DevOps vs. CI/CD
|
|
In this dynamic environment of current software development, companies are pressured to speed up the delivery of quality software. To overcome this requirement, frameworks such as DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) have appeared as critical methodologies that help organizations to increase efficiency, collaboration, and automation within the software development lifecycle.
Although both ideas are intended to optimize the process of software development and your operations, it would be crucial to comprehend their differences and the synergistic correlation between the two in order to unlock their maximum potential.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a cultural change and teamwork system configured around the purpose of aligning development (Dev) and operations (Ops) technology department teams within the software development lifecycle. The objective of this collaborative environment is to break the borders between these teams so that software development, testing, deployment, and monitoring will be quicker and more efficient.
DevOps, at its essence, is the process of accelerating software delivery without compromising on the quality of reliability and performance. The latter is accomplished through promoting a culture in which both development and operations teams are joining forces throughout the product development life cycle, including idea generation, deployment and further maintenance.
Read more about DevOps: What is DevOps?
Key Principles of DevOps
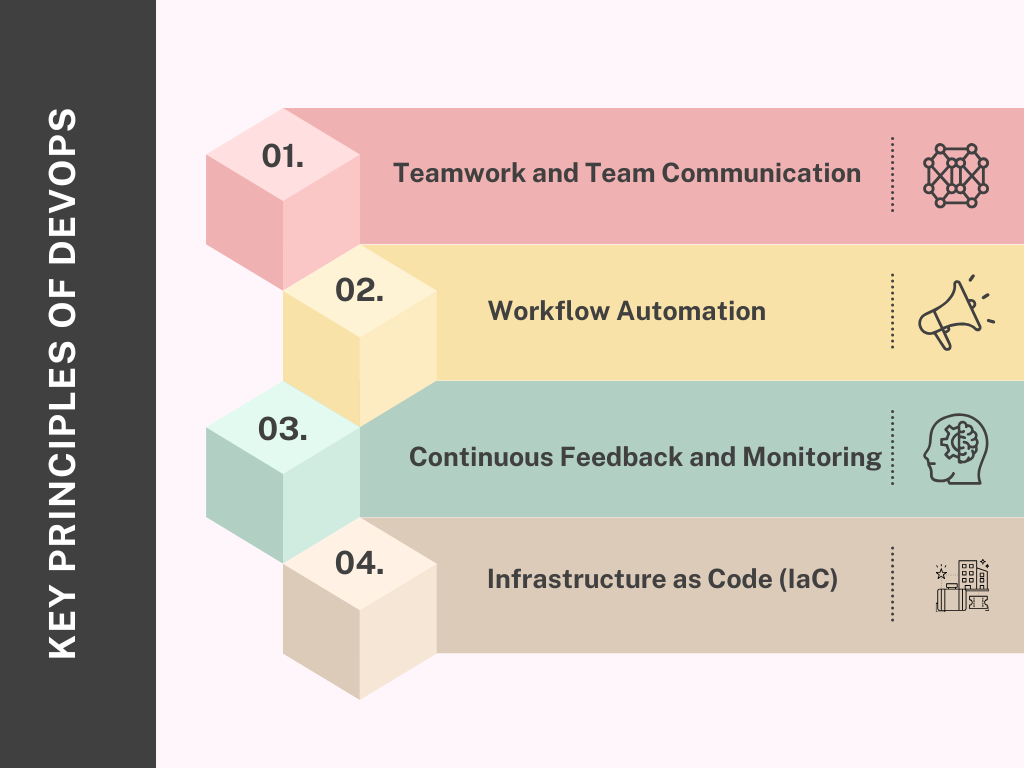
DevOps is built on a set of guiding principles that build collaboration, automation, and continuous improvement across development and operations teams. These principles provide the foundation for delivering high-quality software faster, more reliably, and with greater alignment to business goals.
- Teamwork and Team Communication: The enhancement of continuous cooperation between development, operations, quality assurance and other participating groups is one of the main rules of DevOps. This collaboration improves the development cycle, makes the deployments smoother, and gives a better understanding of requirements.
- Workflow Automation: DevOps depends on automation. Where entire processes involving repetitive tasks like integration, testing, deployment, and monitoring are automated, this ensures that teams are much more productive and error-free throughout the process. The automation increases the release speed, which consequently results in more stable programs.
- Continuous Feedback and Monitoring: In DevOps, feedback loops will always be present. Testers and developers are in close communication with each other and always provide feedback about the application. When feedback is received regularly and at an early stage, teams are able to detect issues earlier than they would otherwise and make amendments before such issues have escalated into significant problems.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): A core concept of DevOps is Infrastructure as Code that automates infrastructure provisioning, management, and monitoring. With the help of IaC, the teams can describe and control the infrastructure by leveraging code and scripts in place of manual operations. Read on Infrastructure as Code: What is Infrastructure as Code (IaC)?
Benefits of DevOps
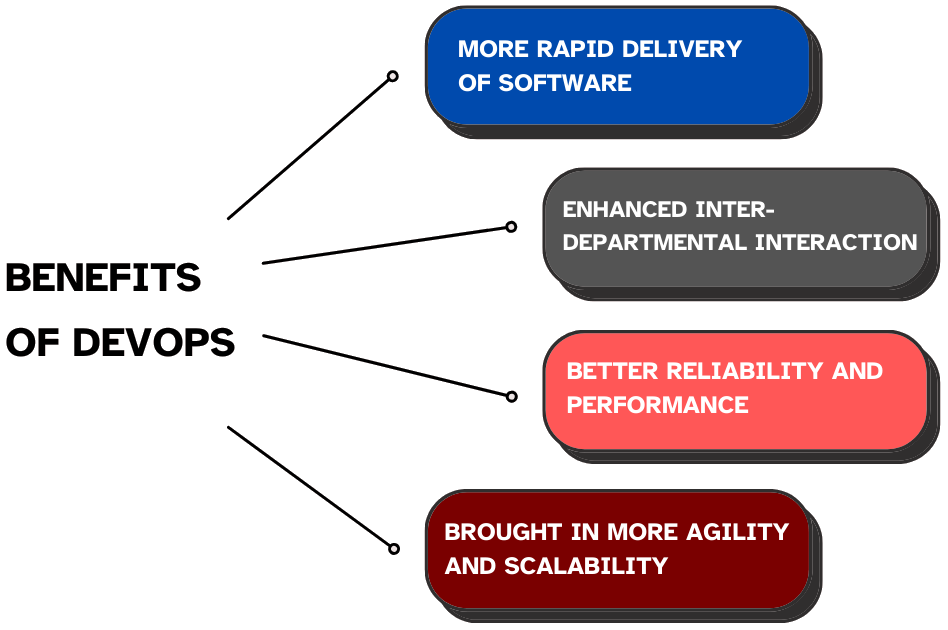
DevOps offers significant benefits by streamlining collaboration between development and operations. It enables faster delivery cycles, improved software quality, and more reliable releases. It empowers teams to respond quickly to changes while maintaining stability and customer satisfaction.
- A More Rapid Delivery of Software: Among the best advantages of implementing DevOps is the rate of software delivery. DevOps can reduce the frequency at which software changes are pushed out and can do it even several times per day by integrating development and operations teams and automating other significant non-development tasks.
- Enhanced Inter-Departmental Interaction: DevOps leads to more productive cooperation between developers and it also enhances cooperation between operations professionals and other stakeholders. DevOps removes pre-conceived notions between teams due to the overlap in goals, open communication channels, and the process to make decisions.
- Better Reliability and Performance: DevOps can be deployed to increase the stability of the software through constant system tracking, performance tracking, and automated testing. Automated tests and monitoring also enable teams to identify problems early.
- More Agility and Scalability: DevOps enhances speed and flexibility within the organization with a combination of automation, cooperation, and incremental development. Teams have the ability to tune to the needs of the market, the customers, or any surprise, much faster, and there is less friction to scale the system, add a feature, or shift their development effort.
What is CI/CD?
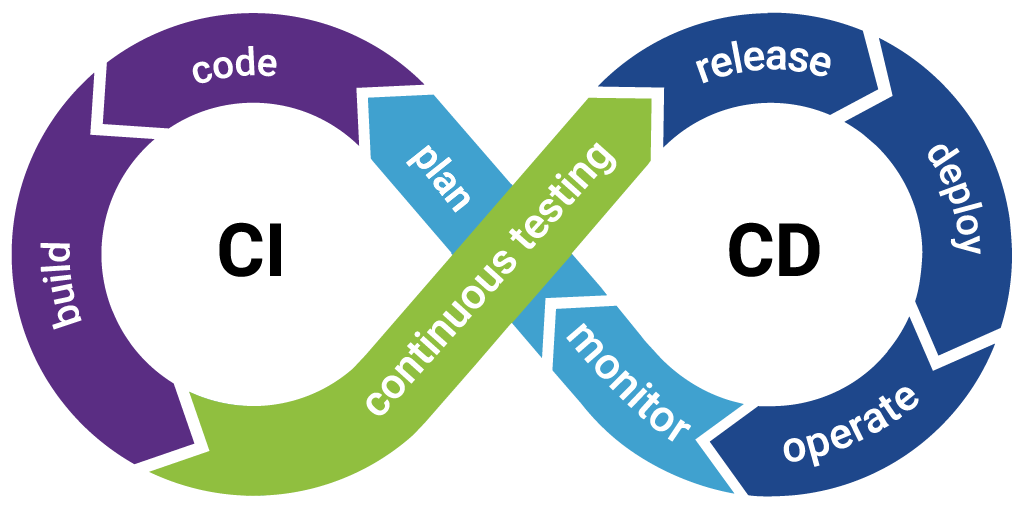
The main purpose of Continuous Integration is to enhance the software quality and ensure faster development through detecting and resolving problems at the initial stages of development in order to achieve faster time-to-market. In CI, integration is made through the process of automation testing, where the new piece of code is tried not to break anything that previously worked properly. The message that CI gives to the habit of continuously building and testing software is that you can make sure that the developers can uncover integration errors at the moment they occur. The sooner the previous bugs and conflicts can be identified, the sooner and easier they can be addressed. Read: Continuous Integration and Continuous Testing: How to Establish?
Continuous Delivery (CD) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are slightly different yet similar concepts that are based on the extension of the concept of CI by simply shifting the focus to releases and deployment, the latter of which is also known as Continuous Deployment. But, there is a great difference between the two:
Continuous Delivery (CD): It is a development approach in which programs are ready to be released to the production environment after every code change, automatically tested and staged, but pre-existing human intervention is then necessary before releasing to production. It implies that as soon as the code successfully gets through the required automated tests, it can be deployed at any given moment, but it is released through manual involvement.
Continuous Deployment (CD): In this dev-ops strategy, there are no decisions made by humans to deploy to production, and once there is code change, it is deployed to production right after all tests are successful. That is, production is perpetually upgraded and any new features or any bug fixes are released in real-time. Read: Continuous Deployment with Test Automation: How to Achieve?
In a simplified form, though Continuous Delivery automates the release process and leaves space for manual approval, Continuous Deployment goes a step further to install automation in the release process and not need to be checked by human beings at all. Read more: What Is CI/CD?
Key Components of CI/CD
The key components of CI/CD work together to automate the software build, testing, and deployment process, ensuring faster and more reliable releases. They form the backbone of modern development pipelines, enabling teams to deliver high-quality software with speed and consistency.
- Automated Build and Testing: Once the code is committed to the repository, it automatically builds the code to compile and do preliminary tests to ensure the new code is working. Automated tests can be used to detect bugs before it’s too late; make sure new code changes do not cause regression issues. testRigor, with its integrated gen AI capabilities, helps to execute test scripts much faster. With its Natural Language Processing capability, any manual tester or any other stakeholder can create automation scripts just by mentioning the steps in plain English. testRigor provides built-in integration with most of the CI/CD tools, making it much easier for the QA team to run the script in CI/CD pipelines.
- Automated Deployment pipeline: This pipeline will be in charge of automation and how it delivers the code all the way to production. The stages of this pipeline are:
- Build: A compilation and packaging of the application code.
- Test: Conducting automated tests to prove the code functionality and integrity.
- Deploy: Deployment of the application to the production or staging environment.
This pipeline enables all code alterations cleared during the testing stage to be rolled out simply by automation and minimizes the chance of human error and accelerates the release.
- Integration and Delivery Automation: It is important in CI/CD because it entails the implementation of automated workflows in the development process. Automation of integration automates the process of combining different developers’ code into a common repository, while delivery automation streamlines the release of software into production and ensures that each upgrade reaches production with minimal manual effort.
Benefits of CI/CD
CI/CD brings substantial benefits by automating the build, testing, and deployment process, enabling faster and more reliable software delivery. It helps teams reduce errors, improve code quality, and respond quickly to changing business needs.
- Accelerated Cycles of Development: CI/CD allows teams to release software in a more frequent way, and it automates the process of integration and deployment. This helps in a quicker development cycle where the new functionalities, bug fixes, or improvements are made available to end users in a shorter duration.
- Early Identification of Bugs and Problems: CI/CD tests and integrates changes in code frequently; thus, issues are spotted at an early stage of development. Automated tests are used every time the code is being integrated, so one can prevent the appearance of bugs in production.
- Concurrence and Repetitiveness in Deployments: CI/CD makes it possible to be certain that the deployments are repeatable. CI/CD removes variability because one can automate the build, test and delivery of the programs. This creates less inconsistencies between environments and applications behave the same way irrespective of the environment they are deployed in.
DevOps vs. CI/CD: Key Differences
While DevOps and CI/CD are closely related, they are not the same thing. DevOps is a broader cultural and operational philosophy that promotes collaboration between development and operations teams to deliver software more efficiently and reliably. CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment) is a set of practices and tools within DevOps that focuses specifically on automating code integration, testing, and release processes.
| Aspect | DevOps | CI/CD |
|---|---|---|
| Scope and Focus | A cultural and organizational transformation aimed at building collaboration, continuous feedback loops, and shared responsibility across the software lifecycle. | A technical practice focused on automating code integration, testing, and deployment for faster and more reliable delivery. |
| Roles and Responsibilities | Involves development, operations, QA, security, and sometimes product teams working together to achieve common goals. | Primarily involves developers, testers, and automation engineers utilizing tools to streamline the delivery pipeline. |
| Cultural vs Technical | Primarily a cultural and process-oriented approach that breaks down silos between teams. | A technical implementation of automation that supports rapid, frequent, and reliable software releases. |
| Primary Goal | Improve collaboration, efficiency, and reliability across the entire software delivery process. | Automate and optimize the build, test, and deployment pipeline for speed and quality. |
| Key Practices | Continuous collaboration, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), monitoring, incident management, and shared ownership. | Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), Continuous Deployment, and automated testing. |
| Implementation Approach | Broad adoption across people, processes, and technology, requiring cultural buy-in. | Specific implementation within the software development lifecycle, often as part of a DevOps strategy. |
| Outcome | Streamlined collaboration, faster releases, better quality, and improved reliability. | Automated, repeatable, and efficient release cycles with reduced manual intervention. |
How DevOps and CI/CD Work Together
DevOps focuses on the cultural changes to collaborate, communicate, and improve continuously, and CI/CD fully fits the requirements. CI/CD, an automated process of integrating, testing and deploying code, is also part of what makes DevOps such a good idea: speeds up, makes more reliable and efficient software releases.
- More Rapid Software Productions: DevOps and CI/CD are used to speed up software delivery. DevOps focuses more on increased speed of software development and delivery and CI/CD also takes care of this by automating the code integration, testing, and deployment.
- Less Manual Errors and More Consistency: The cycle of feedback is important in DevOps, where teams can detect the areas of improvement and adjust them swiftly. The contribution of CI/CD is that it has given continuous feedback on code quality, testing results, and successes in deployment. Continuous testing and deployment also allow teams to have an overview of software in real-time, i.e., the issues can be detected and eliminated as soon as possible.
- On-going Feedback to On-going Improvement: The cycle of feedback is important in DevOps, where teams can detect the areas of improvement and adjust them swiftly. The contribution of CI/CD is that it has given continuous feedback on code quality, testing results, and successes in deployment.
Conclusion
DevOps and CI/CD are not mutually exclusive but deeply intertwined pillars of modern software engineering. DevOps is the overarching strategy that nurtures a collaborative, automation-first culture. CI/CD provides the tactical tools and workflows to implement that strategy effectively.
While DevOps can exist without CI/CD and vice versa, neither reaches its full potential in isolation. Together, they enable organizations to deliver better software faster, respond quickly to changes, and create a resilient and innovative development ecosystem.
Whether you’re starting your DevOps journey or fine-tuning your CI/CD pipelines, understanding their symbiosis is the key to sustained success in today’s AI-powered digital world.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












