What are Docker and Kubernetes and why do I need them?
|
|
Have you ever seen a port or a dockyard? They’re lined with huge cuboidal containers, all in the same dimensions. Despite their symmetry on the outside, they contain a variety of goods within them. These containers can travel across the globe on ships, by roads, or by railways.
In the same breath, software applications can also be packaged in a standard way and then shipped and deployed across various platforms. Tools like Docker and Kubernetes make this possible. Both these tools work with something called a container. Let’s first understand what a container is in software.
What is a container?
A container is a self-contained package of software that includes everything needed to run an application: code, libraries, runtime, system tools, and settings. This package can be shipped and run consistently on any computer, whether it’s your laptop, a server, or a cloud environment.
Imagine a suitcase. It’s a self-contained unit that holds everything you need for a trip: clothes, toiletries, and essentials. You can pack it once and take it anywhere.
Key benefits of containers
Containers are beneficial due to their:
- Portability: Like a suitcase, containers can be moved easily.
- Efficiency: They are lightweight and start quickly.
- Isolation: Each container is independent, preventing conflicts between applications.
Now that you’ve understood what a container is, let’s see how tools like Docker and Kubernetes help manage them.
Docker
Docker is like the shipping container for software. It packages an application and all its dependencies (libraries, settings) into a standardized unit called a container. This container can then be shipped (deployed) to any computer or server.
The five-minute video below provides an excellent overview:
Key components
While working with Docker, you’ll encounter:
- Docker Daemon: This is the background service or the engine that manages images, containers, networks, and volumes. It’s the core of Docker.
- Docker Client: This is the command-line interface (CLI) or other tools that allow users to interact with the Docker daemon. Most Docker commands are executed through the client, which sends requests to the daemon.
- Dockerfile: Set of instructions for building a Docker image.
- Docker Images: These are read-only templates with instructions for creating Docker containers. They contain the application code, runtime, system tools, system libraries, and settings.
- Docker Registry: This is where the images are hosted.
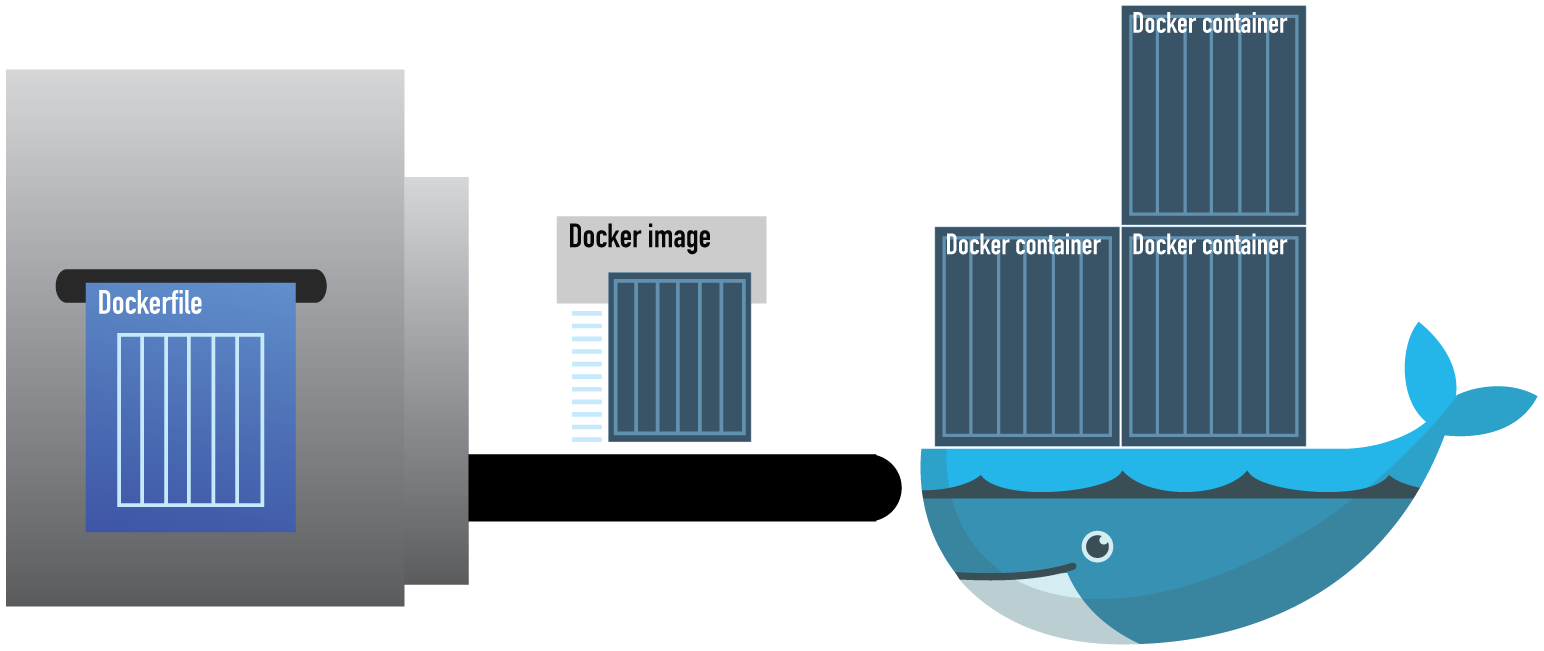
How does Docker work?
Docker operates on a client-server architecture. Here’s a simple flow of how it operates:
- Developers write code and define dependencies in a Dockerfile
- Dockerfile is used to build a Docker image
- Docker images are stored in a registry
- Containers are created from these images and run on any environment that has Docker Engine installed
The contents of the container are declared in “Dockerfile” (similar to Vagrantfile, Makefile, etc.). When Dockerfile is built, it produces a “Docker image” which can be started to create a “Docker container.”
Similarities with Vagrant
Docker is similar to Vagrant (based on VMs) since both:
- Leverage declarative configuration (check out Dockerfile official documentation and Dockerfile examples)
- Produce an image with all the files
- Images can be run multiple times to create “containers”
- Can allow resources like folders to mount from the host computer
Differences with Vagrant
But Docker is different because:
- Images have layers (like VMWare)
- The file system is copy-on-write to allow image layering
- Containers rely on a lightweight, isolated process on the host OS instead of running their own full-blown isolated OS
You can pull images from DockerHub similar to installing packages in NPM. One notable example is the Alpine OS image, which is only 5 MB in size. DockerHub has images for virtually anything, including official images for MongoDB, MySQL, and a 40MB Alpine-based Java image.
Because Docker images are layered, when you deploy (or download) a new image, you only need to download layers you don’t already have. This helps to speed up deployments quite a bit.
Docker v/s VM
Both Docker and Virtual Machines (VMs) are virtualization technologies, but they operate at different levels of abstraction.
- Virtual Machines create isolated environments that emulate a complete computer system, including a dedicated operating system, hardware resources, and applications.
- Docker creates isolated environments called containers, which share the host operating system’s kernel but provide isolation for applications and their dependencies.
| Feature | Docker | Virtual Machine |
| Architecture | Shares the host OS kernel, with containers running as isolated processes | Includes a full guest OS, virtual hardware, and a hypervisor. Each VM runs a separate OS instance |
| Resource Usage | Lightweight, more efficient, with less overhead since containers share the host OS kernel | Resource-intensive and requires more resources due to the overhead of running multiple full OS instances |
| Isolation | Application-level.
Suitable for running multiple instances of an application on the same OS |
Operating system-level.
Provide strong isolation with complete OS separation. Suitable for running multiple different OS environments on |
| Performance | Offers better performance due to reduced overhead | Generally have higher latency due to the overhead of the hypervisor and full OS |
| Portability | Highly portable as containers can run on any system with Docker installed | Less portable due to their larger size and complexity |
| Use Cases | Microservices, web applications, CI/CD, rapid application development and deployment | Legacy applications, multiple operating systems, high-security requirements |
What is Docker Compose?
Docker Compose is used to define and run multi-container applications on a single host. It uses a YAML (yet another markup language or YAML ain’t markup language) file to configure the application’s services, networks, and volumes. For testing purposes, it is convenient to use one file to define and run images for a Web app and a database that work together in a test environment.
The 12-minute video below provides a nice overview:
What is Docker Swarm?
Docker Swarm is Docker’s native clustering and orchestration tool for managing a cluster of Docker engines. It allows you to deploy and manage a swarm of Docker nodes as a single virtual system.
While Docker Swarm is a capable tool, Kubernetes has gained more popularity as a container orchestration platform due to its richer feature set and community support.
Kubernetes
This is the perfect captain to manage your fleet. Kubernetes (K8s) is an open-source platform that can automate the deployment, scaling, and operation of application containers across clusters of hosts.
A lifesaver for DevOps, it provides a robust and flexible system for managing containerized applications in different types of environments, from development to production. It can declare dependencies between Docker Images but uses a different format that is incompatible with Docker Compose.
Here are some fun yet informative resources to understand Kubernetes:
Key components
Some basic terms that pop up when working with Kubernetes are:
- Pod: A pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes and represents a set of running containers that are deployed together
- Service: An abstraction which defines a logical set of pods and a policy by which to access them
- Node: A worker machine which may be a virtual or physical machine. Each node runs pods
- Cluster: A set of nodes (machines) that run containerized applications managed by Kubernetes
- ReplicaSet: Ensures a specified number of pod replicas are running at any given time
- Deployment: Provides declarative updates to applications, managing the deployment of ReplicaSets
- Namespace: Provides a mechanism to partition resources within a cluster
Like a Swiss-army knife, Kubernetes has a lot to offer.
For example, you can simply provide the location to the Docker Image to Kubernetes and it can spawn containers from it. If you want to manage your resources (scale up or down), then Kubernetes can monitor traffic and load, making sure that your application is always up and running. If a container experiences failure during its lifecycle, Kubernetes uses self-healing to detect and restart it. It has useful integrations with mainstream code repos (like BitBucket) that make deployments easier.
Another interesting capability is health-monitored rollout (“blue-green” deployment). This allows you to define ‘health check’ on your system (ping APIs for us). K8s will attempt to roll out a new version and if it starts up well, it will replace the old version. This allows you to achieve de-facto zero downtime.
While you need to configure various parameters within Kubernetes to be able to automate these activities, it is definitely a huge load off.
Additional resources
- DevOps Testing Tools
- Containerization and Test Automation Strategies
- What Is CICD?
- Test Orchestration in Automation Testing
- DevSecOps vs. DevOps: Differences, Tools, and Strategies
- 30+ DevOps Certifications and Training Courses Guide for 2024
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












