Hermetic Testing: Meaning, Benefits & How It Works
|
|
In industries, electronic components often have to face harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures, vacuum, humidity, vibrations, or corrosive atmospheres. These can compromise their reliability and make or break the performance of the entire system. Hence, these systems using electronic components like defense systems, aerospace modules, medical implants, automotive sensors, and advanced semiconductor devices share a common requirement: long-term environmental protection.
This is where hermetic testing plays a crucial role.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
This article explores what hermetic testing is, its significance, the underlying science, test methods, standards, result interpretation, and real-world applications.
What is Hermetic Testing?
Let us first understand the term “Hermetic” before proceeding to hermetic testing.
The term “Hermetic” traditionally refers to airtight, meaning something that is securely sealed so that no gas or vapor can pass through.
In modern engineering, hermeticity refers to the ability of a package or enclosure to resist the ingress of moisture, air, other gases, contaminants, particulate matter, chemicals, or liquid intrusion.

Hermeticity is not just about air leaks; it is about ensuring that even microscopic pathways, called micro-leaks, are sufficiently sealed to maintain internal environmental stability over the product’s operational lifetime.
For electronics components and equipment, moisture is especially damaging. Trapped water vapor can lead to:
- Corrosion of internal circuits
- Dendritic growth leading to shorts
- Fogging or optical interference in photonic components
- Reduced insulation resistance
- Mechanical degradation of bonding materials
As device geometries shrink and semiconductor nodes become thinner, even tiny amounts of moisture can compromise the reliability and performance of the system. Thus, hermetic testing has become indispensable in modern electronics and sensor manufacturing. Now this was the explanation for the manufacturing field.
However, in software testing, hermetic testing has a different view.
In software testing, a hermetic test is a test that is fully independent, self-sufficient, and does not rely on other tests or external systems, such as networks, databases, or APIs. The primary objective of hermetic testing is to ensure a test failure is due to a bug in the code, and not because of an external factor such as a failed external service or component. Hermetic testing is performed by controlling all inputs and outputs, often using mocks or stubs to simulate dependencies between components.
Hermetic testing is a testing methodology where the test environment is completely sealed off from external dependencies.
This means that external interfaces, such as network calls, database connections, and other external services, do not interfere with the testing process. This way, a consistent and reproducible environment is maintained, allowing for accurate validation of software behavior. As “hermetic” means sealed, hermetic testing ensures perfect sealing, whether it’s a software test isolating itself or a physical product sealing itself from the environment.
Key Characteristics of Hermetic Testing
Some of the key characteristics of hermetic testing are:
- Controlled Parameters: In hermetic testing, all inputs are predefined, and outputs are expected. This enables the accurate assessment of the software’s outcomes in various scenarios.
- Seclusion (Isolation): The hermetic tests are performed in isolation or in a secluded environment, for example, by using mocks or stubs instead of connecting to third-party products. This approach to operating independently of external factors helps eliminate variability in test outcomes.
- Predictable Outcome: Each test run yields the same outcome, provided the code and environment remain unchanged. This predictability helps identify real issues in the software.
Benefits of Hermetic Testing
Hermetic testing has various benefits listed below:
- Improved Accuracy: With external variables excluded from the testing, the test results obtained from hermetic testing are more accurate. Developers can be assured that any failures are due solely to changes in the code and not to external factors.
- Speedy Execution: Without the interference of the network and its related factors, hermetic tests tend to execute more quickly.
- Debugging Ease: Hermetic tests do not depend on external variables and rely solely on the code. Hence, they are easier to debug.
Why is Hermetic Testing Critical?
Hermetic testing isolates the application by eliminating external variables and guarantees long-term reliability, safety, and performance, especially in demanding or critical applications.
It is important for the following reasons:
- Reliability in Harsh Environments: Many applications get exposed to harsh conditions in mechanical as well as software environments. By eliminating these external conditions, hermetic testing ensures application survival under such conditions.
- Lifespan Prediction: Using hermetic test data, engineers can estimate how long the sealing will remain intact. This is especially useful for spacecraft electronics, implantable medical devices (pacemakers), weapons and defence systems, and oil & gas drilling sensors.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Hermetic testing verifies compliance in sectors like aerospace and military that require strict adherence to specifications, including MIL-STD-883 (semiconductors), MIL-STD-750 (discrete semiconductors), and MIL-STD-202 (electronic components).
- Quality Assurance and Failure Prevention: Manufacturing defects such as poor seam welds, cracked ceramic substrates, or improper glass-to-metal seals can be identified using hermetic testing. It also helps to prevent failures and assures quality.
- Isolates Failures in Software Testing: Hermetic reduces test flakiness, making failures deterministic, and ensuring that a test fails only when there is a real bug in the code being tested, not due to an issue with an external service.
Hermetic Testing in Semiconductor & Microelectronics Manufacturing
Hermetic testing ensures the reliability and performance of semiconductor and microelectronic devices by preventing moisture and gas ingress. It is critical for applications such as MEMS sensors, optoelectronics, RF packages, medical implants, aerospace systems, and automotive electronics. As devices shrink, even micro- and nano-scale leaks can impact performance, making sensitive detection methods like helium leak testing essential to prevent long-term failure and safety risks.
Hermetic Software Testing
From a software testing point of view, a hermetic test is a test that is completely isolated and self-sufficient. As it is independent of any external factors, including third-party vendors and network calls, it is fully independent. Every time a test is run, you can be assured that a failure is a real code failure and has nothing to do with an external dependency malfunctioning.
End-to-end (E2E) hermetic testing is a combination of end-to-end testing (that validates user workflows across the system) and hermetic testing (isolated from external dependencies). By combining E2E with hermetic testing, you can validate complex applications by ensuring that components interact with each other efficiently, reducing test flakiness, and speeding up the feedback. Read: System Testing vs. End-to-End Testing.
An easy approach to using hermetic testing in E2E testing is to first divide E2E into meaningful, smaller components or chunks. For example, split the system into frontend and backend components. You can then execute the hermetic (isolated) tests in the context of frontend and backend separately. After this is done, there can be additional levels of tests to ensure the application works correctly by conducting contract tests, API tests, and visual tests that were not run earlier. This will improve the unit test coverage significantly.
Here are the key concepts you should keep in mind when testing workflows using hermetic testing:
- E2E testing is used when real user scenarios are to be simulated to ensure that the entire systems, including external components, work seamlessly and data integrity is maintained.
- Hermetic testing eliminates external dependencies and creates an independent, isolated environment for tests. For this purpose, it uses mocks, stubs, or in-memory fakes in place of external components.
- To facilitate hermetic testing of E2E workflows, an approach called “server in a box” (hermetic servers) is used. In this, all dependencies are injected at runtime. This ensures the hermetic tests are executed locally without network access. Basically, this is the scenario where you get the best of both worlds.
Benefits of Hermetic Testing
Hermetic testing offers several advantages as follows:
- Reliability: Hermetic testing gets rid of flakiness in tests that arise due to slow or failing external services.
- Speed: It significantly reduces test execution time as it is performed in isolation without any network dependency. Since there is no network, there is no network latency.
- Consistency: Hermetic testing is performed in an isolated environment without any external dependencies. This reassures developers that the failure is because of the code being tested and not any other factor.
- Full Validation: With hermetic testing, entire user workflows can be validated in isolation.
Challenges for Hermetic Testing
The hermetic testing process has a few challenges as well:
- Setup Complexity: Getting rid of external dependencies and building an isolated environment with mocks and fakes is challenging.
- Resource Intensive: Hermetic servers are complex mechanisms, and running them consumes a great amount of resources.
How to Implement Hermetic Testing
Hermetic testing is implemented with the following sequence of steps:
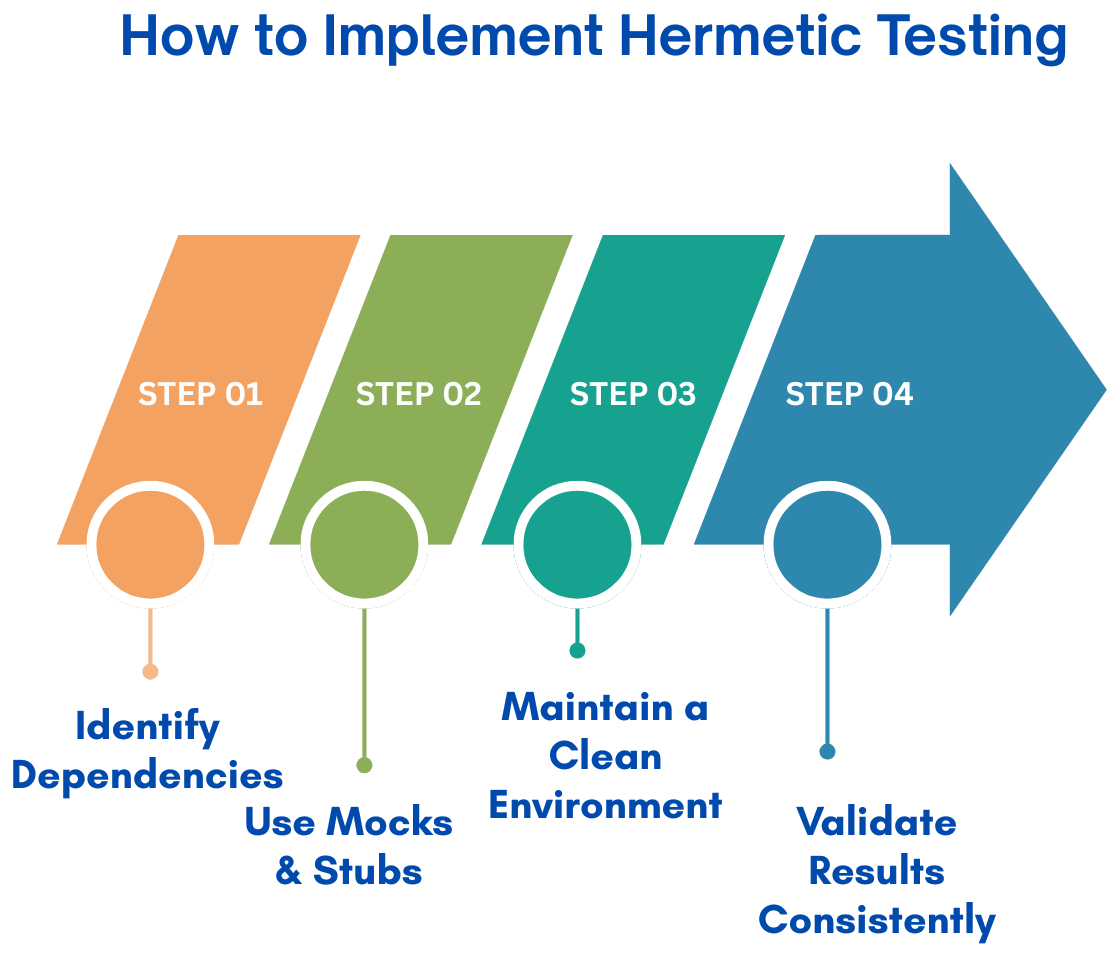
Step 1: Identify External Dependencies
The first step in the hermetic testing process is determining all the external dependencies your application relies on, including databases, APIs, the network, and third-party services.
Step 2: Use Mocks and Stubs for Controlled Testing
Replace all external dependencies with mocks or stubs, allowing testing to be performed in a controlled environment. Using this isolated environment, components can be tested efficiently as they now rely only on their actual implementation.
Mocks: Objects or components used in place of real objects. They simulate the behavior of real objects and are used in hermetic testing to verify interactions between components.
Stubs: Stubs are entities that provide predefined responses to method or database procedure calls made during tests. Stubs are also part of a controlled test environment.
Step 3: Maintain a Clean and Resettable Environment
The test environment used should be free of variants, clean, and easily resettable. Each test should have a deterministic state.
Step 4: Validate Results Properly
Hermetic tests should be regularly executed to verify application behavior. In the event of failure, it should be thoroughly investigated, and only then should the bug be reported.
Conclusion
Hermetic testing is a cornerstone of reliability across aerospace, defense, medical, semiconductor, and automotive industries. As devices shrink in size and performance expectations rise, it is important to ensure the packages remain tightly sealed. It protects mission-critical systems and prevents costly failures in the manufacturing industry by detecting both gross and fine leaks.
In software testing, hermetic testing helps in faster execution of tests, improved accuracy, and easier debugging.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












