Generative AI in Software Testing
|
|
Today, in the advanced world of software development and testing, the constant drive towards automation has prominently featured the introduction of Generative AI in software testing. This innovative approach goes beyond the confines of traditional automation. Unlike systems that merely execute predefined steps, generative AI can autonomously produce novel and valuable outputs. The breadth and depth of AI’s applicability within QA are vast, making it imperative for professionals to grasp this paradigm shift. That is why AI and ML Tops 2025 Agenda for APAC CIOs.

By 2026, Generative AI in software testing will no longer be viewed as an experimental capability. It has become a practical necessity due to AI-generated code, frequent UI changes, microservices architectures, and accelerated release cycles. Modern QA teams now expect AI not only to assist but to autonomously create, adapt, and maintain tests in production environments.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
How to use testRigor’s Generative AI to Build Tests for You
We’re excited to mention that testRigor’s advanced capabilities use Generative AI, Vision AI, AI context, advanced parser logic, and NLP algorithms to create tests. Here is an example of creating an end-to-end test case:
To give you a comprehensive perspective on this topic, let’s take a step back to see where it all started.
A Brief History of the QA Revolution
The world of Quality Assurance has been through a significant evolution since its inception, continually adapting and transforming to meet the demands of a rapidly changing technological landscape. It’s a journey that has taken us from manual testing and scripted automation to data-driven testing and now, generative AI with advanced LLM models revolutionizing the way we approach testing by allowing AI to take care of most of the work in test creation.
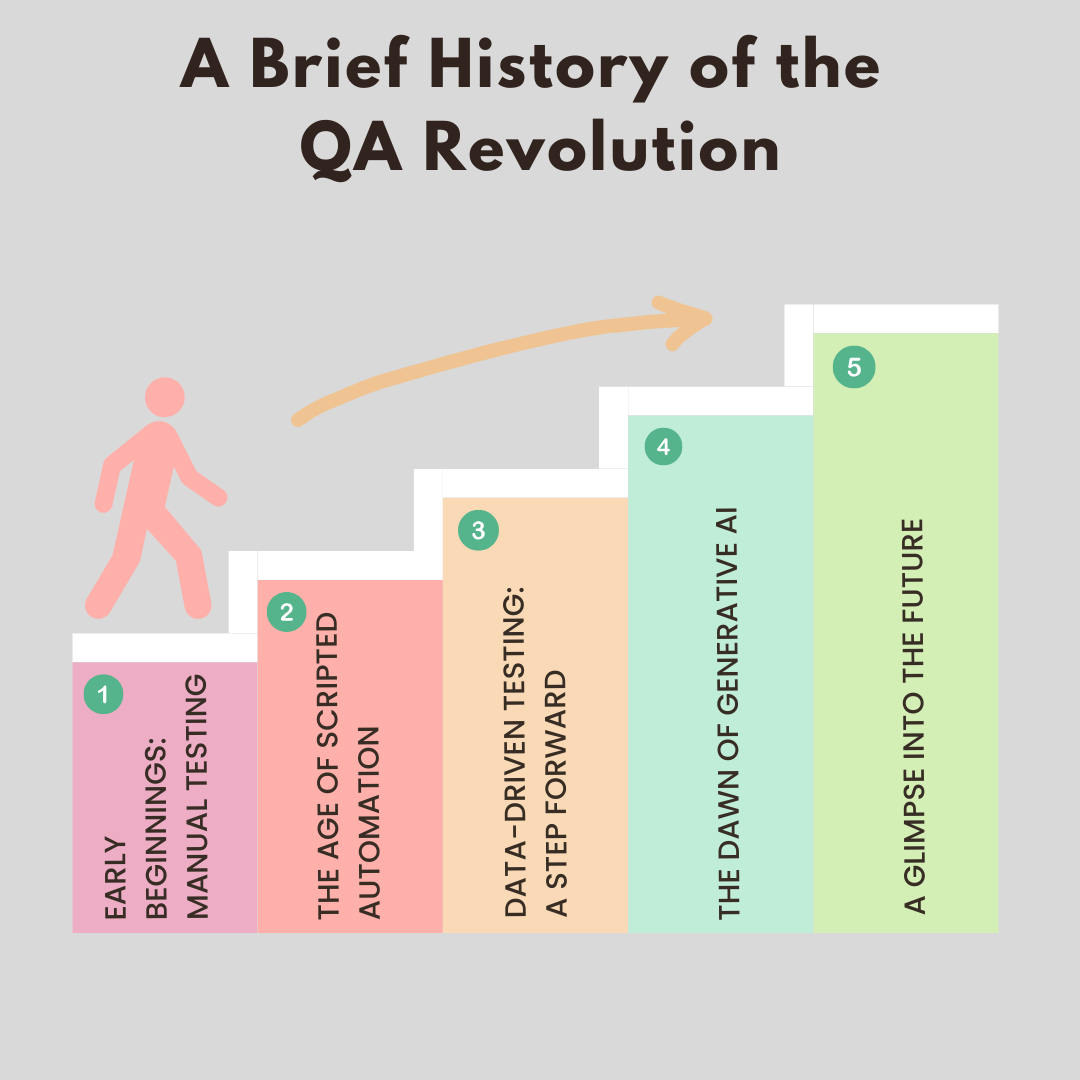
Early Beginnings: Manual Testing
In the early days, QA relied heavily on manual testing, a process that required individual testers to check each software feature for bugs and anomalies, often multiple times. This involved developing test cases, executing these tests, and then recording and reporting the results. While this method allowed for a high level of control and detailed insights, it was a time-consuming and labor-intensive process with its own set of challenges, such as a high risk of human error and difficulties in ensuring comprehensive test coverage.
The Age of Scripted Automation
In an effort to increase efficiency, reduce human error, and facilitate the testing of complex systems, the industry transitioned towards scripted automation. This marked a significant leap in the world of QA, as it enabled the creation of repeatable, predictable test scenarios. Testers could write scripts that automatically executed a sequence of actions, ensuring consistency and saving time. However, despite the clear advantages, scripted automation wasn’t without its limitations. The scripts needed to be meticulously crafted and maintained, which proved time-consuming, and the method lacked adaptability, unable to handle unexpected changes or variations in test scenarios.
Data-Driven Testing: A Step Forward
The advent of data-driven testing offered a solution to the limitations of scripted automation. This methodology allowed testers to input different data sets into a pre-designed test script, effectively creating multiple test scenarios from a single script. Data-driven testing enhanced versatility and efficiency, especially for applications that needed to be tested against varying sets of data. Yet, while this represented a significant advancement, it wasn’t without its drawbacks. There was still a considerable amount of manual input required, and the method lacked the ability to autonomously account for entirely new scenarios or changes in application behavior.
The Dawn of Generative AI
Enter Generative AI — the QA Revolution and a game-changer for the industry. At its core, generative AI is an AI LLM model capable of generating novel and valuable outputs, such as test cases or test data, without explicit human instruction. This capacity for autonomous creativity marked a radical enhancement in testing scope, introducing the potential to generate context-specific tests and significantly reducing the need for human intervention.
In modern QA environments, this autonomy allows AI-driven systems to generate tests continuously as applications evolve, rather than relying on static test design created at a single point in time.
While the idea of generative AI might seem daunting due to the complexity associated with AI models, understanding the basics unveils the massive potential it holds for QA. It’s the power to create, to adapt, and to generate tests tailored to the specific needs of a system or a feature. From creating test cases based on given descriptions to completing code, the applications of generative AI in QA are expansive and continually growing.
A Glimpse into the Future
Today, we stand on the precipice of a new era in QA, driven by advances in AI and machine learning. As generative AI continues to evolve and mature, it promises to further revolutionize our approach to testing, fostering a future where tests are increasingly comprehensive, autonomous, and efficient. And while the journey of QA is far from over, one thing is certain: Generative AI will play a pivotal role in shaping its path forward.
The Benefits and the Challenges
The potential of Generative AI to revolutionize the Quality Assurance (QA) sector is substantial, offering an array of benefits that promise to significantly enhance testing processes. Yet, as with any transformative technology, the journey towards fully leveraging these advantages comes with its unique set of challenges. This calls for a more in-depth examination of the potential rewards and obstacles tied to the integration of Generative AI within QA workflows.
Benefits of Generative AI in QA
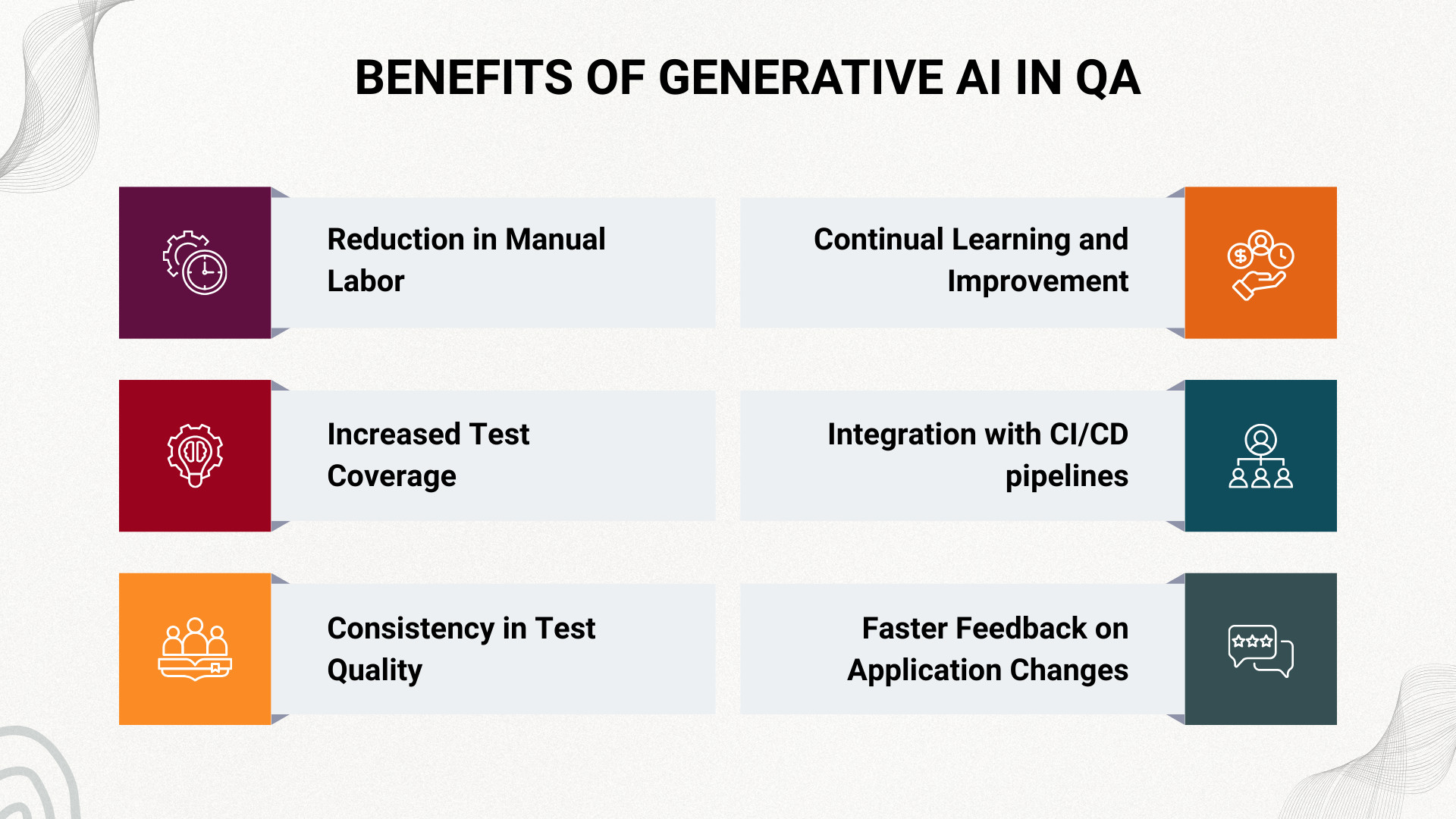
- Reduction in Manual Labor: A primary advantage of generative AI is its capability to automate the creation of tests, thus reducing the necessity for repetitive manual testing, which is especially beneficial for areas such as regression testing. This automation doesn’t just save valuable time and resources; it also allows QA professionals to focus more on complex tasks that require human intuition and creativity.
- Increased Test Coverage: Generative AI can create a wide range of test scenarios, covering more ground than traditional methods. This ability to comprehensively scan the software helps unearth bugs and vulnerabilities that might otherwise slip through, thus increasing the software’s reliability and robustness.
- Consistency in Test Quality: Generative AI provides a level of consistency that’s challenging to achieve manually. By leveraging AI, businesses can maintain a high standard of test cases, thereby minimizing human errors often associated with repetitive tasks.
- Continual Learning and Improvement: AI models, including generative ones, learn and improve over time. As the AI is exposed to more scenarios, it becomes better at creating tests that accurately reflect the system’s behavior.
- Integration with Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) Pipelines: Generative AI can be a game-changer when it comes to implementing DevOps practices. Its ability to swiftly generate tests makes it a perfect fit for CI/CD pipelines, enhancing the speed and efficiency of software development and delivery.
- Faster Feedback on Application Changes: By automatically generating and executing relevant tests when changes occur, Generative AI enables faster feedback for developers. This helps teams detect issues earlier in the development cycle, reducing the cost and impact of late-stage defects.
Read: Agentic AI vs. Generative AI: Differences.
Challenges of Generative AI in QA
While the potential advantages are significant, it’s also crucial to understand the potential obstacles that Generative AI brings to the QA process:
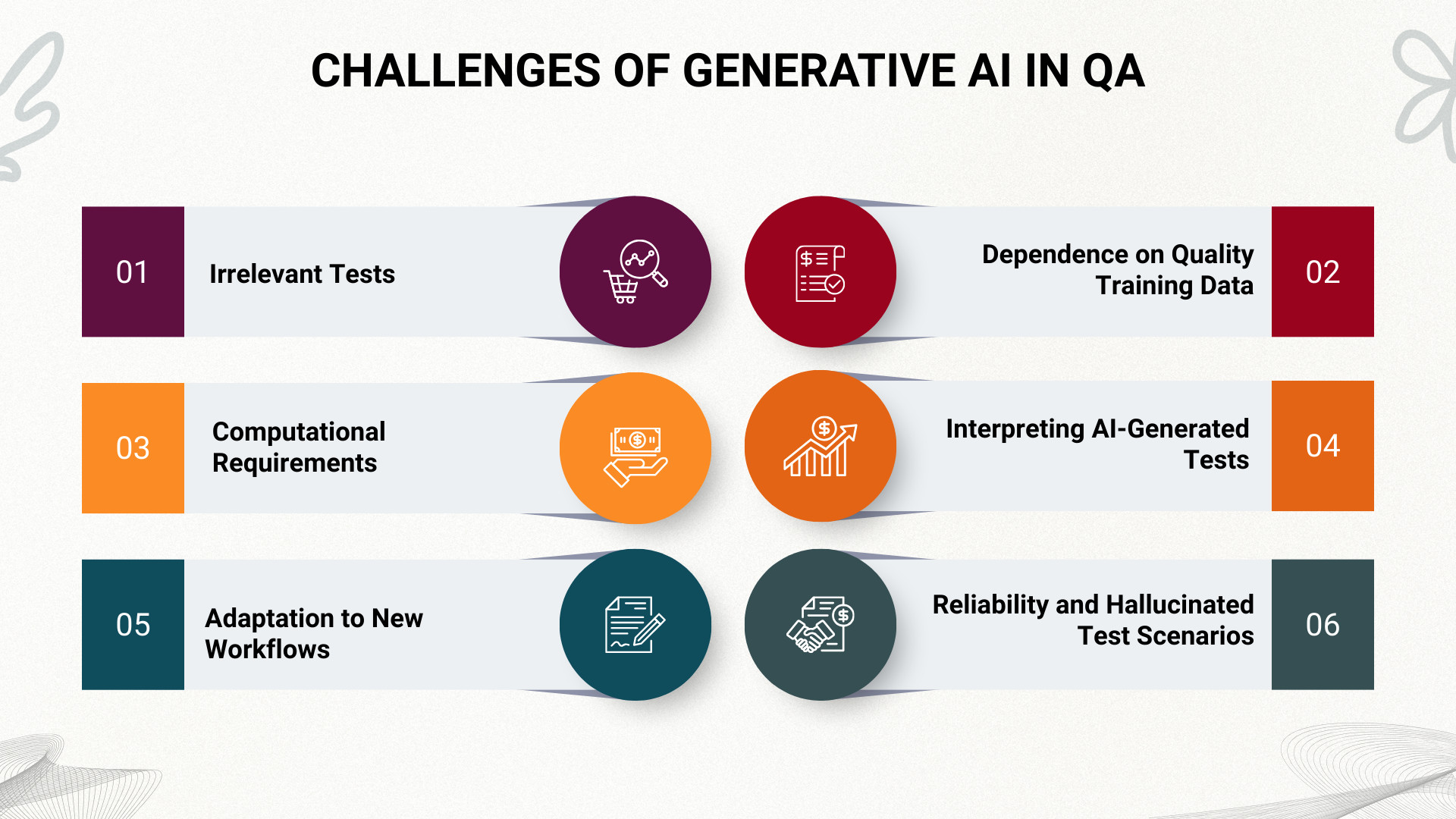
- Irrelevant Tests: One of the primary challenges is that generative AI may create irrelevant or nonsensical tests, primarily due to its limitations in comprehending context or the intricacies of a complex software system.
- Computational Requirements: Generative AI, particularly models like GANs or large Transformers, require substantial computational resources for training and operation. This can be a hurdle, especially for smaller organizations with limited resources.
- Adaptation to New Workflows: The integration of generative AI into QA necessitates changes in traditional workflows. Existing teams may require training to effectively utilize AI-based tools, and there could be resistance to such changes.
- Dependence on Quality Training Data: The effectiveness of generative AI is heavily dependent on the quality and diversity of the training data. Poor or biased data can result in inaccurate tests, making data collection and management a significant challenge.
- Interpreting AI-Generated Tests: While AI can generate tests, understanding and interpreting these tests, especially when they fail, can be challenging. This could necessitate additional tools or skills to decipher the AI’s output effectively.
- Reliability and Hallucinated Test Scenarios: Generative AI can sometimes produce test scenarios that appear logically correct but do not align with real user behavior or actual system intent. These hallucinated tests can create a false sense of coverage if not properly validated, making reliability a key concern for QA teams.
Read: Why Gen AI Adoptions are Failing – Stats, Causes, and Solutions.
Reliability and Control in AI-Generated Testing
As Generative AI becomes more deeply integrated into QA workflows, reliability and control emerge as critical success factors. AI-generated tests must consistently reflect real user behavior and application intent, avoiding scenarios that appear valid but provide little meaningful coverage.
Effective AI-driven testing emphasizes transparency and appropriate human oversight. Human-readable tests, controlled execution boundaries, and validation mechanisms enable teams to trust AI-generated outputs while maintaining confidence in test accuracy and relevance. Achieving the right balance between autonomy and control is essential for scaling Generative AI within quality engineering practices.
Navigating these potential obstacles requires a thoughtful approach to integrating Generative AI within QA workflows, along with ongoing adaptation as technology continues to evolve. Despite the challenges, the benefits that Generative AI offers to QA testing are immense, pointing towards a future where the synergy between AI and human testers will create a more robust, efficient, and innovative software testing paradigm.
Types of Generative AI Models
Modern QA systems primarily rely on Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal AI models. LLMs are trained on large volumes of text, code, and structured data, enabling them to understand application behavior, business intent, and user flows. In software testing, these models are widely used to generate test cases from natural language descriptions, interpret requirements, and reason about complex end-to-end scenarios. Multimodal models extend these capabilities by combining text understanding with visual perception, making them particularly effective for UI and visual testing where recognizing layouts, components, and visual changes is essential.
In addition to these, specialized generative models play supporting roles in QA workflows. Code-aware models help generate and analyze tests aligned with application logic, while reinforcement learning–enhanced approaches assist in exploring applications and uncovering unexpected paths and edge cases. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), though less central to test creation, remain useful for producing realistic synthetic test data in scenarios such as performance, security, and data-intensive testing.
Read: How to Keep Human In The Loop (HITL) During Gen AI Testing?
Integration with Other Technologies
Generative AI is already transforming the landscape of Quality Assurance (QA). Still, when combined with other advanced technologies, its capabilities extend further, promising unprecedented improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and comprehensiveness of testing.
One such integration is with reinforcement learning (RL). In RL, an AI model learns to make decisions by interacting with its environment, receiving rewards for right actions and penalties for wrong ones. This paradigm is particularly useful in complex testing scenarios where the ‘right’ and ‘wrong’ actions are not clearly defined. For instance, testing a highly interactive application with multiple potential user paths and behaviors can benefit from an RL-based generative AI model. The AI system can learn from its past testing actions, iteratively refining its testing strategy to find errors more efficiently and effectively. Read: Machine Learning Models Testing Strategies.
Generative AI can also be combined with computer vision, a field of AI that enables computers to understand and interpret visual information from the real world. This combination is especially powerful in QA for visual-heavy applications, such as UI/UX testing or game testing. Computer vision can help the AI model recognize and understand visual elements, while generative AI can create novel test cases based on these elements. The outcome is a QA system that can handle intricate, image-based testing scenarios, identifying bugs that would be challenging for traditional automation tools to catch.
Ethical Considerations in Generative AI
As generative AI continues to revolutionize QA testing, it also raises important ethical considerations. While AI can bring numerous benefits, it’s crucial to address these ethical concerns to ensure fair and responsible use.
One of the main ethical issues is bias. AI models, including those used for QA, are trained on large datasets, and they can inadvertently learn and replicate any biases present in this data. In QA, this could lead to certain bugs or errors being overlooked if the training data was biased towards particular types of software, features, or errors. Therefore, it’s crucial to use diverse and representative training data and continuously monitor and adjust the AI models to ensure they are not exhibiting bias.
Another ethical concern is privacy. In some testing scenarios, especially in the context of real-world user testing, AI models might need to handle sensitive user data. It’s essential to ensure that this data is handled securely and privacy is preserved, complying with all relevant regulations. This is why, for example, many companies do not authorize their employees to use ChatGPT models.
Read: What is Responsible AI?
Enterprise Adoption and Governance of Generative AI in QA
Widespread enterprise adoption of Generative AI in testing requires more than technical capability. Organizations must address governance concerns such as data privacy, auditability, and compliance with internal and external regulations. These considerations have become increasingly important as AI-driven testing influences release decisions and production readiness.
In 2026, enterprise-ready QA solutions incorporate clear governance models, ensuring that AI usage is transparent, controlled, and aligned with organizational standards. This enables teams to scale Generative AI responsibly while maintaining trust across engineering, security, and leadership stakeholders.
Read: What are AI Guardrails?
Impact on Job Roles and the QA Industry
The introduction and subsequent rise of generative AI within the QA industry will inevitably impact job roles and work dynamics within the field. As the AI begins to take over repetitive, mundane tasks, the emphasis on human roles within QA will shift significantly.
For starters, there will be a reduced need for manual testers, or at least, the nature of their jobs will evolve. Instead of repetitive, hands-on testing, they will need to assume roles that supervise and manage AI-driven testing, ensuring that the AI operates as intended. The role will also involve understanding and interpreting the results produced by the AI, and making informed decisions based on them. Furthermore, manual testers might be required to work more closely with development teams, providing them with valuable insights from AI-generated tests to improve product development and functionality.
Simultaneously, there will be an increased demand for QA professionals who are adept in AI technology. These individuals will not only need to understand how generative AI works, but also how to apply it efficiently in testing environments. They will be responsible for training and tweaking AI models, ensuring they are fit for purpose, and troubleshooting any issues that may arise during testing.
As such, there will be a shift towards more strategic, analytical, and technical roles within QA. This change will necessitate a focus on upskilling and reskilling within the industry to prepare current professionals for the AI-driven future.
Read: Will AI Replace Testers? Choose Calm Over Panic.
Generative AI Use Cases
To demystify generative AI in the context of QA, we can break it down into three primary use cases:
- Generating examples based on a description
- Code completion
- Generating individual tests based on the app or feature description
Prompt engineering plays a crucial role in this regard. Read how: Prompt Engineering in QA and Software Testing.
Generating Examples Based on Description
This use case relies on AI models capable of understanding a description or specification and subsequently generating relevant examples. These examples can take various forms, from test cases to complete code snippets, depending on the provided context.
For instance, OpenAI’s language model, ChatGPT, can be used to generate an example test in a specified programming language based on a brief description. Similarly, at testRigor, we have leveraged generative AI to create example tests directly within our platform using prompts (it’s essential to note that testRigor does not use ChatGPT).
Consider an instance where a tester provides a brief description like, “Test checkout process.” The AI understands the requirement and produces an example test case, significantly reducing the manual effort and time needed.
Code Completion
Generative AI can also be utilized for code completion, a feature familiar to anyone who has written code. Traditional code completion tools are somewhat rigid and limited, often unable to comprehend the broader context. Generative AI can revolutionize this by considering the wider programming context and even a prompt in a comment.
A perfect example is GitHub’s CoPilot, which uses AI to generate code snippets based on existing code and potential prompts. This not only accelerates the coding process but also aids in reducing human error.
Generating Individual Tests Based on Description
Lastly, generative AI can be employed to create complete tests based on provided descriptions. Instead of simply giving examples, the AI comprehends the requirements and generates a full-fledged test. This not only involves generating the required code but also setting up the necessary environment for the test.
For example, given a description like, “Develop a full test for a shopping cart checkout process,” the AI would analyze the requirement, generate the necessary code, and design a test environment, all while minimizing human intervention.
Read: All-Inclusive Guide to Test Case Creation in testRigor.
From Test Automation to Quality Intelligence
Generative AI has expanded the role of QA beyond executing and maintaining tests. Modern testing platforms increasingly function as sources of quality intelligence, analyzing test outcomes, failure patterns, and system behavior to surface insights related to product risk and release readiness.
This shift allows QA teams to use testing data to inform decisions rather than simply validate functionality. As a result, testing evolves into a strategic discipline that provides continuous feedback to development and product teams, enabling organizations to proactively manage quality instead of reacting to defects late in the development lifecycle. Read this guide to understand: How to use AI effectively in QA.
Generative AI Testing Tools
You’ll see many innovative generative AI testing tools available in the market these days. From automatically generating test cases and scripts to predicting bugs and performing self-healing tests, these tools offer a wealth of benefits. They help software teams save time, improve test coverage, and deliver higher-quality software.
Here are some of the common types of use cases that generative AI testing tools help solve:
Automated Test Case Generation Tools
Generative AI testing tools can automatically generate test cases. They do this based on application requirements, user stories or even the application’s code. This helps testers to create comprehensive test scenarios quickly and ensure all aspects of the application are tested.
Test Data Generation Tools
You might have found that generating realistic and varied test data is often time-consuming and challenging. Generative AI tools help solve this by creating large volumes of data that can include both normal and edge cases. This is crucial for testing complex systems that require diverse datasets for thorough testing. Read: Test Data Generation Automation.
Self-Healing Test Automation Tools
In many applications, user interface (UI) or code changes can cause test failures. Self-healing AI tools detect such changes and adjust test scripts automatically to reflect the modifications. This ensures that tests remain functional without requiring manual updates. For example, if a button’s ID changes on a webpage, a self-healing AI tool can detect the change and automatically update the test script to reference the new button ID.
Predictive Analytics Tools
Some generative AI testing tools can analyze historical bug data, code commits, and usage patterns to predict where defects are likely to occur. By flagging these high-risk areas, AI tools help prioritize testing efforts and ensure that bugs are detected early and fixed before they impact users. Read: Predictive Analytics in Software Testing.
Visual Testing Tools
AI-driven visual testing tools help compare UI elements across multiple browsers and devices to detect visual regressions. This helps make sure that the UI remains consistent and that new changes do not negatively affect the appearance or user experience. For example, these tools can automatically compare screenshots of a website across different screen sizes to ensure that layout changes, button sizes, and images are rendered correctly on various devices after an update.
Choosing the Right Testing Tool
It’s important to consider your specific testing needs, team skills, and the nature of your software project. Here are key factors to consider when selecting the best generative AI testing tool for your organization:
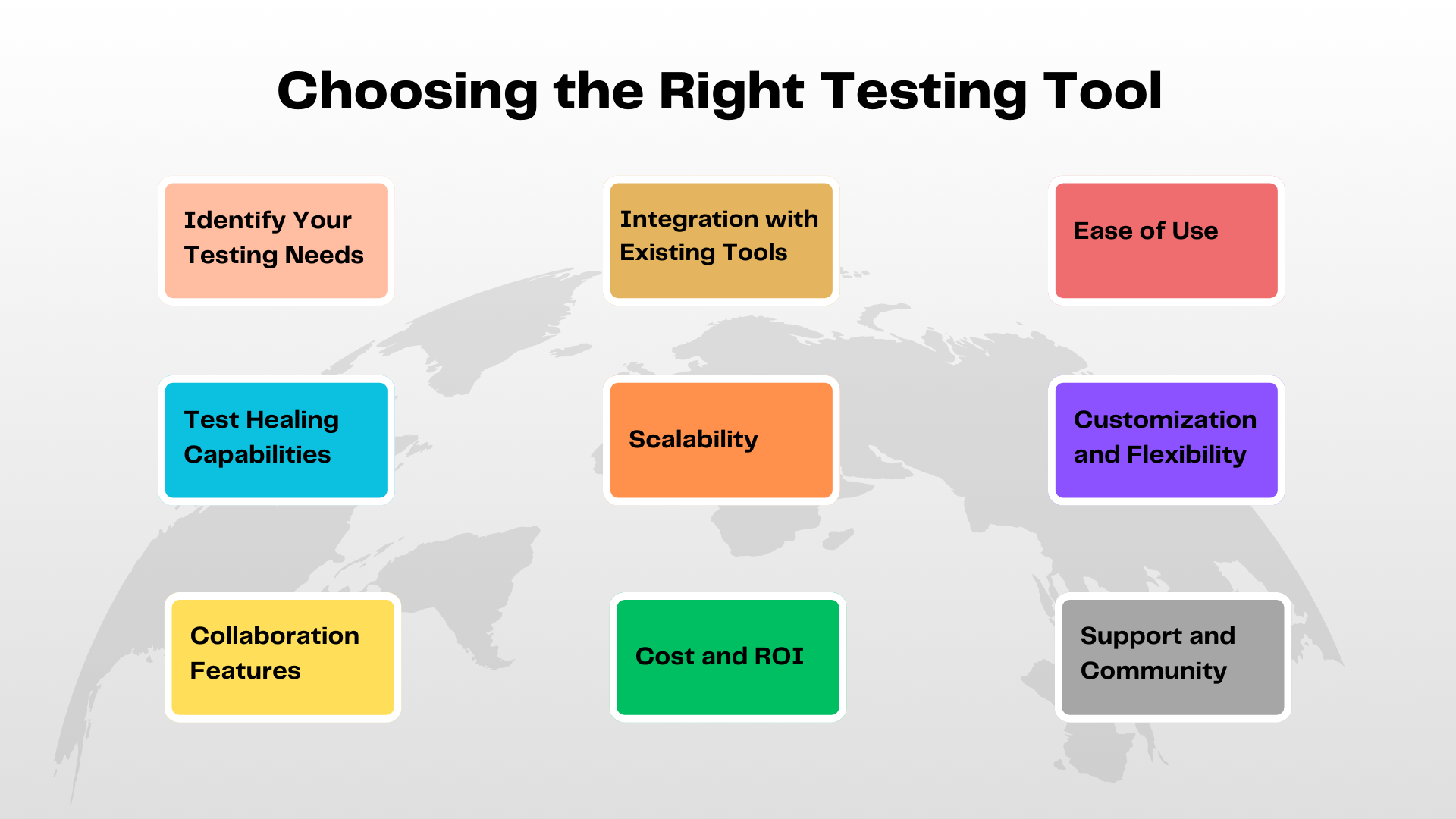
Identify Your Testing Needs
- Test Coverage: Determine the scope of testing your application requires. Does your app require functional, performance or visual testing? Some tools specialize in specific areas, like UI testing or load testing, while others provide broader capabilities.
- Test Automation: Identify the level of automation required. Are you looking to automate repetitive tasks like smoke or regression testing or do you need more advanced features like predictive bug detection and test generation?
- Test Complexity: Consider whether your tests are simple or complex. For example, if your app requires a lot of edge-case testing, you’ll need a tool that can automatically generate comprehensive test scenarios.
Integration with Existing Tools
- CI/CD Integration: Ensure the AI testing tool integrates seamlessly with your CI/CD pipeline.
- Tool Compatibility: Consider how well the AI testing tool integrates with your existing test frameworks and technology stack.
- Cloud/On-Premises: Based on your organization’s needs, determine whether the tool supports cloud environments, on-premises setups, or hybrid infrastructures.
Ease of Use
- User Interface: Choose a tool with an intuitive and user-friendly interface. A clean, easy-to-navigate interface is important, especially if non-technical team members (e.g., product managers or business analysts) need to be involved in writing or interpreting test cases.
- No-Code or Low-Code Features: Some generative AI testing tools provide no-code or low-code capabilities that allow non-technical users to create tests by simply describing business logic or user stories. This is very useful if you have stakeholders who need to contribute to the testing process but don’t have programming expertise.
- Ease of Setup: Look for a tool with straightforward installation and configuration. The faster and easier it is to set up, the sooner you can start leveraging its features.
Test Healing Capabilities
- UI and Code Changes: If your application undergoes frequent UI updates or refactoring, look for tools that can detect changes in the UI or code and automatically adjust the test scripts to ensure they remain valid.
- Test Maintenance: Evaluate how well the tool handles test maintenance as your application evolves. A self-healing tool can reduce the overhead of manual script updates and save valuable time.
Scalability
- Handling Larger Projects: Ensure that the tool can scale with your project as it grows. For large applications or organizations with extensive test suites, the tool should be able to handle a high volume of tests and data.
- Load and Performance Testing: If your app needs stress or performance testing, choose an AI tool that can simulate realistic user behavior and traffic load to ensure scalability under real-world conditions.
- Cross-platform Testing: If your application needs to be tested across multiple devices, browsers or platforms, ensure the AI testing tool supports cross-platform compatibility and testing automation.
Customization and Flexibility
- Custom Test Design: Even with AI-driven automation, customization is important. Ensure the tool allows you to tailor the test generation, test data, and reporting features to meet your specific testing requirements.
- Support for Different Testing Types: Depending on your needs, choose a tool that supports multiple testing types (e.g., functional, regression, performance, security) and can handle both automated and manual tests seamlessly.
Collaboration Features
- Team Collaboration: Some AI testing tools provide collaboration features such as shared test reports, issue tracking, and the ability to assign tasks to different team members. These features are useful for teams working across different departments or locations.
- Integration with Issue Tracking Systems: Tools that integrate with issue tracking platforms like Jira can streamline communication between QA, development, and product teams and can allow easier defect management and faster feedback loops.
Cost and ROI
- Pricing Structure: Review the pricing model to ensure it fits within your budget. Some tools offer pay-as-you-go models, while others may require a subscription or upfront payment.
- Return on Investment: Consider the long-term value and potential cost savings the tool will provide by reducing manual testing efforts, improving test coverage, and accelerating the release cycle. Tools that automate repetitive tasks and improve efficiency often deliver significant ROI over time.
Support and Community
- Customer Support: Choose a tool with strong customer support options that include documentation, tutorials, and access to a knowledgeable support team in case you run into technical issues.
- Active User Community: An active user community can provide valuable insights, share best practices, and offer solutions to common problems. This can be especially beneficial as you scale the use of AI testing tools across your team or organization.
Developing a QA Strategy with Generative AI
Incorporating generative AI into a QA strategy requires careful planning and consideration. Here are some steps that an organization can follow:
- Define Your Goals: Start by identifying what you hope to achieve through implementing generative AI in your QA process. This could range from improving test coverage, reducing the time spent on manual testing, enhancing the detection of bugs and vulnerabilities, or a combination of these.
- Understand Your Testing Needs: Not all applications or software will benefit from generative AI testing in the same way. Understand the specific needs and challenges of your testing scenario and consider whether generative AI can address them effectively.
- Assess Your Infrastructure: Generative AI requires substantial computational resources. Hence, it is necessary to ensure your infrastructure can support these demands. This might mean investing in hardware upgrades or cloud-based solutions.
- Choose the Right Tools: There are various generative AI models and tools available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Evaluate these options in terms of your defined goals and testing needs to select the most suitable ones.
- Train Your Team: Implementing generative AI in QA will require your team to have the necessary skills to work with AI systems effectively. This might involve training in AI fundamentals, how to interpret AI-generated test results, and how to troubleshoot potential issues.
- Implement and Monitor: Once you have defined your goals, understood your testing needs, assessed your infrastructure, chosen the right tools, and trained your team, it is time to implement the strategy. Begin by introducing AI in a few key areas and gradually expanding its use. Regularly monitor and review the performance of the AI in your testing process to ensure it is meeting your goals.
Conclusion
The integration of Generative AI marks a transformative shift in QA, enabling automated, context-aware testing that significantly improves efficiency, coverage, and alignment with CI/CD pipelines while continuously learning and evolving. Although challenges exist in model complexity, workflow integration, and ethical considerations such as bias and privacy, the long-term benefits far outweigh these hurdles when adopted responsibly. Embracing Generative AI is not just a tooling upgrade but a paradigm shift toward a future where AI and human testers collaborate to deliver higher-quality, more reliable software.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












