What is Encryption? Process, Benefits, and Applications
|
|
In the digital age, where we live today, data is constantly being transmitted across networks and stored in cloud servers. To safeguard this information from unauthorized access and cyber attacks, it is important to employ several techniques that can keep the information safe and secure.
Encryption is an important technique for safeguarding information, whether you are sending an email, making an online payment, or simply storing data on your computer.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
This article covers the following topics:
|
This article explores the meaning of encryption, its working, importance, methods, benefit,s and challenges.
What is Encryption?
Encryption converts plaintext (readable data) into ciphertext (unreadable, encoded data) using mathematical algorithms and an encryption key. Encryption ensures that only authorized individuals who has the correct decryption key can access the transmitted data.
In simple words, encryption is a process that locks your data in a secure safe the way you lock your valuables. Only thing, in case of data, the safe you use is digital!

With the encryption process, the digital information that is in readable format is converted to randomized, unreadable format called ciphertext for transmitting. At the receiver’s end. This ciphertext is converted back to plaintext readable form using the process of decryption.
Decryption is exactly opposite to encryption. It converts ciphertext to a readable plaintext format. However, decryption can be done only by those who possess the valid decryption key.
This encryption-decryption process aims to thwart cybercriminals, who may have used quite sophisticated means to intrude on a corporate network, only to find that the data is unreadable and they cannot make it readable.
Additionally, encryption also ensures the confidentiality of data or messages and provides authentication and integrity.Encryption is considered as the basic building block of data security and is widely used by organizations be it large, medium or small. Almost everything we see on the internet has passed through some layer of encryption, be it websites, cloud applications, or mobile apps.
Cryptography is the science of hiding data and information, and encryption is used for this purpose. Read more: What is Cryptography?.
How Encryption Works?
Encryption has evolved over time, from a mere encoded text used to pass secret information between military personnel to a protocol used only by governments for top-secret operations to an everyday must-have policy for organizations to ensure the security and privacy of information.
The process of encryption is summarized in the following points:
- Encryption is a logical process that involves applying an encryption algorithm to the plaintext using an encryption key (a set of mathematical values).
- The encryption algorithm scrambles the data, making it a randomized, unreadable form called ciphertext.
- To convert this scrambled data back to readable form, the receiver of the data needs a decryption key.
- An encryption algorithm uses the key to alter the data predictably. Hence, even if the encrypted data appears random, it can be transformed back into a readable format using the decryption key and algorithm.
- The decryption key must always be kept secret, and may or may not be similar to the key used for encrypting the message.
- Some commonly used encryption algorithms include Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Blowfish, Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA), and Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC). To learn more about encryption types and algorithms, refer to Cryptographic Algorithms: Symmetric vs. Asymmetric.
For example, we may need to encrypt the message “testRigor Encryption” and send it across the network. When encryption is applied to this message using the encryption key, it will generate unreadable text such as “U2FsdGVkX1+Y5wZG509FWH3c09tQy6dy+qs6Ltvj89xpMXP9D/soBnz7twna7IG8.”
As you can see, this generated ciphertext is random and unrelated to the original plaintext.
Encryption protects data from being transmitted or stored by unauthorized personnel. After encryption, the information appears to be useless, concealing it from malicious intent. If you pass the random data generated above to the decryption algorithm with a correct decryption key, the original plaintext will be obtained.
Encryption can be applied to data in two primary ways, or when data is in the following states:
- In transit: In this state, data is moving or being transmitted.
- At rest: At this point, data is stored either in files, a database, etc.
Encryption can be used to protect information both for good and for bad purposes. In fact, proliferated ransomware is an example of bad encryption usage. The ransomware attacks rely on speedy encryption methods to capture more files.
Why is Encryption Important?
Cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized surveillance have been rising in recent years, and the importance of encryption has never been more vital. The primary reasons why encryption is essential are:
- Data Protection: Encryption protects personal data and sensitive information like financial records, health data, and communications from breaches. It also helps protect sensitive data from being stolen and ensures the data that is transmitted is accessed by only those with the proper decryption key. This makes it nearly impossible for cybercriminals to steal or misuse data.
- Data Privacy: Once encrypted, messages and data can only be read or accessed by the legitimate recipients or the data owner. This prevents other users, including cybercriminals, attackers, and legitimate agencies, from accessing or reading personal data, maintaining the privacy of the data.
- Data Integrity: Encryption preserves data integrity by preventing its tampering without detection. Integrity of backups and data in transit is maintained using encryption; it can verify that the data has not been tampered with. This prevents hackers from intercepting communications and tampering with the data.
- Compliance: Encryption is mandatory for certain types of data in regulatory standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. Regulatory and legal requirements for data protection can be fulfilled using encryption. Many industries, such as healthcare and finance, must adhere to strict regulations about how consumer data is used and stored, and encryption helps organizations meet those standards and ensure compliance. Read: AI Compliance for Software.
- Authentication: Encryption is used to verify the identity of users or systems and prevent unauthorized access. Public key encryption ensures that a website’s origin server owns the private key and thus was legitimately assigned an SSL certificate.
- Security: Encryption shields data from hackers, eavesdroppers, and malicious insiders. It provides an additional security layer to protect against data breaches, cyber-attacks, and other threats. Organizations use encryption to protect their sensitive data, making it unreadable and inaccessible unless proper decryption is used. Read: Security Testing.
- Increased Consumer Trust: Encryption boosts consumer trust and confidence in an organization by publicly disclosing the use of encryption technologies. Customers prefer organizations that use encryption and likely recommend it to others.
Applications of Encryption
Encryption plays a crucial role in a wide array of real-world applications as discussed below:
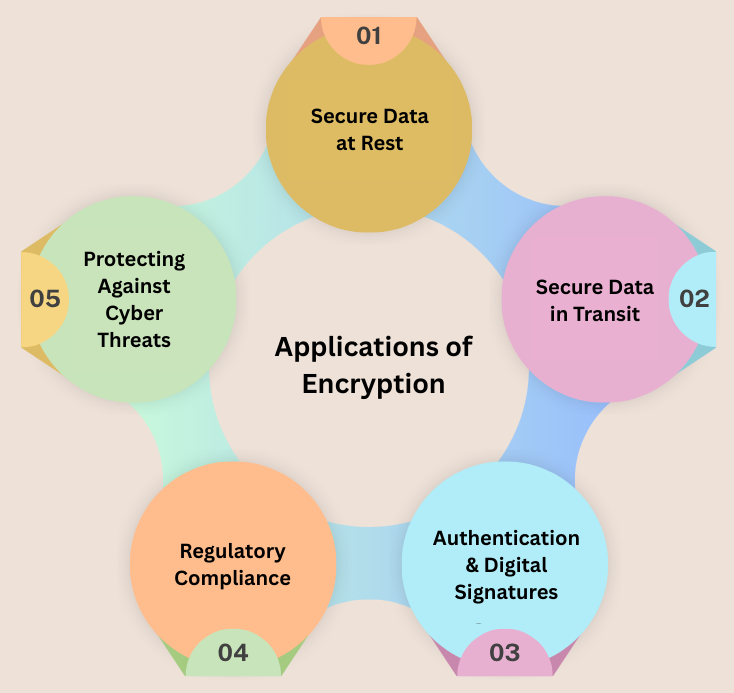
1. Secure Data at Rest
Encryption can secure stored data on hard drives, SSDs, or cloud storage to prevent unauthorized parties from accessing it even if the device is stolen. Encryption is applied to stationary data (data at rest) in the following ways:
- Device Encryption: Protects data stored on computers, laptops, and smartphones.
- Cloud Storage: Keeps data stored in cloud services safe and secure from unauthorized access.
- Hard Drive Encryption: The Entire hard drive is encrypted to protect all stored data.
2. Secure Data in Transit
Data being transmitted over networks like the internet using protocols such as HTTPS, SSL/TLS, and VPNs is protected using encryption in the following ways:
- Online Transactions: Online payments, banking transactions, and other financial activities are secured by encryption.
- Website Security (HTTPS): Data transmitted between users’ browsers and websites is encrypted.
- Email Encryption: Email communication is kept private and secure by encryption using tools like PGP and S/MIME.
- VPNs: Internet traffic is encrypted to protect online activity, mainly when public Wi-Fi networks are used.
- Mobile & Messaging Apps: Applications like WhatsApp, Signal, and Telegram use end-to-end encryption to protect messages transmitted during chatting.
3. Authentication and Digital Signatures
Digital signatures verify document authenticity and integrity. These signatures encrypt documents digitally, and the receiver decrypts the signature upon receiving it.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory standards use encryption to protect sensitive information.
- Meeting Compliance Standards: Various regulatory and compliance standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, require encryption to protect sensitive data.
- Avoiding Penalties: Organizations can avoid penalties for data breaches and compliance by using encryption to protect data.
5. Protecting Against Cyber Threats
Encryption protects from cyber threats:
- Preventing Data Breaches: Data breaches are prevented by protecting against unauthorized access and theft of sensitive information.
- Combating Malware and Viruses: Sensitive information is encrypted, making it more difficult for malware to access and compromise.
- Mitigating Phishing Attacks: Encryption plays a vital role in verifying the authenticity of websites and emails, reducing the risk of phishing attacks.
- Data Integrity: Encryption ensures that data is not tampered with during transmission or storage.
- Secure File Sharing: Files are encrypted before sharing to protect their confidentiality.
Limitations of Encryption
Encryption techniques have several limitations as follows:
- Performance Impact: Some encryption methods, like asymmetric encryption, require higher computational power, impacting the speed and efficiency of data processing and analysis, especially when dealing with large amounts of data.
- Key Management: If encryption and decryption keys are lost, they cannot be recovered, resulting in permanent loss of data access. This improper key management is a significant disadvantage of encryption.
- False Sense of Security: If an organization adopts encryption, it should adopt it completely. Failure to adopt the best practices can result in unrealistic requirements that could compromise data security. This also gives users a false sense of security since the organization shows it uses encryption, but does not in reality use it.
- Complexity: Implementing encryption correctly requires significant technical expertise. Encryption methods use complex mathematical formulae and computations that require expertise.
- Cost: Encryption is expensive to implement and maintain. It requires additional resources and upgrades.
- Compatibility: Using encryption technology on different systems and applications is always tricky. It is also challenging to ensure that all authorized users can read encrypted data, which can limit its visibility and usability.
However, the advantages of encryption outweigh the disadvantages, making it essential for cybersecurity and data protection. Read: Cybersecurity Testing in 2025: Impact of AI.
How to Implement an Effective Encryption Strategy?
Organizations should follow these best practices to implement an encryption strategy:
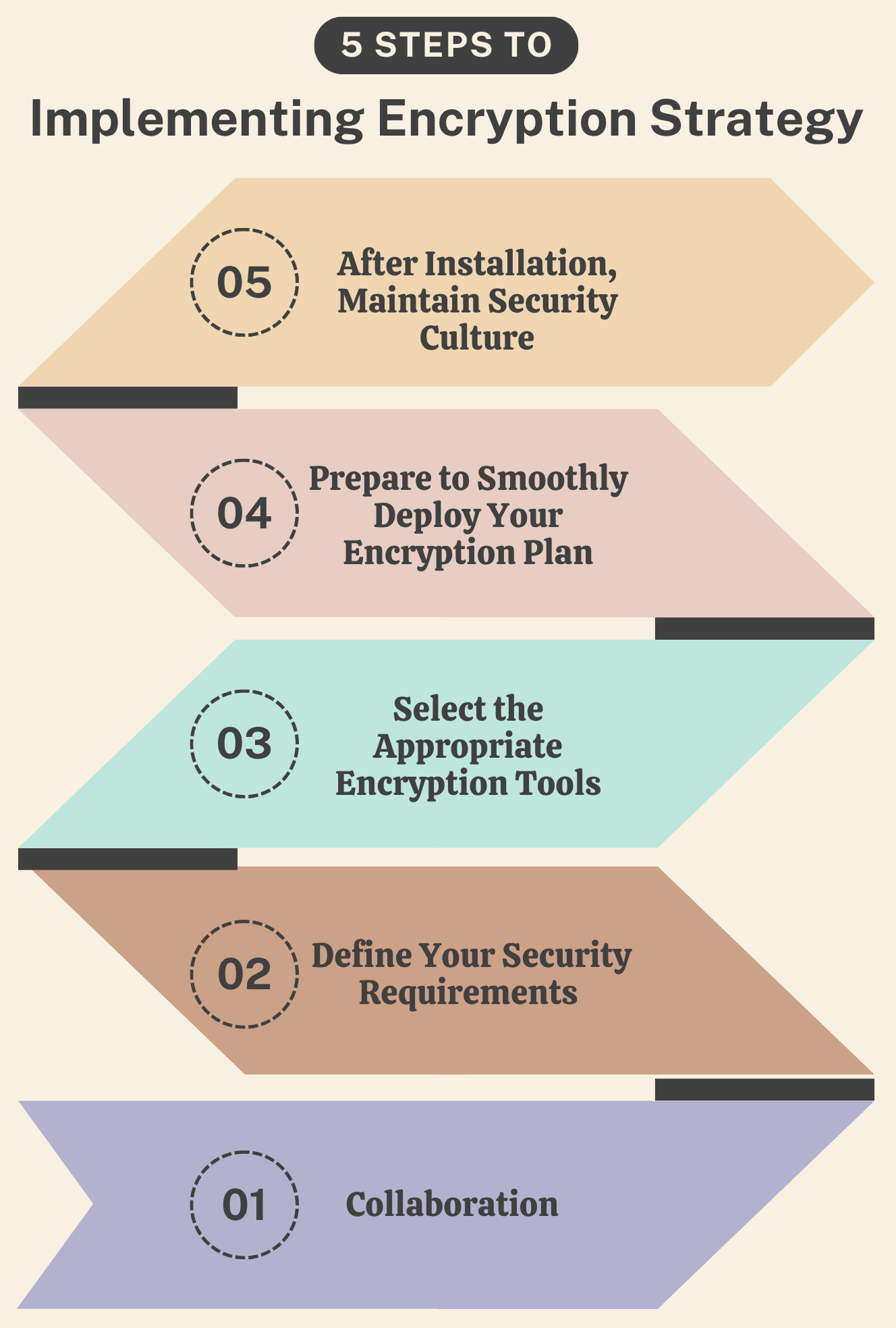
1. Collaboration
Developing and implementing an encryption strategy requires teamwork. It should be approached as a large-scale project and include members of management, IT, and operations.
- Gather essential data from stakeholders.
- Identify the legislation, laws, guidelines, and external forces that may impact the purchase and implementation decisions.
- Identify high-risk places such as wireless networks, data backups, laptops, and mobile devices where encryption is necessary.
2. Define Your Security Requirements
Having a general concept of your security requirements is always helpful.
- Start with threat assessment, as it will help to identify what data needs to be encrypted.
- Assess the systems’ security, as the strengths and processing requirements of different encryption methods may vary.
3. Select the Appropriate Encryption Tools
At this stage, the security requirements are determined.
- Start looking for the solutions that best suit these requirements.
- Remember to install various data encryption algorithms to protect your network effectively.
- To keep company data as safe as possible, use correct encryption technologies at each level of data storage and transit.
- Use encrypted applications such as encrypted email services to ensure overall security.
4. Prepare to Smoothly Deploy Your Encryption Plan
The implementation of the encryption strategy should be well-planned.
- Integrate the encryption strategy with the customer-facing applications, if any.
- Check if additional procedures are required to integrate the new encryption methods with legacy systems.
- Implement the changes with minimal disturbance to the existing environment by planning ahead of time.
- Work with a third-party IT service provider if necessary, as it may also aid in the transition.
5. After Installation, Maintain Security Culture
Now that the encryption system has been installed successfully, maintain the security culture to get the expected outcomes.
- Ensure the entire team is educated on the proper use of encryption and key management strategies.
- Prevent human errors like putting encryption keys on insecure servers to prevent hostile attackers from accessing company data.
- Use encryption in conjunction with other security techniques to maximise security.
- Deploy security hardware and a strong firewall, along with an encryption system.
Conclusion
Encryption is the foundation of modern cybersecurity. It ensures confidentiality, integrity, and trust by safeguarding personal data to secure global financial transactions. By understanding the encryption process, types, applications, and best practices, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions about effectively implementing encryption.
Encryption techniques evolve with technology. Investing in modern, efficient, and future-proof encryption techniques is necessary to stay ahead of the ever-changing cybersecurity landscape.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












