What is Ad Hoc Testing?
|
|
In the software world, testing is an important step to maintaining software quality. Various testing techniques are used to make sure that the application developed is ready to hit the market and that it is well-received by end users.
One such step is ad hoc testing. This is a software testing technique that does not have any predetermined steps. It does not even have a specific test plan. Testers perform testing solely based on their intuition and knowledge about the application to find defects that other testing techniques may not have found.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
What is Ad Hoc Testing?
Ad hoc testing can be considered an unstructured software testing technique. It is done randomly to find possible errors or defects. It is a flexible yet random approach that helps to point out unpredictable crashes, functional defects, and other errors in the application that may go unnoticed when the application is tested with structured and planned testing techniques.
For example, if you are testing a banking system that will be released soon, considering that banking systems usually operate with real-time data and cannot be compromised, it becomes necessary to make sure that they are infallible before being released. Hence, even after it has been tested for functionality and performance, a round of ad hoc testing can be carried out to find any unknown defects or errors.
Now that we have understood the basic definition of ad hoc testing, let’s discuss the main features of ad hoc testing.
Features of Ad Hoc Testing
Ad hoc testing involves deviating from standard testing methods to identify defects. Here are some of the main features of Ad hoc testing.
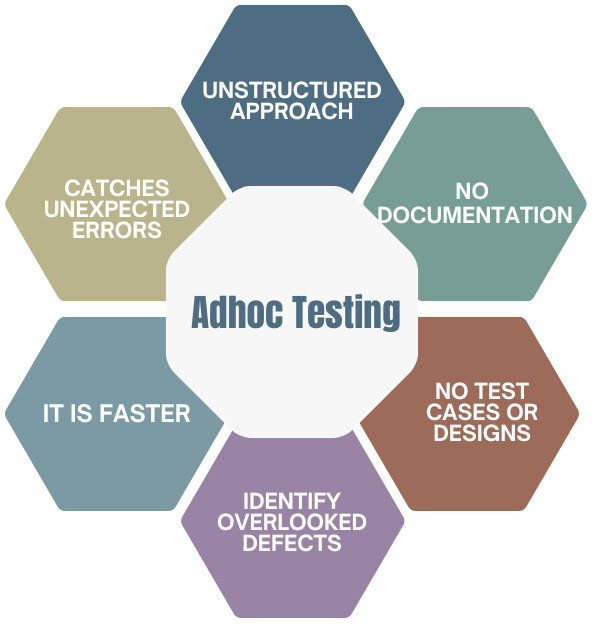
The key features shown in the above image are explained below.
- Unstructured Approach: The ad hoc testing approach is completely unstructured and exploratory. A tester or software professional randomly tests the application system to find defects.
- No Documentation: Professionals do not use product/application documentation to perform ad hoc testing. They are generally well-informed about the system.
- No Test Cases or Designs: Ad hoc testing does not have test cases or test designs. As a result, bugs identified are not linked to any test case.
- Identify Overlooked Defects: The defects that are generally overlooked when testing with a structured approach that follows a test plan can be identified using ad hoc testing.
- It is faster: Ad hoc testing is much faster because there is no structured approach involved, no test plan to follow, and no test cases.
- Catches Unexpected Errors: Any unexpected errors, such as crashes, that are not identified using a documented sequence can be caught using ad hoc testing.
Thus, ad hoc testing is basically an unstructured approach that relies only on the experience and knowledge of the professionals testing the application. So why is it so important? Let’s find out.
Importance of Ad Hoc Testing
As already mentioned, ad hoc testing plays a very important role in identifying overlooked defects. Ad hoc testing is important because:
- Ad hoc identifies unpredictable crashes, unexpected bugs, and defects.
- It helps professionals to explore the software functionality randomly and perform in-depth testing.
- Ad hoc testing provides quick user feedback and insights into the application.
- With ad hoc testing, test coverage is enhanced further as its scope is beyond predefined test cases.
- In dynamic testing environments such as real-time banking software, ad hoc testing offers flexibility and efficiency.
Ad hoc testing is crucial as well as beneficial to software testing system. But there are some areas/situations where it might fit perfectly where as some situations in which you would like to avoid ad hoc testing entirely. The following sections discuss the situations/events where you can employ ad hoc testing and also those where you should not use it.
The Ad Hoc Testing Approach
Ad hoc testing is all about being curious rather than following a set plan. Here’s a general overview of how one can go about it:
- Understand Your Mission: Before you get busy clicking, be clear about what it is that you want to check. E.g., it could be a security feature or the registration form within the application. This loose goal will be your guide.
- Approach the Application as a User: You’ll generally want to adopt two personas here. First, as the end user, try to mimic their journey. Then, as the tester who tries to outsmart the developers and look at areas or functionalities that the developer likely missed.
- Use Your Experience and Intuition: This is more of an error-guessing exercise. Remember past bugs, think about the edge cases, and trust your gut.
- Maintain a Log: The biggest challenge with ad hoc testing is reproducing bugs. Hence, maintain a log with the details you might need to remember what you tested and how to reproduce issues that came up.
When to Use Ad Hoc Testing?
There are various situations in which professionals can rely on ad hoc testing. Below are a few examples.
- During UAT Testing: As part of user acceptance testing (UAT), end users test the application system in their environments to see the suitability of the new system. Ad hoc testing can be used here to ensure that no unwanted or unnoticed errors occur in the user environment.
- For Exploratory Testing: During exploratory testing, professionals can dig deep into the application using ad hoc testing to uncover defects and issues.
- Quick Assessment of New Features: In situations where it is essential to validate the functionality quickly and also identify any bugs related to a new feature, ad hoc testing can be employed.
- Testing in the Early Stages of Development: Apart from using ad hoc testing before formal testing, it can also be used early in the development cycle to identify potential errors. This helps identify defects and errors in the development cycle itself.
- When there is Little to No Time for Testing: Ad hoc testing is of great help in situations where the time available for testing is limited and structured testing approaches cannot be used.
- For Testing Error-Prone Areas: Many a time in a software application system, certain areas are quite error-prone or risky. For example, client-server interactions or API programming calls mostly pose a threat. Ad hoc testing performed randomly can catch errors in these areas and find errors randomly.
When Not to Use Ad Hoc Testing
As there are situations where ad hoc testing can be used, there are also situations or cases where ad hoc testing cannot be used. These are discussed here:
- During Beta Testing: In beta testing, clients check the software for features or enhancement suggestions, and also to provide feedback. In such situations, testing according to structured approach, using test plans is more appropriate so that entire functionality of the application is covered.
- On Defective Test Cases: In structured testing, when some of the test cases fail, the issues should be documented and linked to the test cases. Once these issues are resolved, they should be retested. In this scenario, it is not advisable to use ad hoc testing.
- For Basic UI Changes: Whenever certain simple and basic changes are made to UI, there is no need for ad hoc testing. Only basic positive and negative testing should suffice.
Types of Ad Hoc Tests
After discussing various aspects of ad hoc testing, it is time to discuss the types of ad hoc tests performed on the application. The key ad hoc types are shown in the figure below.
- Buddy Testing: In this approach, developer and tester collaborate with each other for testing thus ensuring early bug detection and quick bug resolution. Two buddies can mutually work on the same feature or module to identify defects. Testers can develop better test cases using buddy testing and developers can make early design changes. Buddy testing takes place after Unit Testing completion.
- Monkey Testing: This approach employs random inputs to test system behavior. The approach, since it is ad hoc, does not have predefined test cases. It is because of the randomness of the approach that this is called “Monkey Testing”.
- Pair Testing: Same as buddy testing, in this approach as well, two testers work together. But in this case, one tester executes test scenarios and other one records findings. In doing this, both the testers share ideas, and work on same module and machine.
Advantages and Limitations of Ad Hoc Testing
Ad hoc testing offers several advantages to applications in general, including helping create a robust product. At the same time, it also impacts testing efficiency and accuracy. The following table summarizes the advantages and limitations of ad hoc testing.
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Flexibility: The Ad hoc testing approach adapts easily to changing situations or requirements. | Lack of Documentation: Tracking and reproducing issues are challenging as there is no documentation or predefined test cases. |
| Creativity: Professionals using ad hoc testing can enhance their creativity and use their intuition to identify defects. This is not possible in a structured testing approach. | Requires Expertise: Since the ad hoc testing approach is unstructured and without any documentation, a thorough understanding of the system is desired to identify defects. |
| Early defect detection: Ad hoc testing can be performed in the early stages of the development cycle. This can help identify issues and also facilitate early issue resolution. | No Guaranteed Defect Detection: With an ad hoc approach, it is not guaranteed that all the issues will be detected, as this approach is unstructured and random. |
| Time and cost savings: Since there is no documentation and no test plans to follow, professionals are not bound by time. Hence, testing can be faster and cost-saving. | Time Uncertainty: In an ad hoc approach, making plans and estimations are difficult, and finding issues can also take an unpredictable amount of time. |
| Improved testing coverage: When ad hoc testing is performed along with structured testing, it can cover more areas and thus find more defects. In an ad hoc approach, testers use their creativity and intuition, thus enhancing the testing coverage. |
Best Practices for Ad Hoc Testing
The ad hoc testing approach can be improved further by refining strategies and following certain best practices. These best practices maximize the effectiveness and efficiency of the ad hoc testing. The key best practices to follow are:
Well-Trained Testers with Good Business Knowledge
Make sure to ensure that professionals (testers or developers involved in testing) understand the application thoroughly and they have good business knowledge. They should also possess clear understanding of the features and requirements. At the same time, they are expected to know end to end business process. With this preparation, more defects can be identified to make the application stable.
Effective Documentation
Professionals should record observations, steps, and identification of issues so that the process is tracked for future reference. Defects can also be recorded or written down. Further, test cases can be written for each defect so that when it is resolved, it can be retested in a structured manner.
Session-Based and Collaborative Testing
Ad hoc testing should be done with time-boxed sessions to ensure goals are achieved. Multiple professionals, such as testers, developers, and so on, should be involved in testing so that they can collaborate effectively to find maximum defects. Also, key business modules and areas should be identified and targeted for ad hoc testing on a priority basis.
Continuous Learning and Feedback Mechanism
Training sessions should be conducted regularly to keep professionals updated on application changes/ Feedback should also be gathered in order to refine the testing process.
Using Automation Testing Tools
Different tools for capturing the screen, taking notes, and recording sessions should be utilized for better documentation. Also, tools such as debuggers, profilers, and task monitors should be used as and when necessary.
Test automation tools such as testRigor can be utilized to enhance the quality of ad hoc testing. testRigor supports web and mobile browser testing, mobile app testing, desktop testing, API testing, etc. With testRigor, testers can easily automate test cases in plain English. The AI engine, moreover, ensures that these tests are resilient to small UI changes. This helps make the ad hoc testing process smoother.
Explore the extensive features supported by testRigor here.
Risk-Based Focus
Ad hoc testing should prioritize areas with critical functionalities and high risk. This will maximize the impact.
Stable Test Environment
Environment used for testing should be stable and identical to production environment so that accurate or near accurate results are obtained during testing.
Exploratory Techniques
Ensure that testing approach applies scenario-based testing and also applies boundary value analysis and other methods to get better results.
Encourage Creativity and Error Guessing
Professionals involved in testing should have an innovative mindset. At the same time, they should use their intuition and experience to guess potential problem areas in the application.
Balance with Formal Testing
All these best practices will work more effectively when ad hoc testing is integrated with structured approaches to ensure comprehensive coverage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ad hoc testing is without doubt a valuable technique to identify issues that structured approaches might have missed. It is a flexible approach and using this approach, testers can explore the application freely and use their expertise and knowledge to identify issues.
However, due to a lack of documentation, defect tracking can sometimes become challenging in ad hoc testing. Secondly, formal testing cannot be replaced by ad hoc testing. But by complementing it with formal structured testing, software quality can be greatly enhanced.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












