Silex Testing
What is Silex?
Silex is a PHP micro-framework used for developing web applications. It is built on top of the popular PHP frameworks such as Symfony, and Pimple. Silex can be used in small-scale web applications like Rest APIs for micro-architecture frameworks. It can also be used in full-stack MVC frameworks.
Silex provides a simple, lightweight structure for building and deploying web applications and websites. To tie in third-party libraries, Silex uses an extension system based on the Pimple micro service container. Symfony HTTP Kernel is used for HTTP request and response handling.
- Fat: This version is fully featured and includes database support, a template engine, and other Symphony components.
- Slim: This version is only a basic routing engine.
Why companies choose Silex
- Lightweight: Silex is designed to be a lightweight framework, which means it provides only the essential components needed to build web applications and doesn't include a lot of unnecessary overhead. This makes it easy to get started with and allows developers to focus on writing the code they need for their specific use case.
- Flexibility: Silex is a micro-framework, which means it can be easily extended or customized to fit the needs of individual projects. Developers can choose to use only the components they need, or add additional components as needed.
- Good for prototyping: Silex's lightweight and flexible design makes it well-suited for prototyping ideas and building proof-of-concept applications.
- Built on Symfony: Silex is built on top of the Symfony PHP framework, which means it can take advantage of the many features and components available in Symfony, such as routing, middleware, and security components.
- Easy to learn: Silex has a relatively small learning curve compared to other PHP frameworks, making it a good choice for developers who are new to web development or who are already familiar with PHP.
- Good documentation: Silex has good documentation, which makes it easier for developers to get started with the framework and to find answers to questions they may have.
How to test Silex applications
Pre-requisites
- Install composer. Refer here.
- Install PHPUnit with the composer, refer to here.
Unit testing
Unit testing is a software testing method in which individual units or components of a software application are tested in isolation from the rest of the application. The purpose of unit testing is to validate that each unit of the software application is working as intended, to detect and fix bugs early in the development process, and to ensure that changes made to the code do not break existing functionality. Unit tests can also serve as documentation of the expected behavior of the code and make it easier to maintain the application over time. We can use PHPUnit for unit testing, which is an open-source testing framework for PHP. It is used to write and run automated tests for Silex applications. PHPUnit provides a comprehensive set of testing tools, including assertions, mock objects, and test doubles, for verifying the behavior and functionality of PHP code. It supports multiple testing styles, including unit testing, integration testing, and functional testing. PHPUnit also provides support for testing code that interacts with databases, web services, and other external systems.- Creating an XML file in the root directory of the application
- Creating a folder called tests
Sample phpunit.xml
<phpunit
backupGlobals = "false"
backupStatisticAttributes = "false"
colors = "true"
convertErrorsToExceptions = "true"
convertNoticesToExceptions = "false"
processIsolation = "false"
stopOnFailure = "false"
syntaxCheck = "false"
bootstrap = "vendor/autoload.php"
<testsuites>
<testsuite name="Sample Silex test Suite">
<directory>tests/</directory>
</testsuite>
</testsuites>
</phpunit>
The main purpose of this XML is to help PHP find in which folder are the tests and also the folder where the auto load file is kept to load all the libraries needed for the project.
Let's take the example of a unit test, the sample code looks like the below:
<?php
class Test extends PHPUnit_Framework_TestCase
{
public function testName()
{
$expected = "Tom";
$actual = "Ruth";
// Assert function to test whether expected
// value is equal to actual or not
$this->assertEquals(
$expected,
$actual,
"Actual value is not equals to expected"
);
}
}
?>
Integration testing
Integration testing focuses on the interaction between different components or systems of an application. The scope of integration testing is to validate that the components of an application work together as a single system and meet the specified requirements. Integration testing is typically performed after unit testing, when individual components have been successfully tested in isolation. The scope of integration testing can vary depending on the complexity and size of the application, but typically includes testing the communication between components, the transfer of data between systems, and the handling of errors and exceptions.1. PHPUnit
Can be used to write numerous integration tests for a Silex application.Below is an example of an API test in PHPUnit:
<?php
class HTTPTest extends PHPUnit_Framework_TestCase
{
public function test_post_method()
{
$request = $client->post('/api/programmers', null, json_encode($data));
$response = $request->send();
$this->assertEquals(201, $response->getStatusCode());
$this->assertTrue($response->hasHeader('Location'));
$data = json_decode($response->getBody(true), true);
}
}
?>
2. Codeception
Codeception is an open-source PHP testing framework. It provides an easy way to write, run, and manage tests for PHP applications, including Silex applications. Codeception supports multiple testing styles, including integration testing. It has a simple, readable syntax and provides many useful testing functions and assertions. Additionally, Codeception integrates well with popular PHP frameworks and libraries, including Silex, making it a convenient and flexible tool for testing. Codeception also includes a built-in web server for functional testing, and supports parallel testing, which can speed up test execution times.Below is an example of an integration test:
<?php
class SilexAppCest
{
public function _before(AcceptanceTester $I)
{
$I->amOnPage('/');
}
public function homePageLoads(AcceptanceTester $I)
{
$I->see('Welcome to Silex');
}
public function aboutPageLoads(AcceptanceTester $I)
{
$I->click('About');
$I->see('About Silex');
}
}
?>
This example uses Codeception's AcceptanceTester class to write two tests: one to verify that the home page loads and displays the expected text, and one to verify that the about page can be accessed and displays the desired text.
Performance testing
Performance testing measures the behavior and performance of an application under certain conditions and loads. The goal of performance testing is to identify bottlenecks, measure system and application responsiveness, and validate that the application can meet the performance and scalability requirements and expectations.- Response time: Measuring the time it takes for the application to respond to user requests.
- Throughput: Measuring the number of requests the application can handle per unit of time.
- Scalability: Measuring how the application performance changes as the load increases.
- Resource utilization: Measuring the usage of system resources such as memory, CPU, and disk.
- Capacity: Measuring the maximum load the application can handle without breaking or becoming unresponsive.
1. Apache Jmeter
JMeter is an open-source software tool used for performance and load testing of web applications, APIs, and databases. It allows you to test the response time, throughput, and stability of an application under various loads, helping identify bottlenecks and optimize performance. JMeter can simulate a large number of users making requests to a web application, enabling you to test the application's behavior and performance under heavy loads. It can also be used to measure the response time of web services, databases, and other components that make up a web application. The tool supports a variety of protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SMTP, and more, and it provides a visual interface for designing, executing, and analyzing load tests. JMeter can be used to test both static and dynamic resources, and it provides a range of useful plugins for adding additional functionality and for integrating with other tools and systems. Overall, Apache JMeter is a powerful, flexible, and widely used tool for web applications and APIs.2.LoadRunner
LoadRunner is a proprietary performance testing tool developed by Micro Focus. It allows you to simulate large numbers of users making requests to a web application, providing a means of testing the application's behavior and performance under real-world conditions. LoadRunner provides a visual interface for designing and executing load tests, as well as a range of features for analyzing performance results. It supports a variety of protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, and more, and it provides a scripting language for creating custom test scenarios. LoadRunner also provides a range of advanced features, such as the ability to perform distributed testing, test complex user journeys, and test applications with dynamic data. It integrates with other testing tools and systems, providing a comprehensive solution for performance testing and optimization.Functional testing, end-to-end testing
Functional testing verifies the application's behavior and functionality against the requirements and specifications. The goal of functional testing is to ensure that the application is working as expected and meets the specified requirements in terms of functionality, usability, and reliability. Similarly, end-to-end(E2E) testing verifies the flow of an application from start to finish, including interactions with any external systems or dependencies. The goal of E2E testing is to simulate real-world usage scenarios and ensure that the application works correctly and as expected in a real-world environment.1. PHPUnit
- Complex Test Scenarios: PHPUnit is designed for testing individual units of code, and it may not be well-suited for testing complex functional scenarios that involve multiple components and interactions.
- UI Testing: PHPUnit is not designed for testing user interfaces, and it may not be able to test the look and feel of a web application effectively.
- Difficulty in Debugging: Debugging functional tests can be challenging with PHPUnit, especially when the tests involve multiple components and interactions.
- Lack of Browser Simulation: PHPUnit does not provide a means of simulating a web browser, so it may not be possible to test a web application's behavior in a real-world environment.
2. testRigor
testRigor is an extremely easy to master no-code tool that is best suited for complex end-to-end testing scenarios, involving many components. It is a cloud-hosted AI-enhanced system, allowing the entire team to build tests in plain English commands. The ease of use, robustness, and minimal test maintenance make it one of the best options on the market for functional and end-to-end testing. Let's see sample code below to test web portals and API.Below is an example of a testRigor test:
open URL "https://www.phdadmissions.com" check that page contains "PhD-ADMISSIONS" click "Institutes" check that page contains "Courses offered" check that page contains "Place :" check that page contains "Fee Structure" check that page contains "Admission Start Date:" check that page contains "Enroll Course" click "Enroll Course" enter "name" into "Enter name:" select "Science" from "Stream" enter "01/01/2000" into "Date of Birth:" enter "[email protected]" into "Email:" enter "+1894342401" into "Mobile:" click "Submit" check page contains "Details saved"
Here's an example of an API test:
call api post "http://dummy.restapiexample.com/api/v1/create" with headers "Content-Type:application/json" and "Accept:application/json" and body "{\"name\":\"DemotTest\", \"employmentStatus\":\"employed\",\"age\":\"32\"}" and get "$.data.name" and save it as "createdName" and get "$.data.employmentStatus" and save it as "eStatus" and get "$.data.age" and save it as "age" and then check that http code is 201
// Assertions
check that stored value "createdName" itself contains "DemoTest"
check that stored value "eStatus" itself contains "employed"
check that stored value "age" itself contains "32"
Since testRigor has only been on the market for a few years and is still fairly new, it's important to highlight some of the key features that might help give you a better opinion.
- Easy implementation and use of plain English language for creating test cases.
- Tests do not rely on details of implementation and require minimal test maintenance.
- Supports integrations with tools such as Jira, TestRail, most CI/CD tools, and many others.
- Fast test execution allows receiving test results in under an hour.
- Supports cross-browser and cross-platform testing.
- Supports BDD approach out of the box, and overall optimizes and simplifies the QA workflow.
How to do End-to-end Testing with testRigor
Let us take the example of an e-commerce website that sells plants and other gardening needs. We will create end-to-end test cases in testRigor using plain English test steps.
Step 1: Log in to your testRigor app with your credentials.
Step 2: Set up the test suite for the website testing by providing the information below:
- Test Suite Name: Provide a relevant and self-explanatory name.
- Type of testing: Select from the following options: Desktop Web Testing, Mobile Web Testing, Native and Hybrid Mobile, based on your test requirements.
- URL to run test on: Provide the application URL that you want to test.
- Testing credentials for your web/mobile app to test functionality which requires user to login: You can provide the app’s user login credentials here and need not write them separately in the test steps then. The login functionality will be taken care of automatically using the keyword
login. - OS and Browser: Choose the OS Browser combination on which you want to run the test cases.
- Number of test cases to generate using AI: If you wish, you can choose to generate test cases based on the App Description text, which works on generative AI.
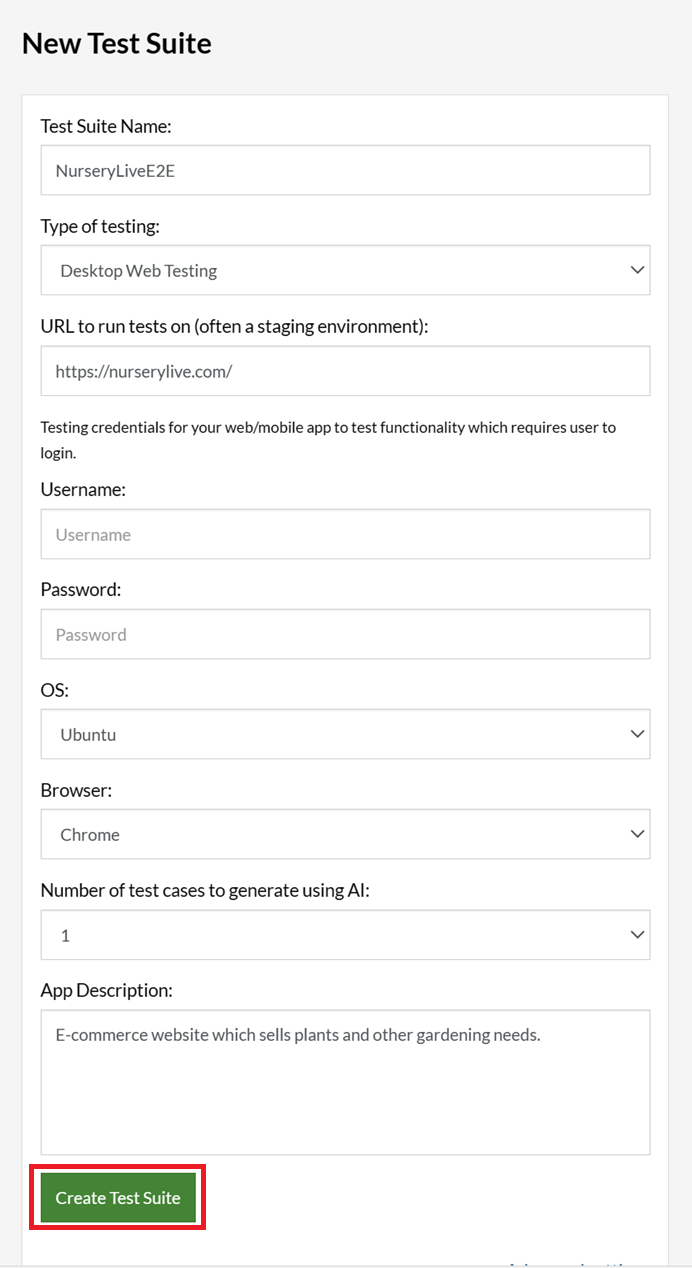
Step 3: Click Create Test Suite.
On the next screen, you can let AI generate the test case based on the App Description you provided during the Test Suite creation. However, for now, select do not generate any test, since we will write the test steps ourselves.
Step 4: To create a new custom test case yourself, click Add Custom Test Case.
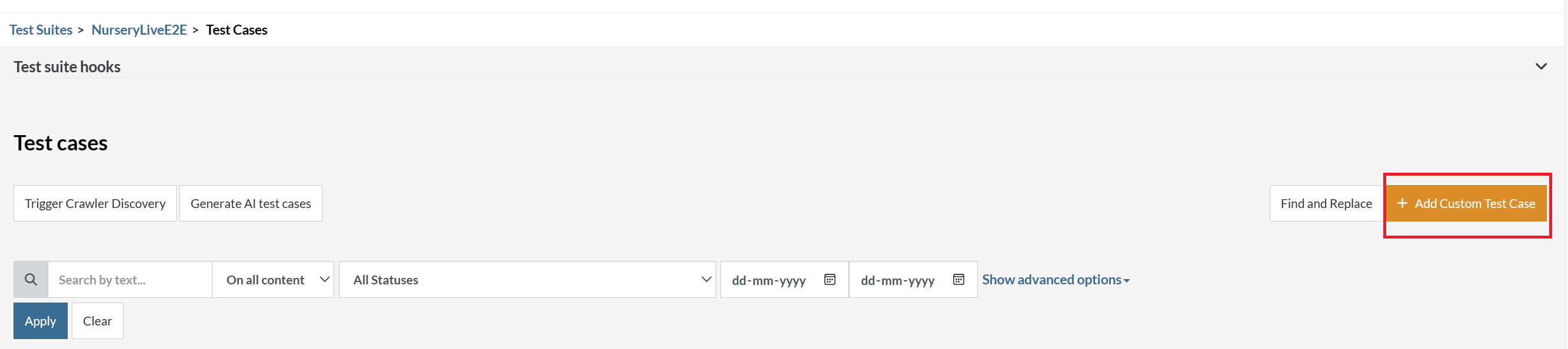
Step 5: Provide the test case Description and start adding the test steps.
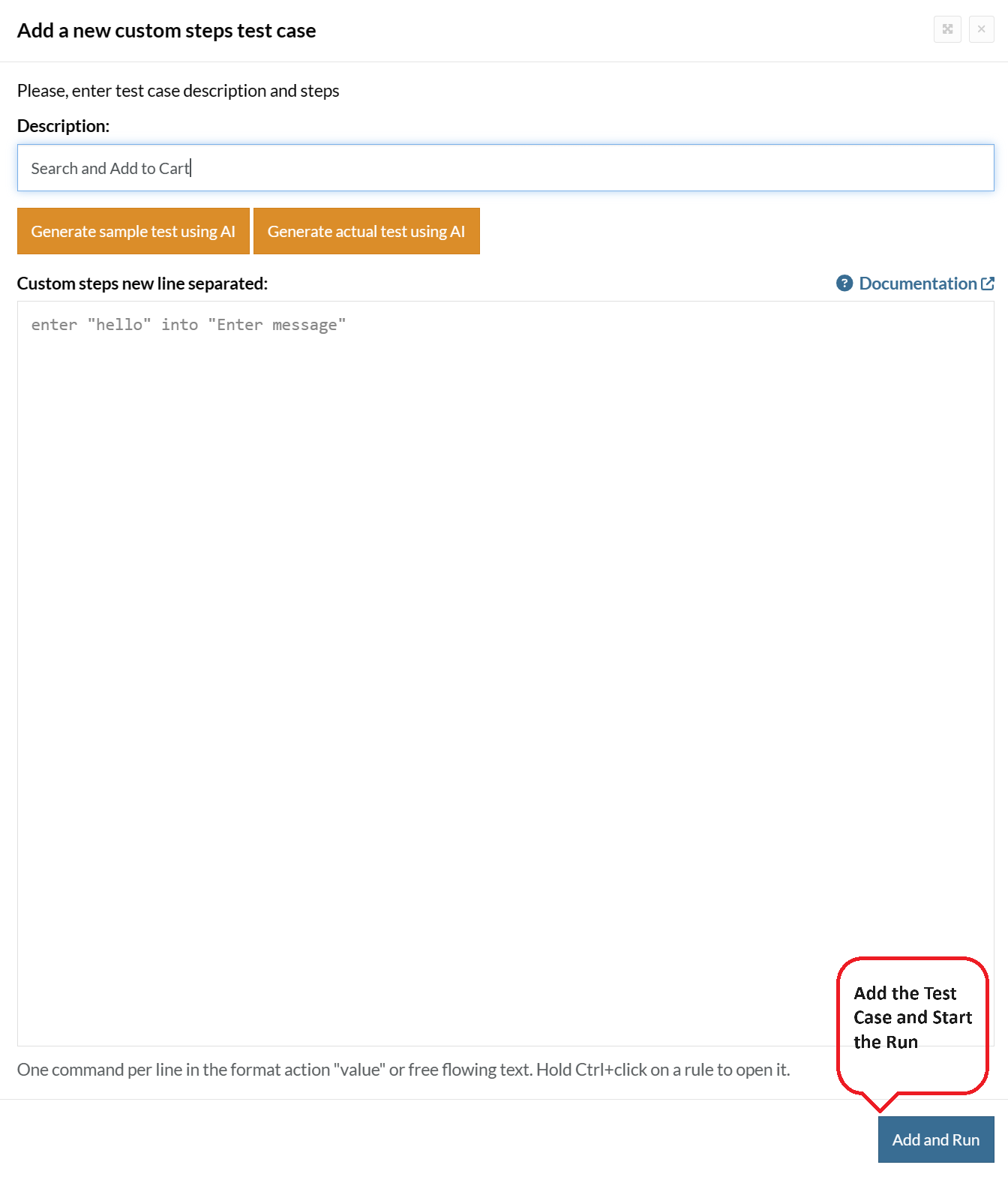
For the application under test, i.e., e-commerce website, we will perform below test steps:
- Search for a product
- Add it to the cart
- Verify that the product is present in the cart
Test Case: Search and Add to Cart
Step 1: We will add test steps on the test case editor screen one by one.
testRigor automatically navigates to the website URL you provided during the Test Suite creation. There is no need to use any separate function for it. Here is the website homepage, which we intend to test.
First, we want to search for a product in the search box. Unlike traditional testing tools, you can identify the UI element using the text you see on the screen. You need not use any CSS/XPath identifiers.
click "What are you looking for?"
Step 2: Once the cursor is in the search box, we will type the product name (lily), and press enter to start the search.
type "lily" enter enter
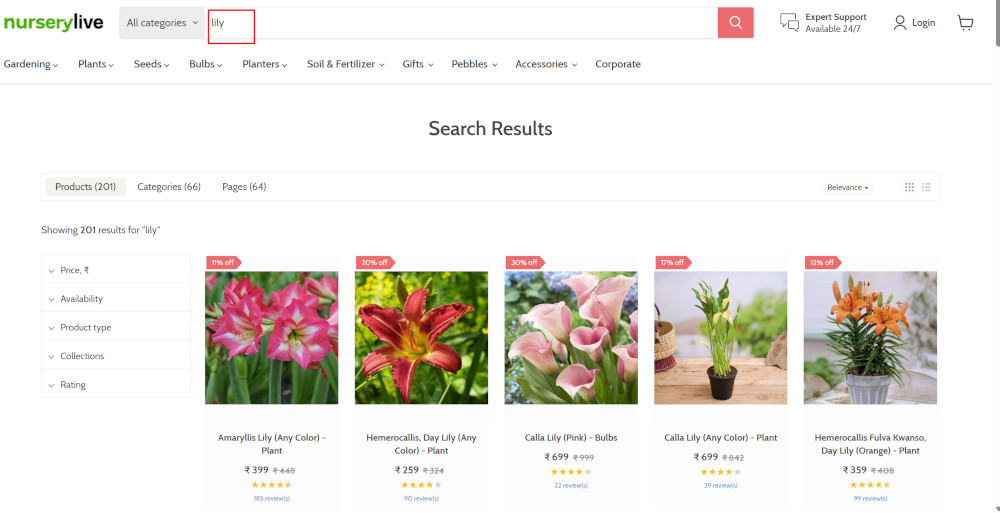
Search lists all products with the “lily” keyword on the webpage.
Step 3: The lily plant we are searching for needs the screen to be scrolled; for that testRigor provides a command. Scroll down until the product is present on the screen:
scroll down until page contains "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)"
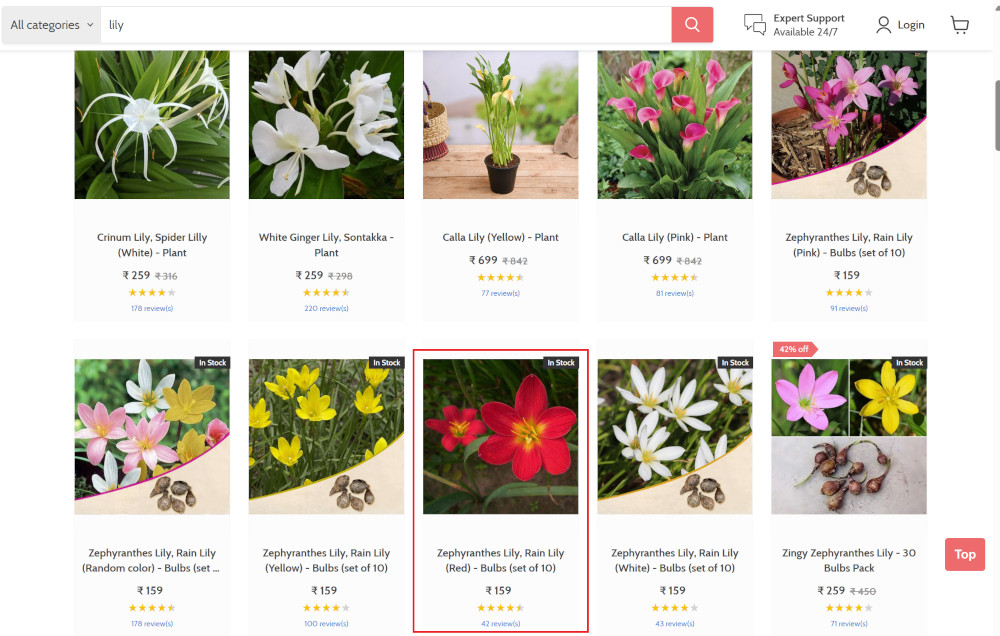
When the product is found on the screen, testRigor stops scrolling.
Step 4: Click on the product name to view the details:
click "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)"
After the click, the product details are displayed on the screen as below, with the default Quantity as 1.
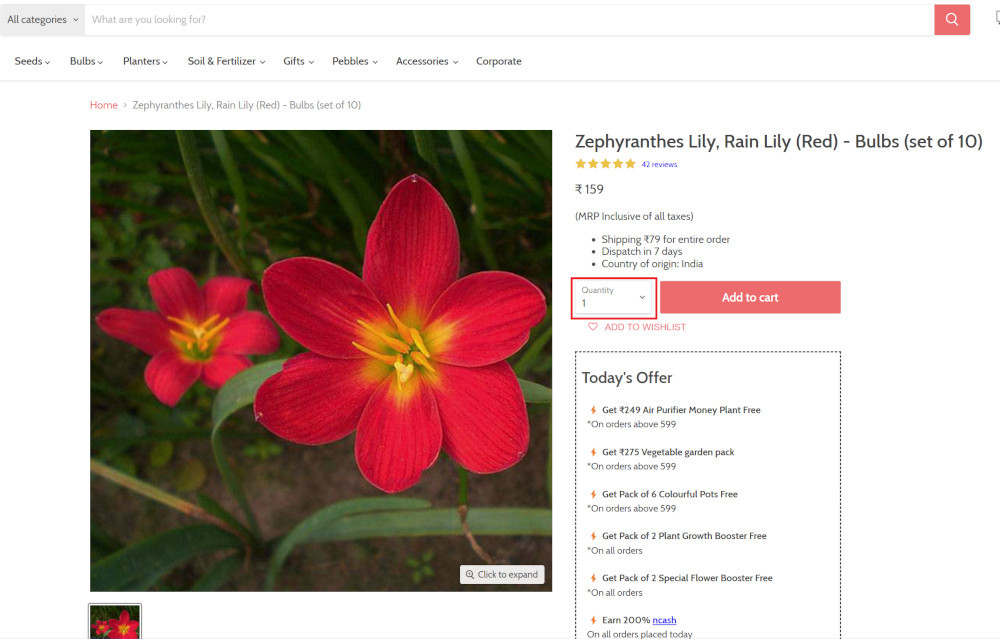
Step 5: Lets say, we want to change the Quantity to 3, so here we use the testRigor command to select from a list.
select "3" from "Quantity"
click "Add to cart"
The product is successfully added to the cart, and the “Added to your cart:” message is displayed on webpage.
Step 6: To assert that the message is successfully displayed, use a simple assertion command as below:
check that page contains "Added to your cart:"
Step 7: After this check, we will view the contents of the cart by clicking View cart as below:
click "View cart"
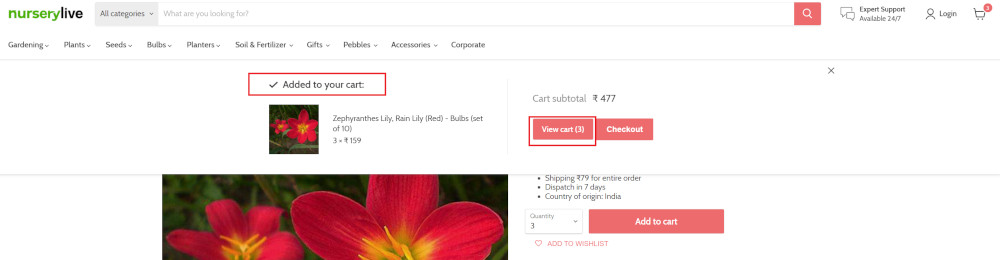
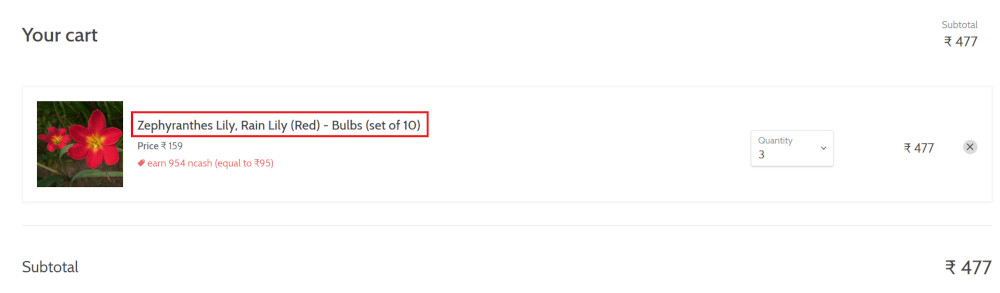
Step 8: Now we will again check that the product is present in the cart, under heading “Your cart” using the below assertion. With testRigor, it is really easy to specify the location of an element on the screen.
check that page contains "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)" under "Your cart"
Complete Test Case
Here is how the complete test case will look in the testRigor app. The test steps are simple in plain English, enabling everyone in your team to write and execute them.
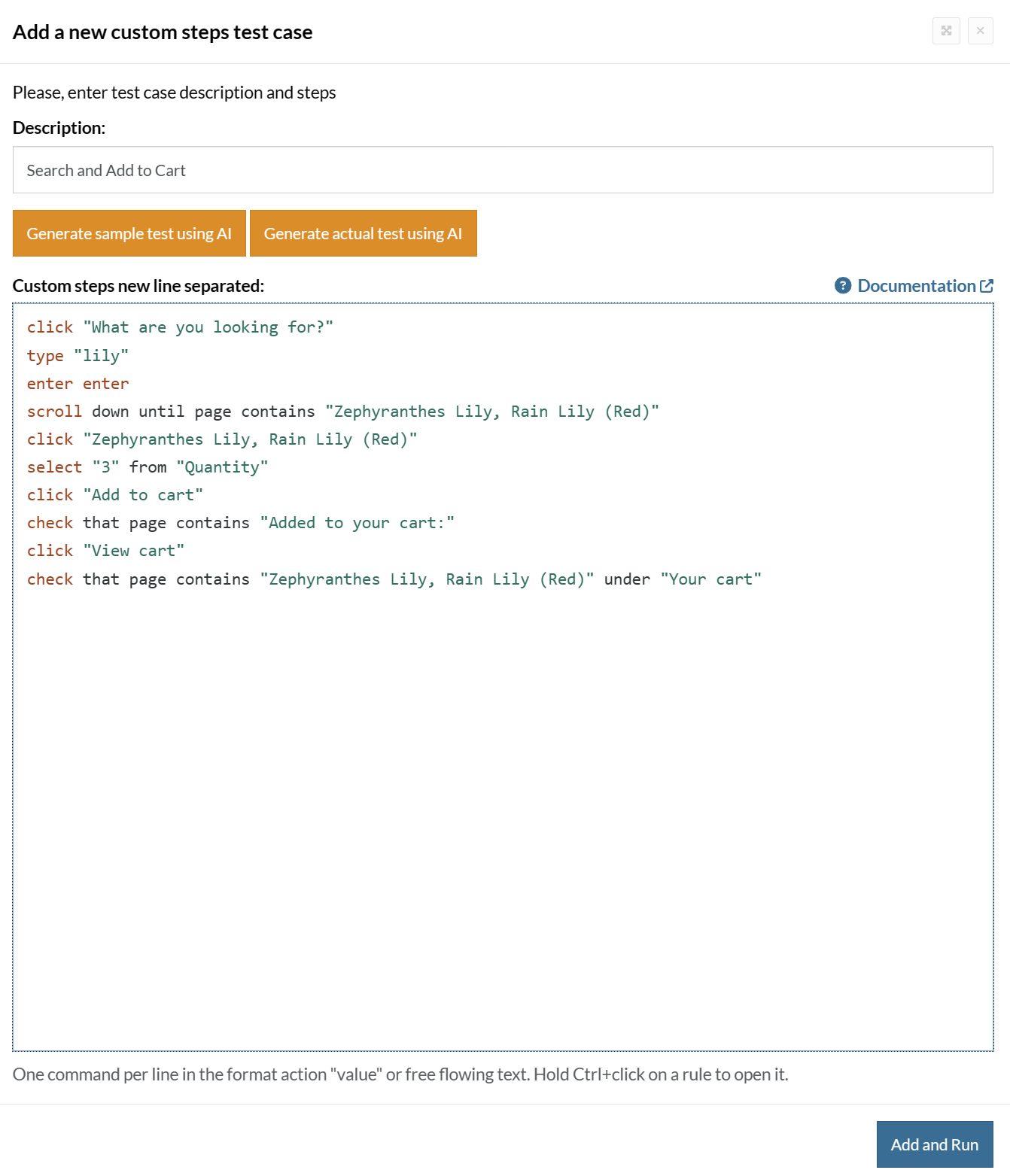
Click Add and Run.
Execution Results
Once the test is executed, you can view the execution details, such as execution status, time spent in execution, screenshots, error messages, logs, video recordings of the test execution, etc. In case of any failure, there are logs and error text that are available easily in a few clicks.
You can also download the complete execution with steps and screenshots in PDF or Word format through the View Execution option.
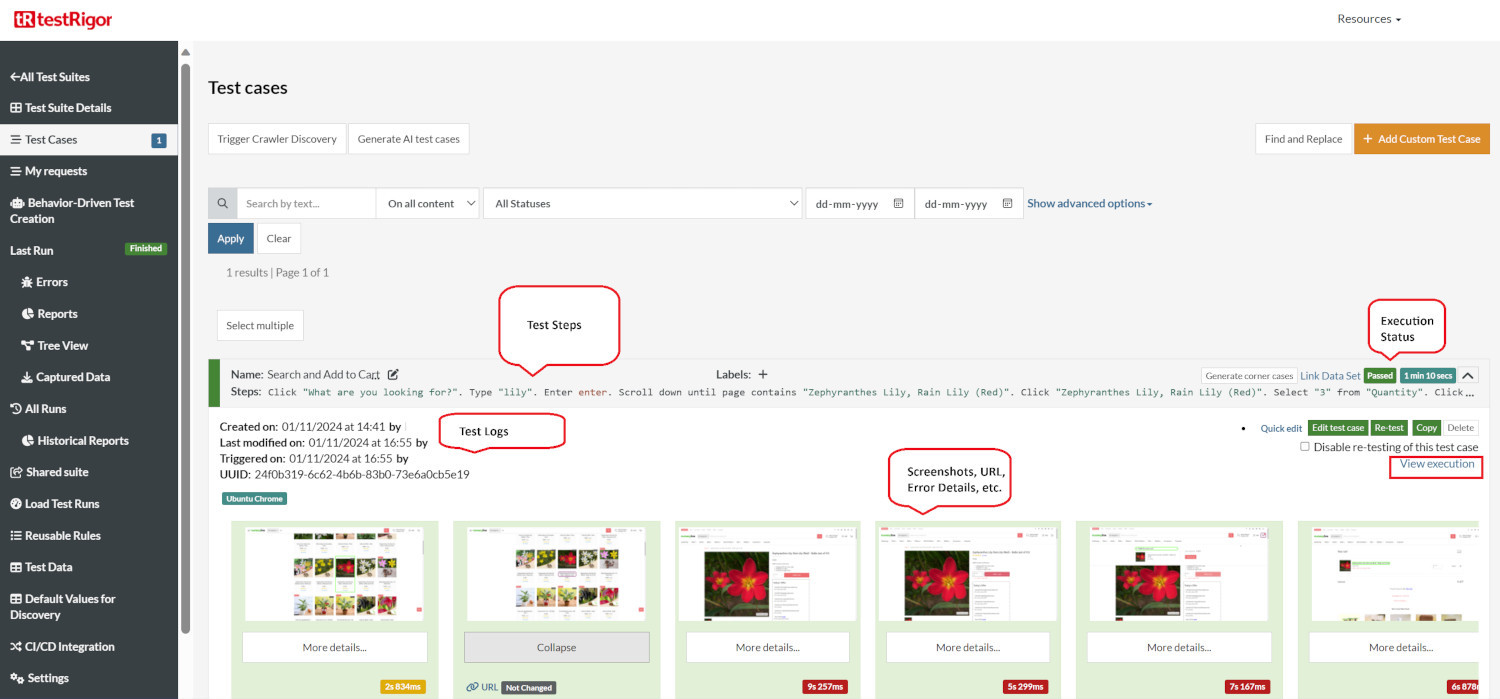
testRigor’s Capabilities
Apart from the simplistic test case design and execution, there are some advanced features that help you test your application using simple English commands.
- Reusable Rules (Subroutines): You can easily create functions for the test steps that you use repeatedly. You can use the Reusable Rules to create such functions and call them in test cases by simply writing their names. See the example of Reusable Rules.
- Global Variables and Data Sets: You can import data from external files or create your own global variables and data sets in testRigor to use them in data-driven testing.
- 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha Resolution: testRigor easily manages the 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha resolution through its simple English commands.
- Email, Phone Call, and SMS Testing: Use simple English commands to test the email, phone calls, and SMS. These commands are useful for validating 2FA scenarios, with OTPs and authentication codes being sent to email, phone calls, or via phone text.
- File Upload/ Download Testing: Execute the test steps involving file download or file upload without the requirement of any third-party software. You can also validate the contents of the files using testRigor’s simple English commands.
- Database Testing: Execute database queries and validate the results fetched.
testRigor enables you to test web, mobile (hybrid, native), API, and desktop apps with minimum effort and maintenance.
Additional Resources
- Access testRigor documentation to know about more useful capabilities
- Top testRigor’s features
- How to perform end-to-end testing
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












