Web Testing, Native and Hybrid Mobile, based on your test requirements.
- URL to run test on: Provide the application URL that you want to test.
- Testing credentials for your web/mobile app to test functionality which requires user to login: You can provide the app’s user login credentials here and need not write them separately in the test steps then. The login functionality will be taken care of automatically using the keyword
login. - OS and Browser: Choose the OS Browser combination on which you want to run the test cases.
- Number of test cases to generate using AI: If you wish, you can choose to generate test cases based on the App Description text, which works on generative AI.
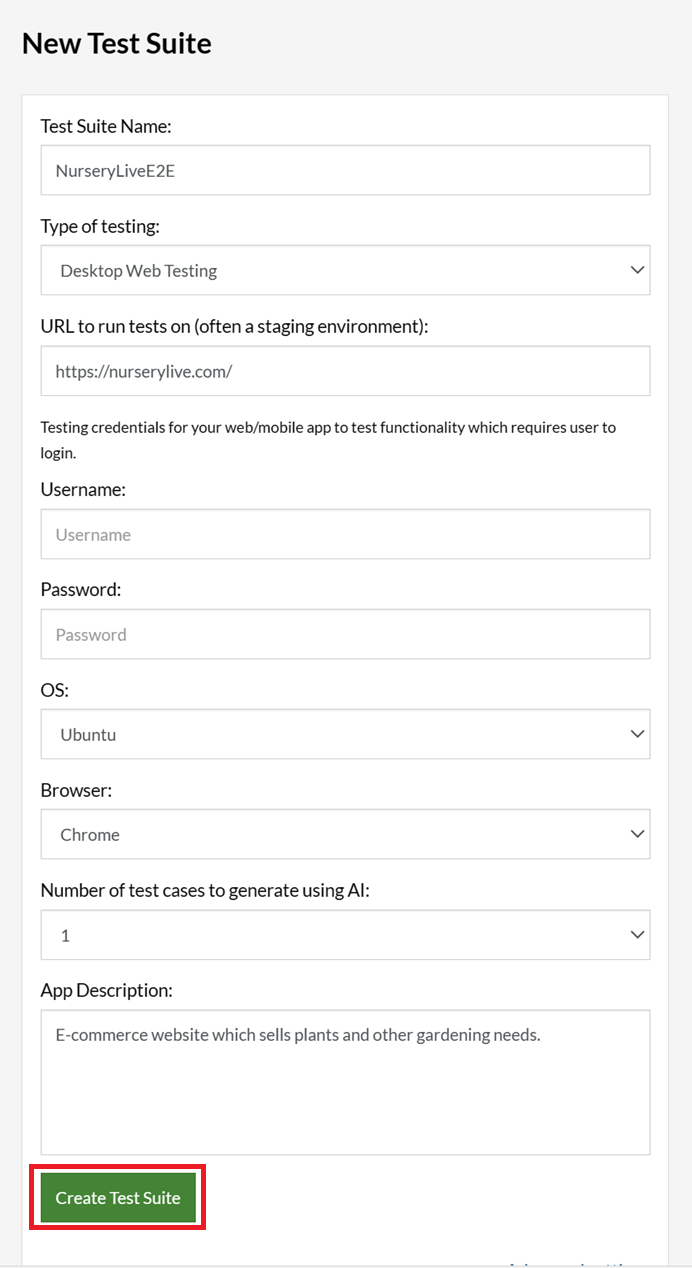
Step 3: Click Create Test Suite.
On the next screen, you can let AI generate the test case based on the App Description you provided during the Test Suite creation. However, for now, select do not generate any test, since we will write the test steps ourselves.
Step 4: To create a new custom test case yourself, click Add Custom Test Case.
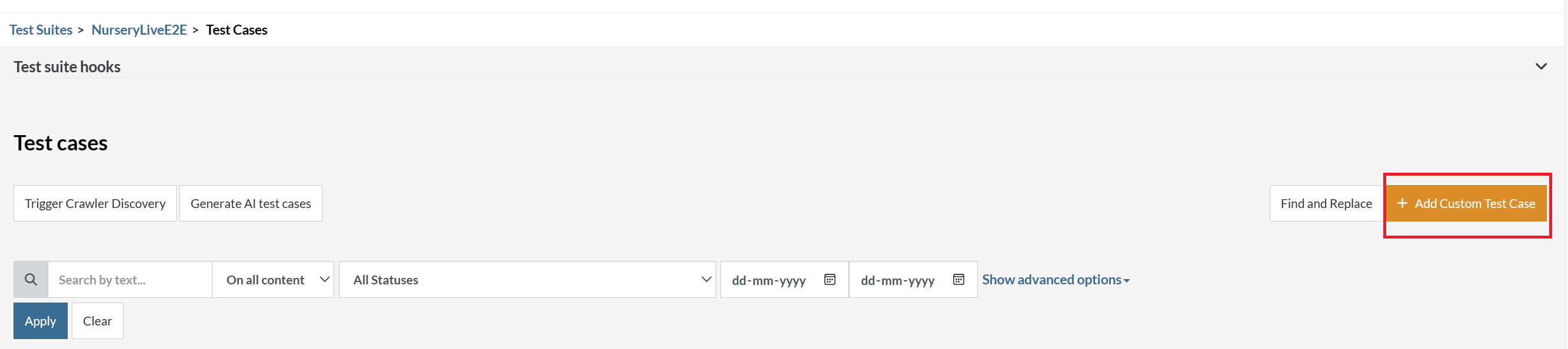
Step 5: Provide the test case Description and start adding the test steps.
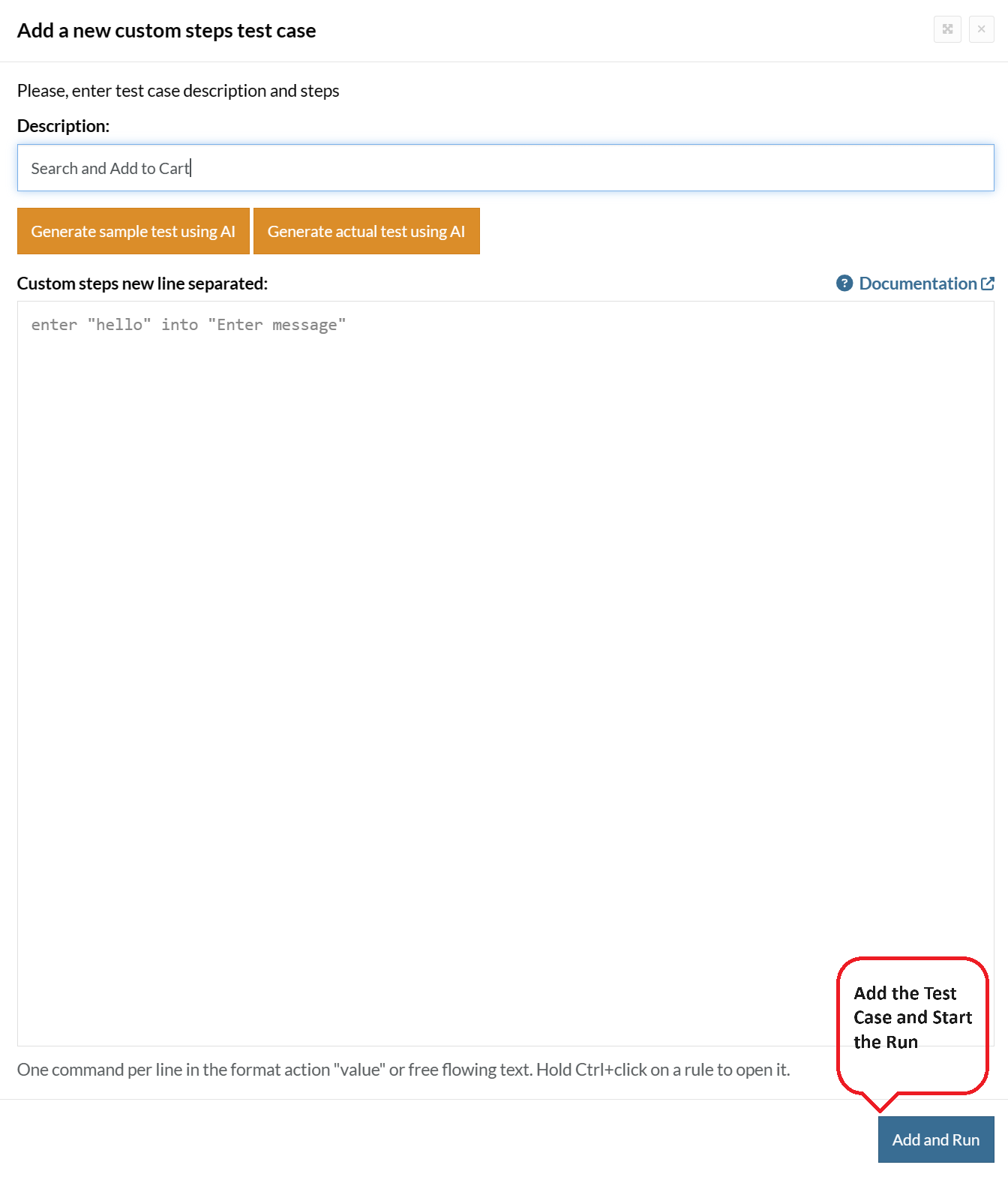
For the application under test, i.e., e-commerce website, we will perform below test steps:
- Search for a product
- Add it to the cart
- Verify that the product is present in the cart
Test Case: Search and Add to Cart
Step 1: We will add test steps on the test case editor screen one by one.
testRigor automatically navigates to the website URL you provided during the Test Suite creation. There is no need to use any separate function for it. Here is the website homepage, which we intend to test.
First, we want to search for a product in the search box. Unlike traditional testing tools, you can identify the UI element using the text you see on the screen. You need not use any CSS/XPath identifiers.
click "What are you looking for?"
Step 2: Once the cursor is in the search box, we will type the product name (lily), and press enter to start the search.
type "lily" enter enter
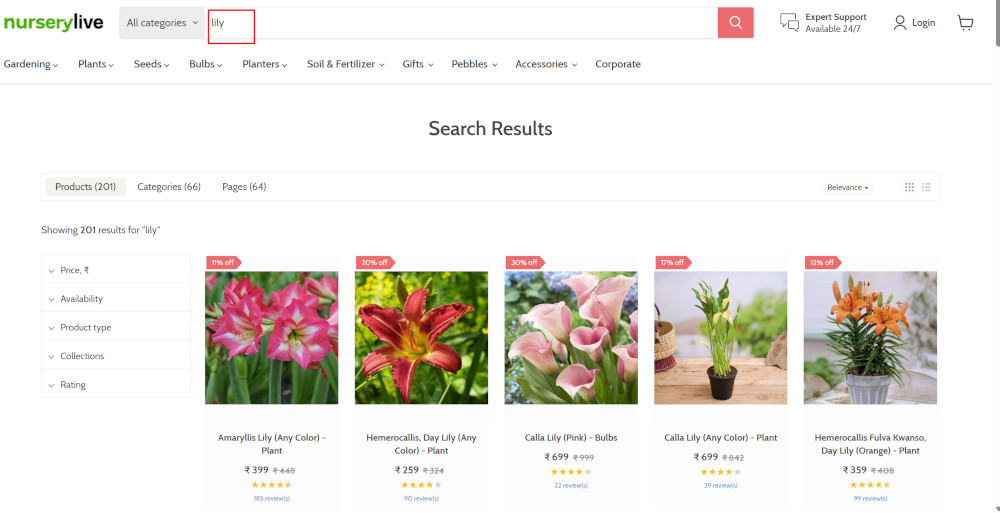
Search lists all products with the “lily” keyword on the webpage.
Step 3: The lily plant we are searching for needs the screen to be scrolled; for that testRigor provides a command. Scroll down until the product is present on the screen:
scroll down until page contains "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)"
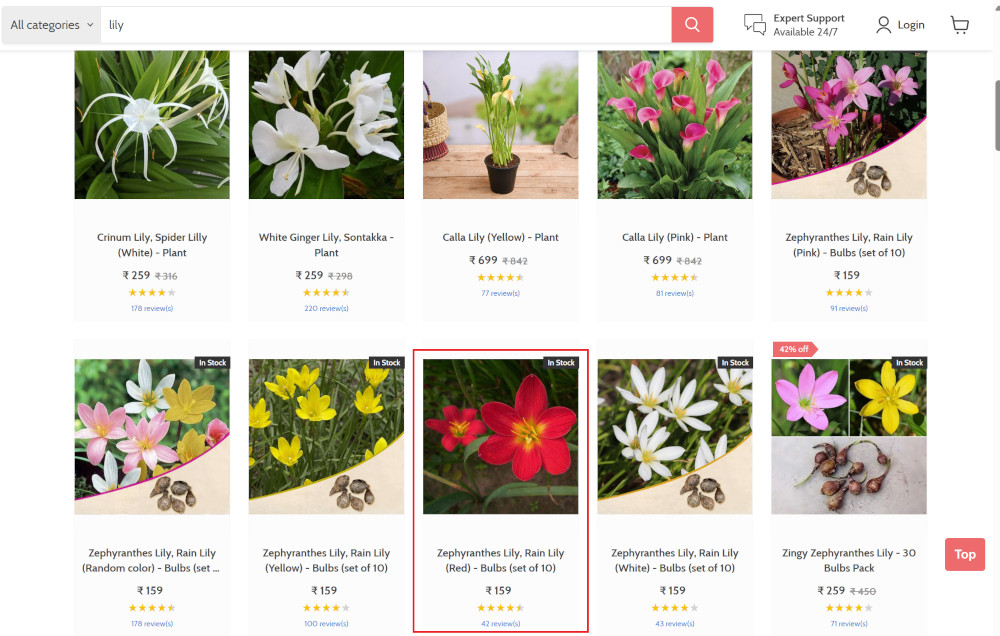
When the product is found on the screen, testRigor stops scrolling.
Step 4: Click on the product name to view the details:
click "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)"
After the click, the product details are displayed on the screen as below, with the default Quantity as 1.
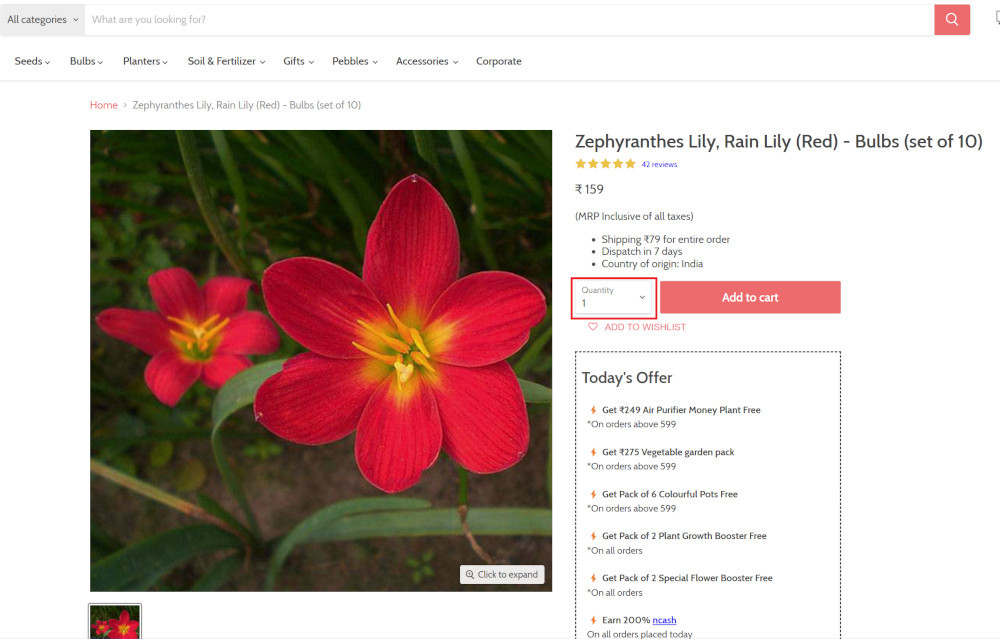
Step 5: Lets say, we want to change the Quantity to 3, so here we use the testRigor command to select from a list.
select "3" from "Quantity"
click "Add to cart"
The product is successfully added to the cart, and the “Added to your cart:” message is displayed on webpage.
Step 6: To assert that the message is successfully displayed, use a simple assertion command as below:
check that page contains "Added to your cart:"
Step 7: After this check, we will view the contents of the cart by clicking View cart as below:
click "View cart"
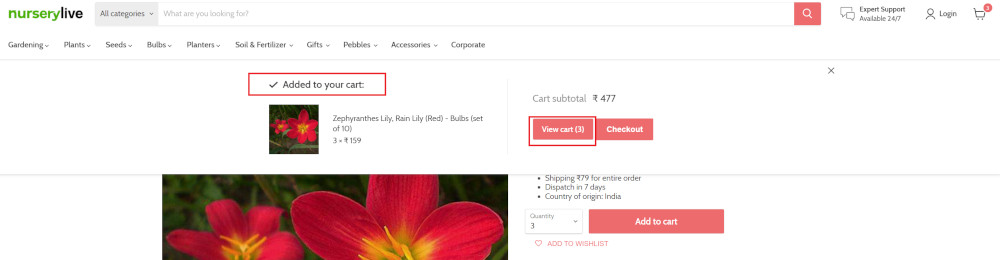
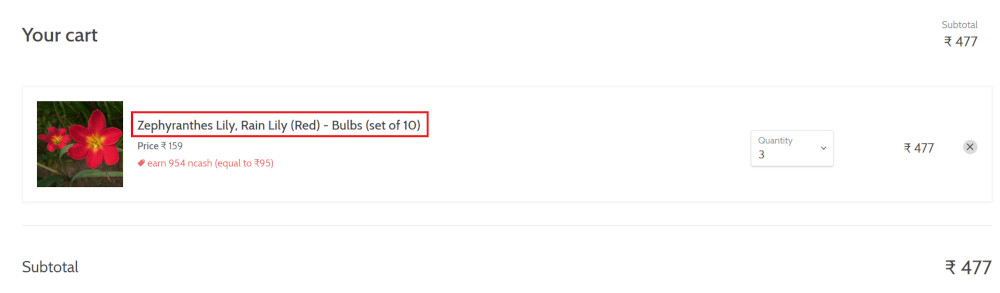
Step 8: Now we will again check that the product is present in the cart, under heading “Your cart” using the below assertion. With testRigor, it is really easy to specify the location of an element on the screen.
check that page contains "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)" under "Your cart"
Complete Test Case
Here is how the complete test case will look in the testRigor app. The test steps are simple in plain English, enabling everyone in your team to write and execute them.
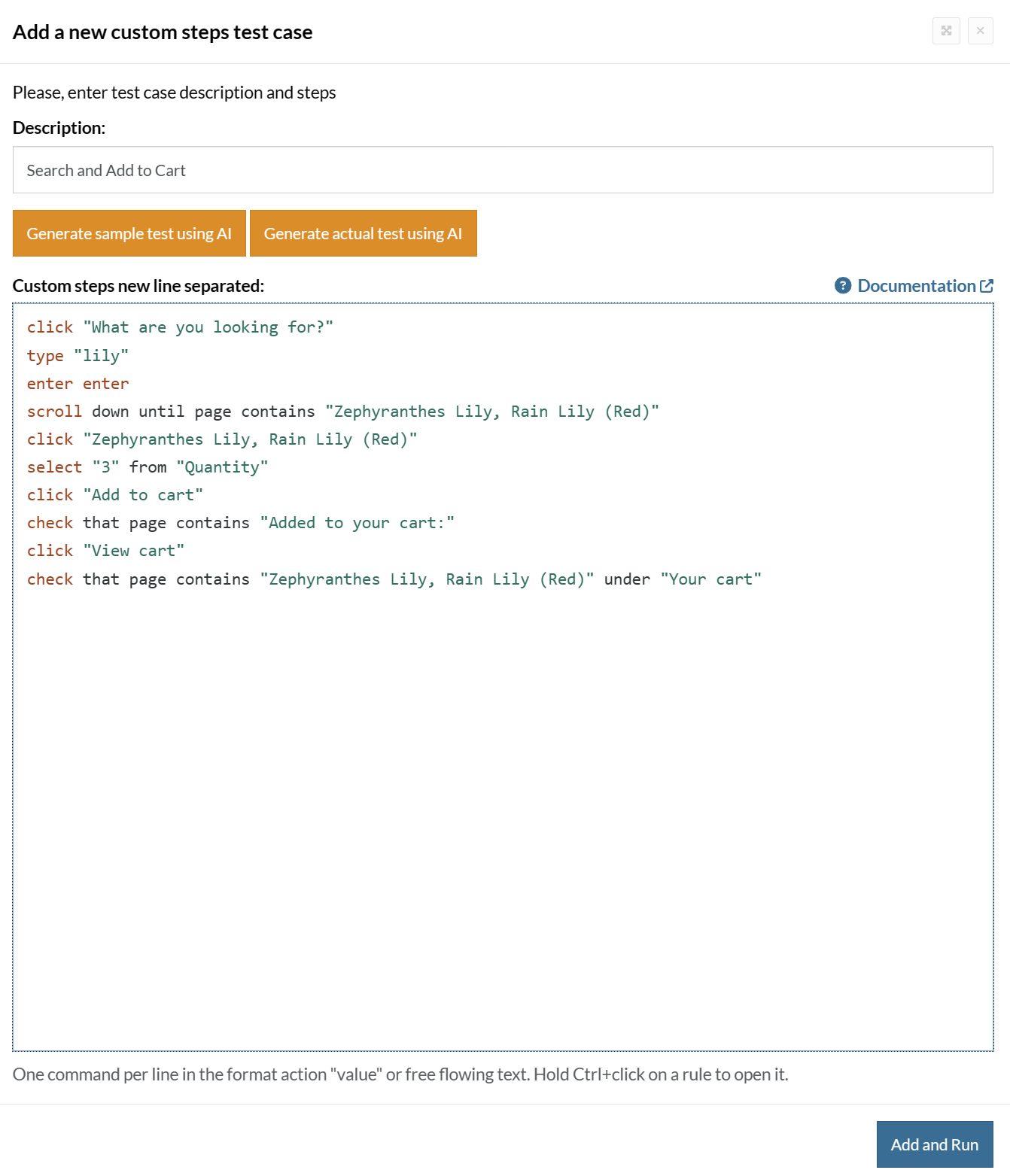
Click Add and Run.
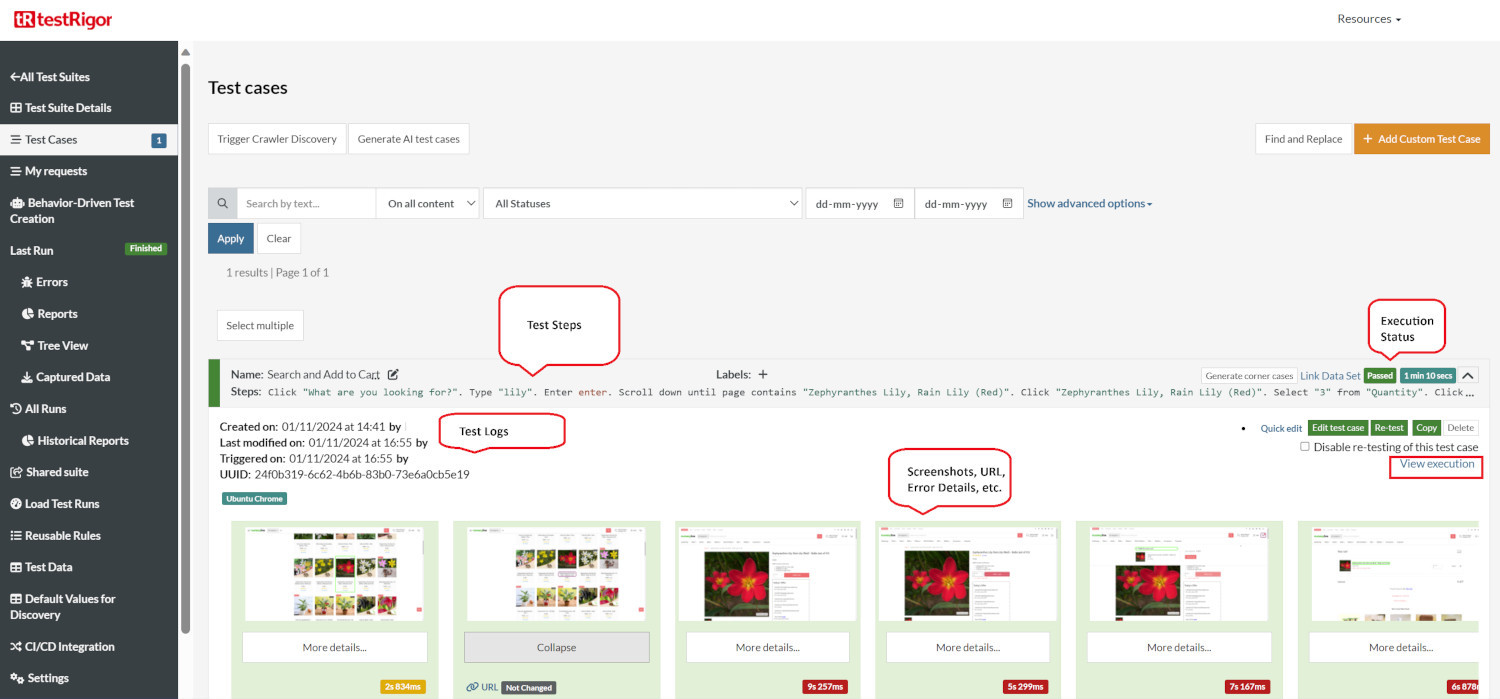
Execution Results
Once the test is executed, you can view the execution details, such as execution status, time spent in execution, screenshots, error messages, logs, video recordings of the test execution, etc. In case of any failure, there are logs and error text that are available easily in a few clicks.
You can also download the complete execution with steps and screenshots in PDF or Word format through the View Execution option.
testRigor’s Capabilities
Apart from the simplistic test case design and execution, there are some advanced features that help you test your application using simple English commands.
- Reusable Rules (Subroutines): You can easily create functions for the test steps that you use repeatedly. You can use the Reusable Rules to create such functions and call them in test cases by simply writing their names. See the example of Reusable Rules.
- Global Variables and Data Sets: You can import data from external files or create your own global variables and data sets in testRigor to use them in data-driven testing.
- 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha Resolution: testRigor easily manages the 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha resolution through its simple English commands.
- Email, Phone Call, and SMS Testing: Use simple English commands to test the email, phone calls, and SMS. These commands are useful for validating 2FA scenarios, with OTPs and authentication codes being sent to email, phone calls, or via phone text.
- File Upload/ Download Testing: Execute the test steps involving file download or file upload without the requirement of any third-party software. You can also validate the contents of the files using testRigor’s simple English commands.
- Database Testing: Execute database queries and validate the results fetched.
testRigor enables you to test web, mobile (hybrid, native), API, and desktop apps with minimum effort and maintenance.
Additional Resources
- Access testRigor documentation to know about more useful capabilities
- Top testRigor’s features
- How to perform end-to-end testing
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












