Smart Framework PHP Testing

Having a robust web development framework is pivotal for crafting high-quality websites. Smart Framework PHP stands out as a web development platform allowing developers to utilize both PHP and JavaScript. As an open-source framework, it enables the development of web-based applications tailored for web clients, mobile devices, and desktops. Notably, Smart Framework employs the MVC (model-view-controller) pattern, which comes with built-in dependency injection. In this pattern, the model embodies the data and business logic of the application, the view manages the presentation layer, and the controller serves as a liaison between the model and the view. Compared to other PHP frameworks such as Zend, Laravel, or Symphony, Smart Framework is lightweight, packed with features, and boasts superior performance.
In this article, we'll look into methods for testing the PHP code you craft using this framework. Many of these testing strategies remain applicable for frontend code, though the specific frameworks for unit and integration testing may differ. By adhering to the testing pyramid, you can evaluate your application developed with Smart.Framework through:
Unit Testing
Unit tests are the base of the testing pyramid and comprise the biggest chunk of test cases. The intention of these tests is to validate every single unit of code like functions, classes, or APIs. Just like the areas these tests focus on, unit tests are expected to be small and concise, focusing on just a single outcome per test. There are many test frameworks available for performing unit and integration testing on PHP code. Let’s look at some of the common ones that are used with this framework. PHPUnituse PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
final class GreeterTest extends TestCase
{
public function testGreetsWithName(): void
{
$greeter = new Greeter;
$greeting = $greeter->greet('Alice');
$this->assertSame('Hello, Alice!', $greeting);
}
}
Codeception
namespace Tests\Unit;
use \Tests\Support\UnitTester;
class UserTest extends \Codeception\Test\Unit
{
public function testValidation()
{
$user = new \App\User();
$user->setName(null);
$this->assertFalse($user->validate(['username']));
$user->setName('toolooooongnaaaaaaameeee');
$this->assertFalse($user->validate(['username']));
$user->setName('davert');
$this->assertTrue($user->validate(['username']));
}
}
PHPSpec
PHPSpec is a testing framework that follows a behavior-driven development (BDD) approach, focusing on specifying the behavior and design of classes and objects. While PHPUnit is a widely used unit testing framework in PHP, PHPSpec takes a different approach by encouraging developers to describe the expected behavior of code through specifications. PHPSpec aims to create more expressive and readable tests that describe how objects should behave.
Integration Testing
Just testing the different units of an application in isolation is not enough. It is important to see if all these units are working together in sync. Integration testing helps in achieving this. By targeting integrations between various components of the application like an API and a database. Here are some scenarios where integration testing is likely to be used.
- Testing if the application interacts smoothly with the database during various read and write operations.
- Testing the integration with external services, such as payment gateways, email providers, or APIs. This involves handling requests and responses, along with error and exception handling.
- Testing the integration of file uploads and downloads.
- Verifying the integration of authentication and authorization mechanisms, such as login, registration, and user access control. This can also include the integration of identity providers, such as OAuth or LDAP.
- Testing the integration of internal APIs or web services with other components of the application.
Most of the unit testing tools can be used to write integration tests. Many of these test frameworks offer features such as environment configurations and capabilities to interact with the modules without fully booting the system to make the process faster.
End-to-end Testing
The top tier of the testing pyramid is reserved for end-to-end tests. These tests should be framed from an end user’s perspective, meaning that they will comprise user journeys, and can often be lengthy and complex. Members from other teams like business analysts, manual testers, and product owners sometimes all collaborate to create these tests. End-to-end tests tend to exercise all layers of the application and quite often start from the UI, since that is where the user would interact with the application. Let’s take a look at some tools to do end-to-end testing of applications built using Smart Framework.
Codeception
use Codeception\Attribute\Given;
use Codeception\Attribute\When;
use Codeception\Attribute\Then;
class AcceptanceTester extends \Codeception\Actor
{
use _generated\AcceptanceTesterActions;
#[Given('I have product with :num1 price in my cart')]
public function iHaveProductWithPriceInMyCart($num1)
{
$productId = $this->haveRecord('Product', ['name' => 'randomProduct'.uniqid(), 'price' => $num1]);
$this->amOnPage("/item/$productId");
$this->click('Order');
}
#[When('I go to checkout process')]
public function iGoToCheckoutProcess()
{
$this->amOnPage('/checkout');
}
#[Then('I should see that total number of products is :num1')]
public function iShouldSeeThatTotalNumberOfProductsIs($num1)
{
$this->see($num1, '.products-count');
}
#[Then('my order amount is :num1')]
public function myOrderAmountIs($num1)
{
$this->see($num1, '.total');
}
}
Selenium
Selenium is a popular open-source framework for automating web-based test cases. It enables testers to automate the testing of web applications across different browsers and platforms. Selenium provides a suite of tools that allows users to interact with web browsers programmatically, mimicking user actions and verifying the behavior of web applications. It supports various programming languages like Java, Python, C#, Ruby, and more.
WebDriver is a key part of Selenium and allows users to automate browser actions, such as opening web pages, clicking links, filling out forms, and extracting data from web pages. Selenium also provides methods to assert and verify various elements and attributes on web pages, allowing users to validate expected behaviors and content. However, Selenium has certain limitations like requiring intensive test maintenance efforts, difficulty in cross-platform testing, and instability due to element-based locators like CSS and XPaths.
testRigor
testRigor is an AI-based end-to-end testing tool that ensures that you can automate your test cases without worrying about test maintenance. It uses AI to reduce test maintenance time by 99.5%, thus doing the heavy lifting for you. This is not the only place it uses AI though. It makes use of generative AI to help you create test cases for your application as well. Moreover, thanks to its smart AI-based engine, you get the liberty of writing test cases in plain English language, without having to code it. As we discussed earlier, end-to-end testing requires writing tests from an end user’s perspective which may not be possible if different team members are unable to collaborate. If you want a testing tool that is truly codeless and is effective in terms of ease of use, scalability, test creation, execution, and maintenance, then opt for testRigor.
login //pre-defined rule navigate to catalog //pre-defined rule check that page contains "Bluetooth earphones (Black)" to the left of "$600" click on "Order" below "Bluetooth earphones (Black)" check that page contains "Bluetooth earphones (Red)" to the left of "$600" click "Order" below "Bluetooth earphones (Red)" click "cart" click "checkout" check that page contains "2 items" check that page contains "Order total : $1200"
You might have noticed that testRigor makes referencing UI elements very easy, by just mentioning where you see the element on the screen. With testRigor, playing around with table data, diving into email and SMS content, or using test data is super easy. Plus, you can chat with APIs to see how they're doing and even peek into databases. Oh, and bonus: testRigor plays nice with all sorts of test management tools, databases, and those fancy infrastructure frameworks.
How to do End-to-end Testing with testRigor
Let us take the example of an e-commerce website that sells plants and other gardening needs. We will create end-to-end test cases in testRigor using plain English test steps.
Step 1: Log in to your testRigor app with your credentials.
Step 2: Set up the test suite for the website testing by providing the information below:
- Test Suite Name: Provide a relevant and self-explanatory name.
- Type of testing: Select from the following options: Desktop Web Testing, Mobile Web Testing, Native and Hybrid Mobile, based on your test requirements.
- URL to run test on: Provide the application URL that you want to test.
- Testing credentials for your web/mobile app to test functionality which requires user to login: You can provide the app’s user login credentials here and need not write them separately in the test steps then. The login functionality will be taken care of automatically using the keyword
login. - OS and Browser: Choose the OS Browser combination on which you want to run the test cases.
- Number of test cases to generate using AI: If you wish, you can choose to generate test cases based on the App Description text, which works on generative AI.
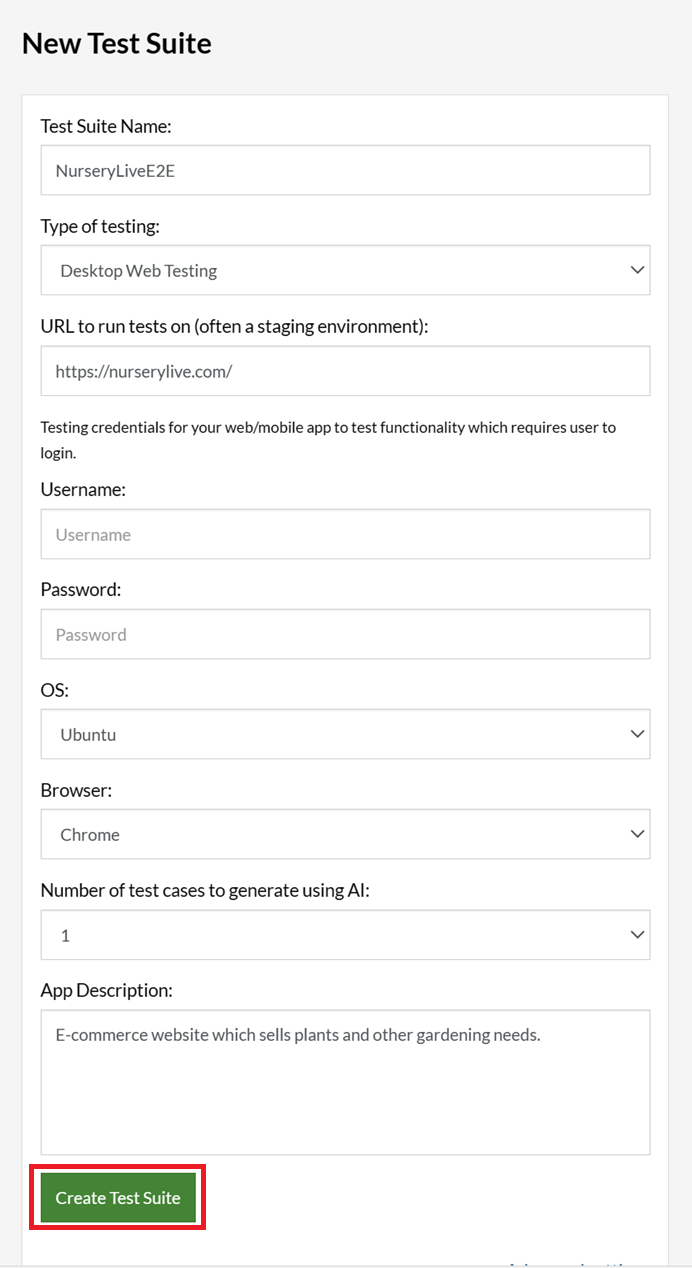
Step 3: Click Create Test Suite.
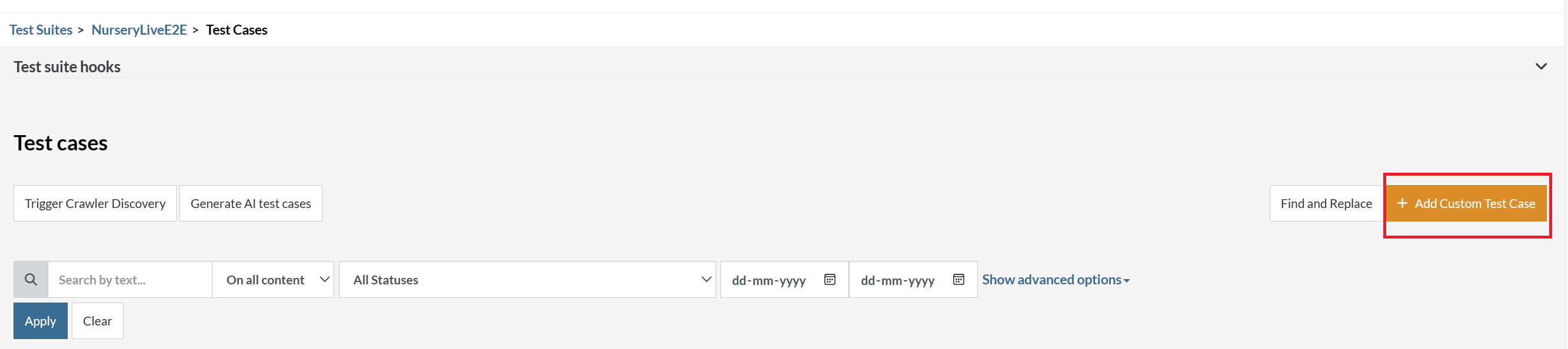
On the next screen, you can let AI generate the test case based on the App Description you provided during the Test Suite creation. However, for now, select do not generate any test, since we will write the test steps ourselves.
Step 4: To create a new custom test case yourself, click Add Custom Test Case.
Step 5: Provide the test case Description and start adding the test steps.
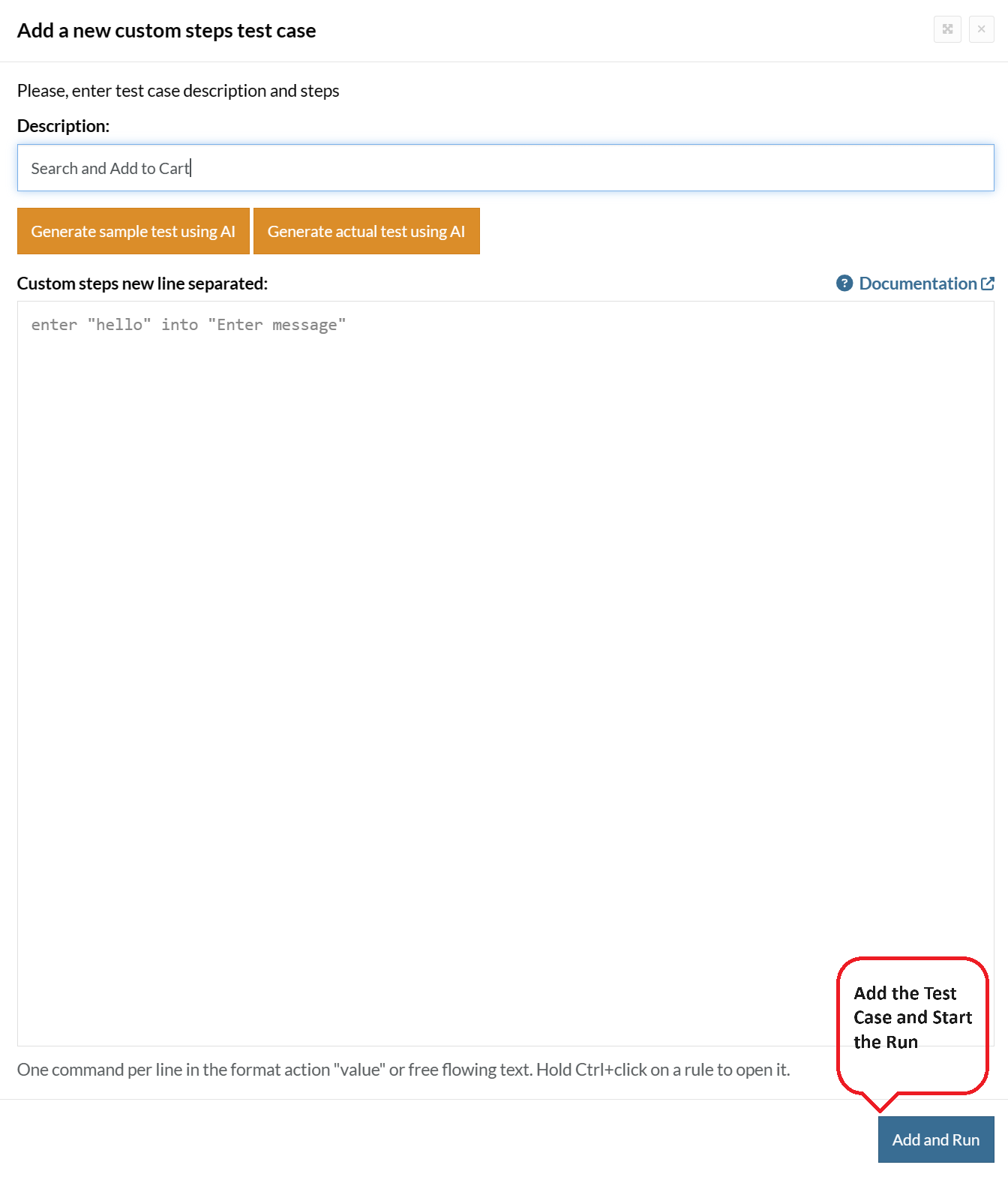
For the application under test, i.e., e-commerce website, we will perform below test steps:
- Search for a product
- Add it to the cart
- Verify that the product is present in the cart
Test Case: Search and Add to Cart
Step 1: We will add test steps on the test case editor screen one by one.
testRigor automatically navigates to the website URL you provided during the Test Suite creation. There is no need to use any separate function for it. Here is the website homepage, which we intend to test.
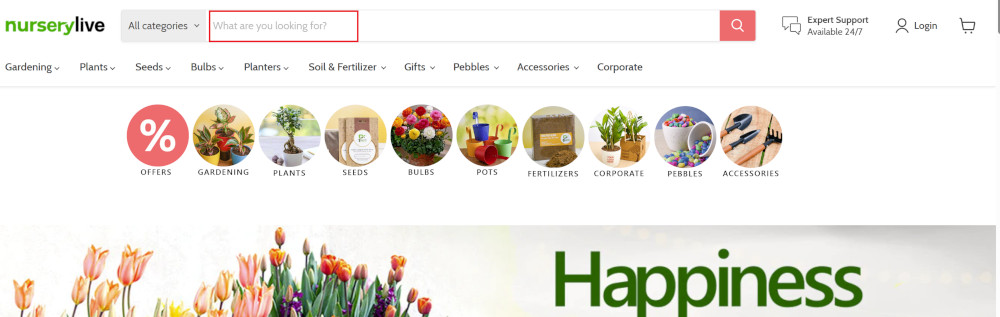
First, we want to search for a product in the search box. Unlike traditional testing tools, you can identify the UI element using the text you see on the screen. You need not use any CSS/XPath identifiers.
click "What are you looking for?"
Step 2: Once the cursor is in the search box, we will type the product name (lily), and press enter to start the search.
type "lily" enter enter
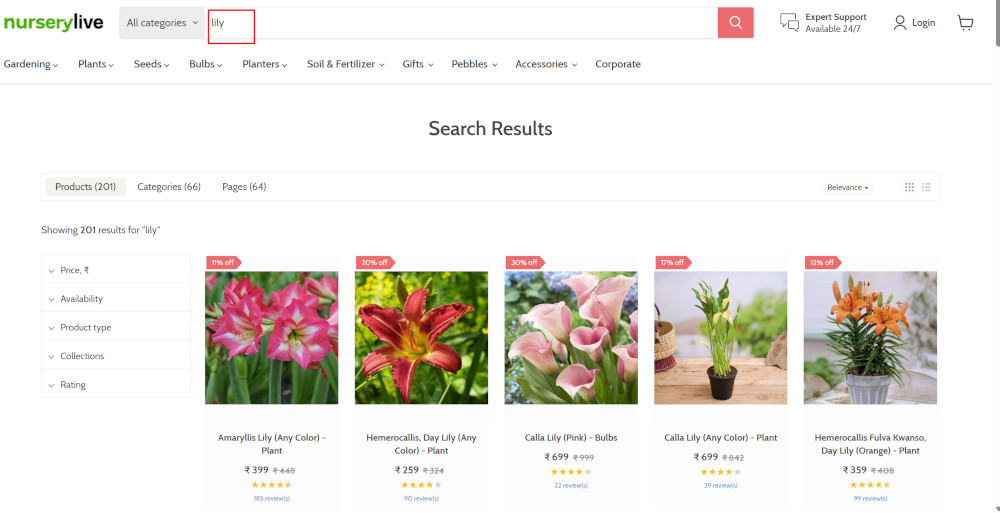
Search lists all products with the “lily” keyword on the webpage.
Step 3: The lily plant we are searching for needs the screen to be scrolled; for that testRigor provides a command. Scroll down until the product is present on the screen:
scroll down until page contains "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)"
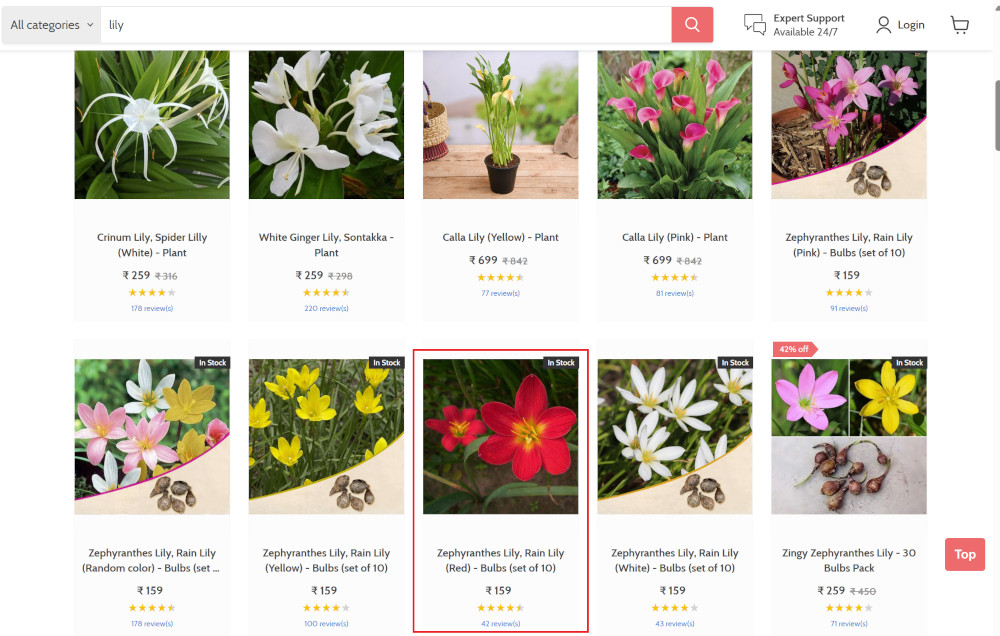
When the product is found on the screen, testRigor stops scrolling.
Step 4: Click on the product name to view the details:
click "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)"
After the click, the product details are displayed on the screen as below, with the default Quantity as 1.
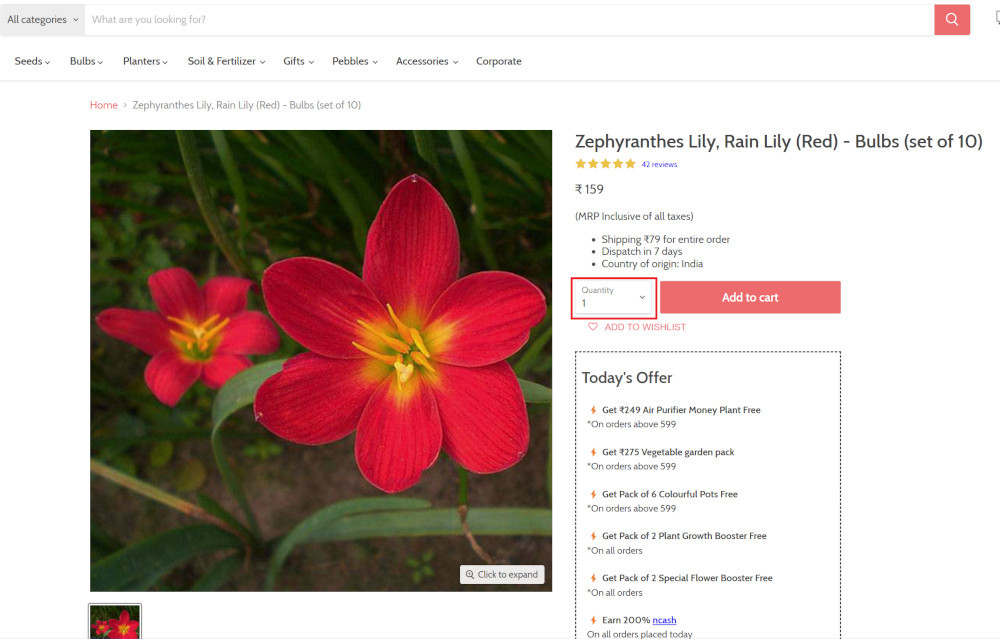
Step 5: Lets say, we want to change the Quantity to 3, so here we use the testRigor command to select from a list.
select "3" from "Quantity"
click "Add to cart"
The product is successfully added to the cart, and the “Added to your cart:” message is displayed on webpage.
Step 6: To assert that the message is successfully displayed, use a simple assertion command as below:
check that page contains "Added to your cart:"
Step 7: After this check, we will view the contents of the cart by clicking View cart as below:
click "View cart"
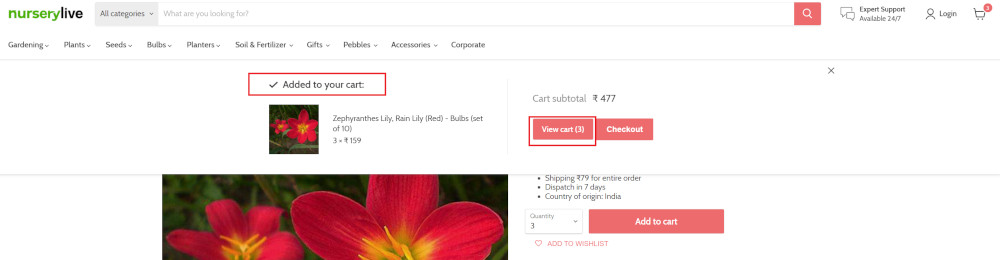
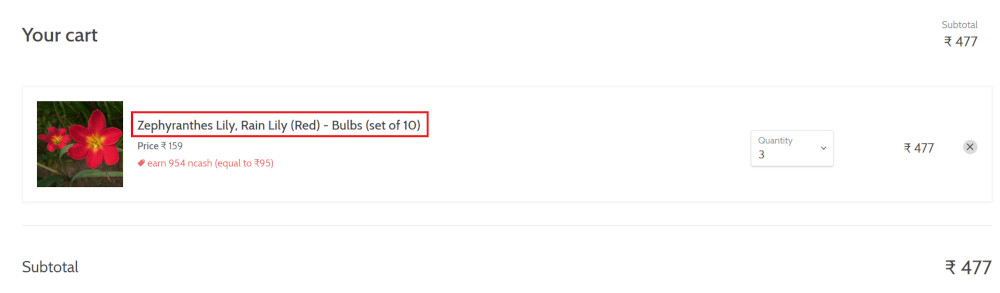
Step 8: Now we will again check that the product is present in the cart, under heading “Your cart” using the below assertion. With testRigor, it is really easy to specify the location of an element on the screen.
check that page contains "Zephyranthes Lily, Rain Lily (Red)" under "Your cart"
Complete Test Case
Here is how the complete test case will look in the testRigor app. The test steps are simple in plain English, enabling everyone in your team to write and execute them.
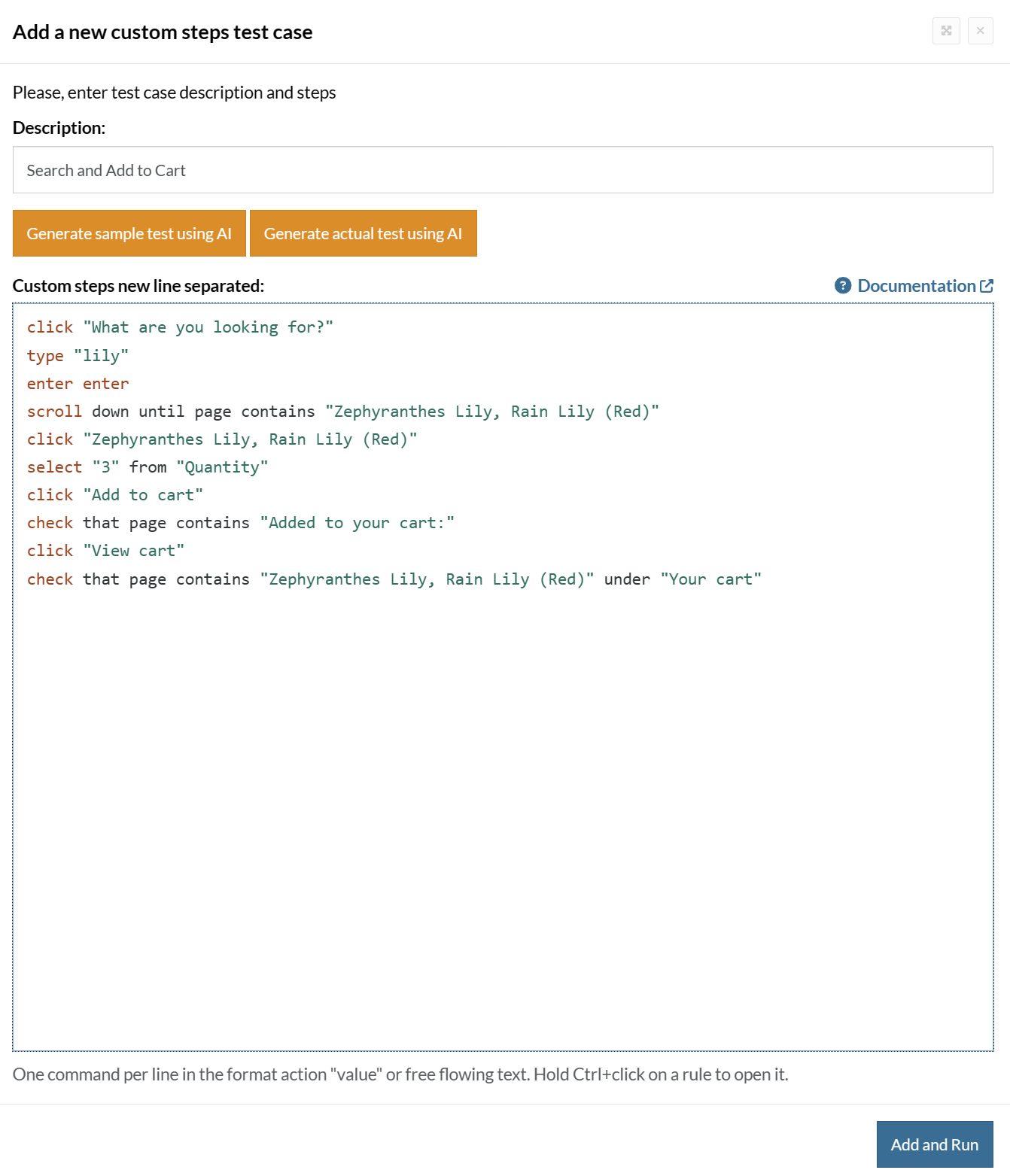
Click Add and Run.
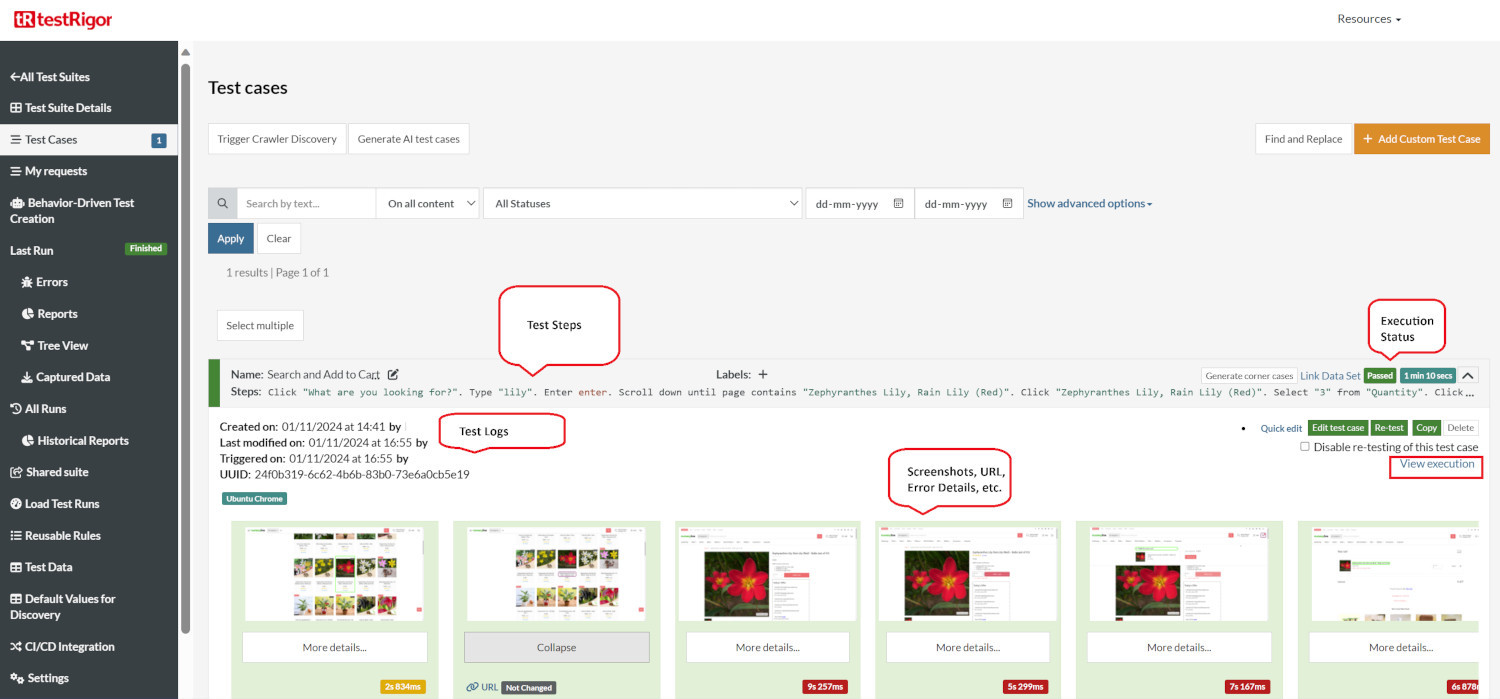
Execution Results
Once the test is executed, you can view the execution details, such as execution status, time spent in execution, screenshots, error messages, logs, video recordings of the test execution, etc. In case of any failure, there are logs and error text that are available easily in a few clicks.
You can also download the complete execution with steps and screenshots in PDF or Word format through the View Execution option.
testRigor’s Capabilities
Apart from the simplistic test case design and execution, there are some advanced features that help you test your application using simple English commands.
- Reusable Rules (Subroutines): You can easily create functions for the test steps that you use repeatedly. You can use the Reusable Rules to create such functions and call them in test cases by simply writing their names. See the example of Reusable Rules.
- Global Variables and Data Sets: You can import data from external files or create your own global variables and data sets in testRigor to use them in data-driven testing.
- 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha Resolution: testRigor easily manages the 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha resolution through its simple English commands.
- Email, Phone Call, and SMS Testing: Use simple English commands to test the email, phone calls, and SMS. These commands are useful for validating 2FA scenarios, with OTPs and authentication codes being sent to email, phone calls, or via phone text.
- File Upload/ Download Testing: Execute the test steps involving file download or file upload without the requirement of any third-party software. You can also validate the contents of the files using testRigor’s simple English commands.
- Database Testing: Execute database queries and validate the results fetched.
testRigor enables you to test web, mobile (hybrid, native), API, and desktop apps with minimum effort and maintenance.
Additional Resources
- Access testRigor documentation to know about more useful capabilities
- Top testRigor’s features
- How to perform end-to-end testing
Conclusion
The task of building a web application can be simplified if one chooses the right framework not just for development, but also for testing. Using modern frameworks like testRigor that are truly capable of handling the load of end-to-end testing of a matured web application can help cut down costs so that you and your team can focus on the activities that really matter rather than on repetitive and cumbersome tasks like test maintenance.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












