How to Become a QA Manager?
|
|
Today, the role of a Quality Assurance (QA) Manager has become increasingly vital to the success of software development teams. As a QA Manager, you bridge the gap between the QA team and higher management.
But what does it take to transition from a QA Tester or Engineer to a managerial role? In this blog post, we’ll explore the essential skills, experiences, and steps you need on your journey to become a successful QA Manager. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance your career, this guide will provide you with insights and actionable tips to help you achieve your goal.
Let’s get started!
Roles and Responsibilities of a QA Manager
Before exploring the steps to becoming a QA Manager, it is crucial to understand what the role entails. A QA Manager ensures that QA processes are completed on time, within budget, and result in high-quality products. You are responsible for nurturing talent, driving team productivity, and aligning QA efforts with the company’s strategic goals.
Here are the roles and corresponding responsibilities of a QA Manager.
| Roles | Responsibilities |
| Lead teams |
|
| Recruit and train |
|
| QA strategizing and risk management |
|
| Oversee testing processes |
|
| Manage defects |
|
| Analyze metrics |
|
| Facilitate cross-functional and stakeholder communication |
|
| Continuous improvement |
|
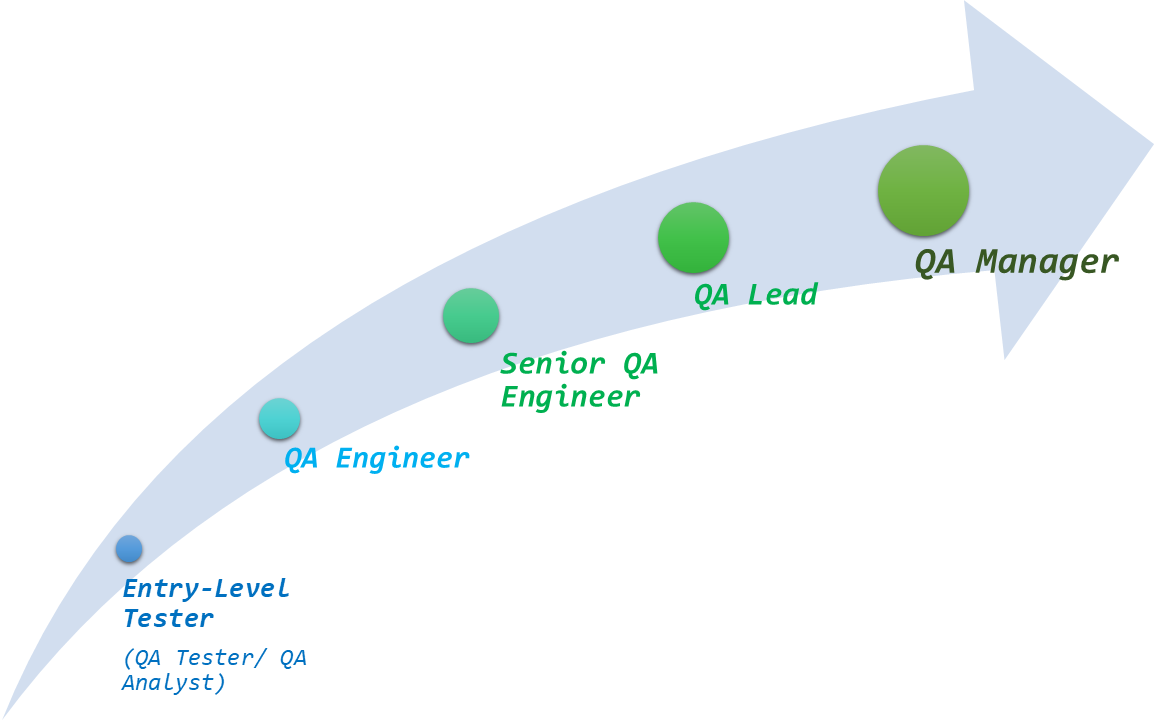
What is Needed to Become a QA Manager?
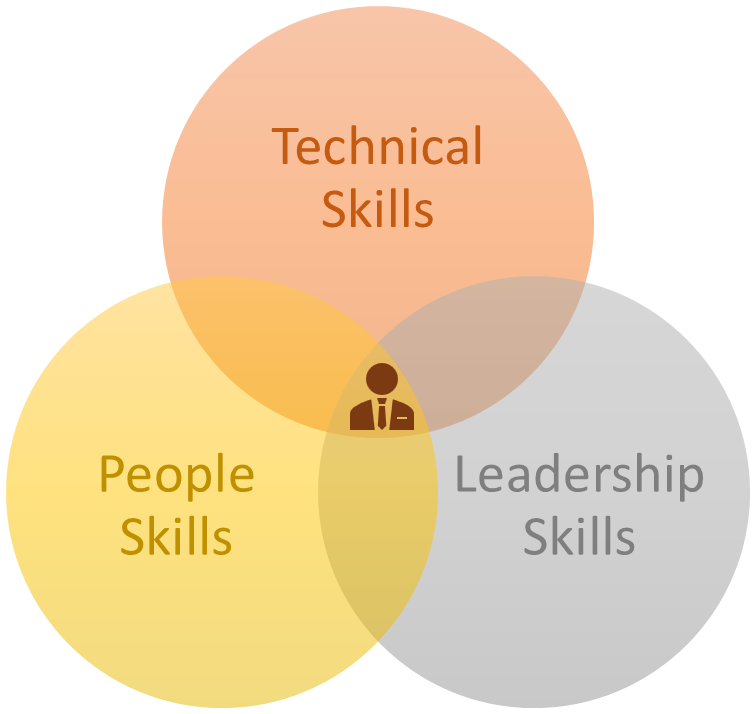
This role requires a mix of technical skills, leadership qualities, strategic thinking and business acumen. Here’s what you’ll need to become a QA Manager.
Educational qualifications
While there is no specific degree requirement to become a QA Manager, having a solid foundation in computer science or a related field is highly beneficial. Here are some common educational paths:
- Bachelor’s degree: A bachelor’s degree in computer science, software engineering, information technology, or a similar field is required. It provides a solid understanding of programming, software development methodologies, and problem-solving skills.
- Master’s degree: A master’s degree in software engineering, computer science, or a related field can give you a deeper understanding of advanced concepts and research methodologies. This can be especially valuable for those aspiring to senior-level QA management positions.
- Certifications: Completing industry certifications can demonstrate your expertise and knowledge of QA principles and practices. These certifications can also help you stand out in the job market.
Hands-on experience in QA
Gaining hands-on experience is a crucial aspect of becoming a QA Manager, as it equips you with practical knowledge and skills necessary for effectively overseeing quality assurance processes.
Here’s a detailed look at the types of hands-on experience that can help you on your journey:
- Entry-level QA roles: Starting your career in entry-level positions such as QA Tester or QA Analyst is essential. In these roles, you will engage in various testing activities, including functional testing, regression testing, and performance testing. This experience helps you understand the day-to-day tasks involved in quality assurance as well as the common challenges faced during testing.
- Understanding testing tools: Familiarity with testing tools is vital. As you work in entry-level positions, you’ll gain experience using various testing tools for automation, performance, and defect tracking.
- Exposure to different testing methodologies: Working with different software development methodologies such as Agile, Scrum, and Waterfall is crucial for a well-rounded understanding of QA processes. Engaging in Agile teams, for instance, will allow you to participate in sprint planning, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives. This will give you insights into how quality fits within an iterative development cycle.
- Collaboration with cross-functional teams: Quality assurance is a collaborative effort, so gaining experience working alongside developers, product managers, and other stakeholders is essential. Participate in team meetings and discussions to develop strong communication skills and learn how to advocate for quality within a team setting.
- Continuous learning and adaptation: The tech industry constantly evolves, so staying updated on the latest testing trends, tools, and best practices is crucial. Attend workshops, webinars, and industry conferences to expand your knowledge and network with other professionals in the field.
Strong leadership and management skills
You will need strong leadership and management skills to become a QA Manager. Here are key areas to focus on:
- Visionary thinking and strategic planning: Develop the ability to set a long-term vision for the QA function that aligns with the company’s goals. This involves understanding market trends/customer needs and anticipating potential technical challenges.
- Team building and development: Build a high-performing team by hiring the right talent, fostering a collaborative culture, and providing mentorship and growth opportunities. As a leader, you should focus on developing your team’s skills and encouraging continuous improvement.
- Effective communication skills: As a QA Manager, you must communicate effectively with both technical and non-technical stakeholders. This includes the ability to convey complex technical information in a clear and understandable manner.
- Negotiation: You will need the ability to negotiate with stakeholders to balance quality requirements with project constraints and deadlines.
- Mentorship: You have to mentor and develop team members, help them grow their skills and advance their careers.
- Decision-making and problem-solving: A QA Manager must be decisive, making quick yet informed decisions about project priorities, resource allocation, and technical direction. Problem-solving skills are also crucial, as you’ll face complex challenges requiring innovative solutions.
- Project management and resource allocation: Develop strong project management skills to handle multiple projects simultaneously, allocate resources effectively, and ensure that QA activities are completed on time and within budget.
QA expertise
Possessing a robust technical foundation is essential to excel as a QA Manager. You will need knowledge of:
- Understanding of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Proficiency in different testing methodologies
- Experience with automation tools
- Defect tracking and management tools
- Familiarity, if not proficiency, in scripting and programming languages
- Knowledge of database and SQL
- Performance testing
- Familiarity with Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
- Awareness of security testing
- Data analysis and reporting Skills
Business understanding
As a QA Manager, you have now entered the realm of the hierarchy that can affect change at a large scale within the organization. Understanding the business context will be crucial for making informed decisions that align QA efforts with organizational goals.
Here’s how you can go about that:
- Understand the company’s vision and strategy: Familiarize yourself with the company’s mission, vision, and strategic objectives. This knowledge allows you to align your team’s projects and goals with broader organizational priorities to ensure that QA contributes to overall success.
- Learn the financial aspects: Gain a basic understanding of financial metrics, budgeting, and how QA impacts the bottom line. Understanding these implications will help you make decisions that optimize resources and justify investments in technology and personnel.
- Engage with other departments: Collaborate with product management, marketing and sales teams to understand their challenges and objectives. These interactions provide insights into how QA impacts other functions and customer satisfaction.
- Participate in business meetings: If you have the opportunity, attend strategy sessions, product planning meetings, and other business-related gatherings. Participating in these discussions will help you understand the company’s direction and priorities while allowing you to contribute a QA perspective.
- Stay informed about market trends: Stay current with industry trends, competitors, and emerging technologies that could affect your business.
Strong professional network
Networking is a powerful tool for aspiring QA Managers. Here’s how to build and leverage a strong professional network:
- Join professional organizations: Join industry organizations, technology forums, and professional groups relevant to QA and management. These platforms offer networking opportunities, learning, and gaining visibility.
- Attend conferences and seminars: Participate in QA and technology conferences, seminars, and workshops. These events are excellent opportunities to learn from industry leaders, stay updated on trends, and expand your professional network.
- Seek mentorship and peer groups: Find mentors who can guide your career progression. Join peer groups or mastermind groups where you can share experiences, challenges, and learn from others in similar roles.
- Publish and speak: Establish yourself as a thought leader by publishing articles, white papers, or case studies on relevant topics. Speaking at conferences or webinars can also help you gain visibility and credibility in the industry.
Executive experience
As you progress in your career, gaining executive experience is critical to moving into a QA Manager role:
- Look for opportunities to move into senior management positions: Focus on building executive-level skills, such as strategic planning, budgeting, and stakeholder management.
- Build relationships with executive teams: Engage with the executive team to understand the organization’s broader strategic objectives. This exposure will help you align your QA strategy with business goals and demonstrate your value as a strategic partner.
- Lead organizational change initiatives: Drive initiatives that require cross-functional collaboration and impact the entire organization. Leading change initiatives demonstrates your ability to influence at the highest levels and manage complex projects.
The Path to Become a QA Manager

What Not to do as a QA Manager
Being a manager can be difficult and exciting at the same time. You might find yourself falling into patterns that might have adverse consequences in the long run. Here is a no-no list of some things that you need to watch out for:
- Micromanaging: This will stifles creativity and autonomy and lead to frustration and disengagement. Trust your team to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
- Neglecting communication: Failing to provide clear communication about project goals, expectations and feedback can be a problem. It can lead to misunderstandings, decreased productivity, and a lack of alignment within the team.
- Ignoring team dynamics: Overlooking interpersonal conflicts or team dynamics can create a toxic work environment and affect collaboration.
- Being Unapproachable: Creating a barrier that makes team members hesitant to come to you with issues or ideas.
- Failing to recognize contributions: Not acknowledging or celebrating team achievements and individual contributions can cause problems. Recognition boosts morale and motivates team members. Make it a habit to celebrate successes, both big and small.
- Becoming too focused on metrics: While metrics are important, they shouldn’t be the sole focus. Balance quantitative data with qualitative insights to understand team dynamics and health.
- Resisting change: Being inflexible or resistant to new ideas, technologies, or processes hinders growth.
All these points are subtle but affect your career and team in the long run.
How to Prepare for the QA Manager Interview
Once you’re on the path to becoming a QA Manager, you’ll eventually need to prepare for the interview.
Here are some key tips:
- Understand the company’s needs: Research the company thoroughly to understand its technology stack, business model, market position, and competitive landscape. Be ready to discuss how your experience and vision align with the company’s goals.
- Highlight both technical and leadership skills: Demonstrate your ability to bridge the gap between technology and business. Be prepared to discuss both your technical achievements and your experience with strategic planning, team management, and business growth.
- Showcase leadership qualities: Highlight examples of your leadership experience, such as managing teams, leading projects or driving change initiatives. Be ready to discuss your management style and how you handle conflicts, motivate teams, and build a positive culture.
- Discuss your vision for QA: Be prepared to share your vision for the company’s QA strategy. This could include new tools or methodologies you’d like to implement, areas for improvement or potential innovations that could drive product quality and efficiency.
The Future of the QA Manager Role
The role of the QA Manager is constantly evolving. Here are some trends that will shape the future of this position:
- Increased emphasis on automation: With the rise of Agile and DevOps methodologies, automation is becoming a cornerstone of quality assurance. QA Managers need to stay updated on automation tools and lead automation initiatives.
- Integration of AI and ML: AI and ML are beginning to play significant roles in quality assurance. AI can help create smarter test scripts that adapt to application changes. QA Managers should explore how AI can be used for predictive analytics to identify potential defects before they arise.
- Focus on continuous testing: As organizations adopt CI/CD practices, the emphasis on continuous testing will grow. QA Managers must embed testing into the development process and adapt to rapid release cycles.
- Quality as a shared responsibility: The shift towards collaborative cultures means that quality assurance is becoming a shared responsibility across teams.
- Emphasis on performance and security testing: With the increasing complexity of applications and growing cybersecurity threats, performance and security testing are becoming more critical. QA Managers need to enhance their skill sets and implement comprehensive testing strategies.
- Data-driven decision-making: Data analytics is becoming increasingly crucial in QA. QA Managers should utilize testing metrics and analytics to make informed decisions about testing strategies and team performance. They should also familiarize themselves with reporting tools that provide insights into testing outcomes, defect trends, and process efficiencies.
Conclusion
As quality assurance continues to evolve in response to emerging technologies and methodologies, the demand for skilled QA Managers is rising. As a QA Manager, you will uphold the principles of quality and lead your team in delivering exceptional products that meet and exceed customer expectations.
By building a solid foundation of technical knowledge, developing strong leadership skills, and embracing continuous learning, you can position yourself for success in this vital role. As you prepare for this exciting career path, focus on gaining diverse experiences, honing your skills, and staying attuned to industry trends.
Additional Resources
- Top-24 QA Manager Interview Questions (+Answers)
- Metrics for QA Manager
- How to become a Director of QA?
- Test Automation in Scrum: How to do it Effectively?
- Test Automation Frameworks: Everything You Need to Know in 2024
- Manual Testing vs Automation Testing: What’s the Difference?
- Is There any Future for Manual Testing?
- What is the Cost of Quality in Software Testing?
- 10 Quality Myths Busted
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












