How Testers Need to Prepare for a Job in 2026
|
|
The software testing landscape has evolved more rapidly in the last three years than in the previous twenty. With the fast adoption of AI, rapid releases, no-code automation, and cross-functional product teams, the expectations of organizations for testers are changing dramatically. As 2026 approaches, testers must prepare themselves to contribute, collaborate, and remain relevant in a world where machines are increasingly handling repetitive tasks while humans focus on strategy, reasoning, and quality leadership.
This article examines the preparation required for a testing job in 2026, including the necessary skills, tools, and knowledge to excel in the role.
| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
The Testing Landscape of 2026
By 2026, the quality function in most organizations will no longer be limited to executing test cases or running regression suites; instead, it will encompass a broader range of activities. Quality is becoming a holistic discipline spanning development, design, operations, and customer experience.
To prepare for a testing job in 2026, testers need strong fundamentals, proficiency in one programming language (Python, Java, JS), mastery of automation tools, API testing, CI/CD knowledge, Git, Jira, and DevOps. They also require essential soft skills, such as data analysis, product thinking, and clear communication, to shift from test management to quality intelligence. AI-assisted testing, cloud, and performance testing will also be relevant.

Key trends defining 2026
Here are the key trends in testing that will be prominent in 2026:
-
AI-Driven Development and TestingAI is already being utilized in the testing world for generating code, writing unit tests, analyzing logs, assisting teams in detecting anomalies, and even suggesting fixes. These agents are expected to become standard assistants that handle routine tasks (up to 40% by 2026). Read: What are Vibe Coding and Vibe Testing?
-
Shift-Left and Shift-Right ConvergenceShift-left encourages early quality involvement in requirements and architecture, while shift-right emphasizes monitoring in production. By 2026, these two approaches will merge into the idea of continuous quality and feedback, where testers influence quality at every stage. Read: Shift Everywhere in Software Testing: The Future with AI and DevOps
-
No-Code and Low-Code Test AutomationThe rise of human-readable, AI-powered automation platforms reduces dependence on automation scripting skills. Organizations want testers who can design intelligent test flows using no-code/low-code automation tools like testRigor, rather than maintaining brittle scripts. Read: The Differences Between Low-Code and No-Code Platforms That You Need to Know
-
Continuous Delivery and Rapid ReleasesMost organizations will release updates multiple times per day. This demands smarter automation, faster failure detection, and real-time feedback loops.
-
Self-Healing TestsTest scripts requiring minor changes will be automatically updated by AI, reducing maintenance. Read: AI-Based Self-Healing for Test Automation
-
Cloud-Native TestingCloud infrastructure will be utilized extensively for scalable and efficient testing. Read: Cloud Testing: Needs, Examples, Tools, and Benefits
-
IoT and EdgeA significant amount of automation effort will be dedicated to the Internet of Things (IoT) and edge computing.
-
Security FirstIntegrating security testing and secure practices from the beginning of the development cycle.
Technical Skills Testers Must Build by 2026
To remain relevant by 2026, software testers must develop technical skills beyond manual testing, with a strong focus on automation, AI collaboration, and a comprehensive understanding of the entire software development lifecycle (SDLC). The goal is to transition from executing tests to becoming quality enablers who contribute to faster and more stable releases.
The technical skills that testers must focus on are:
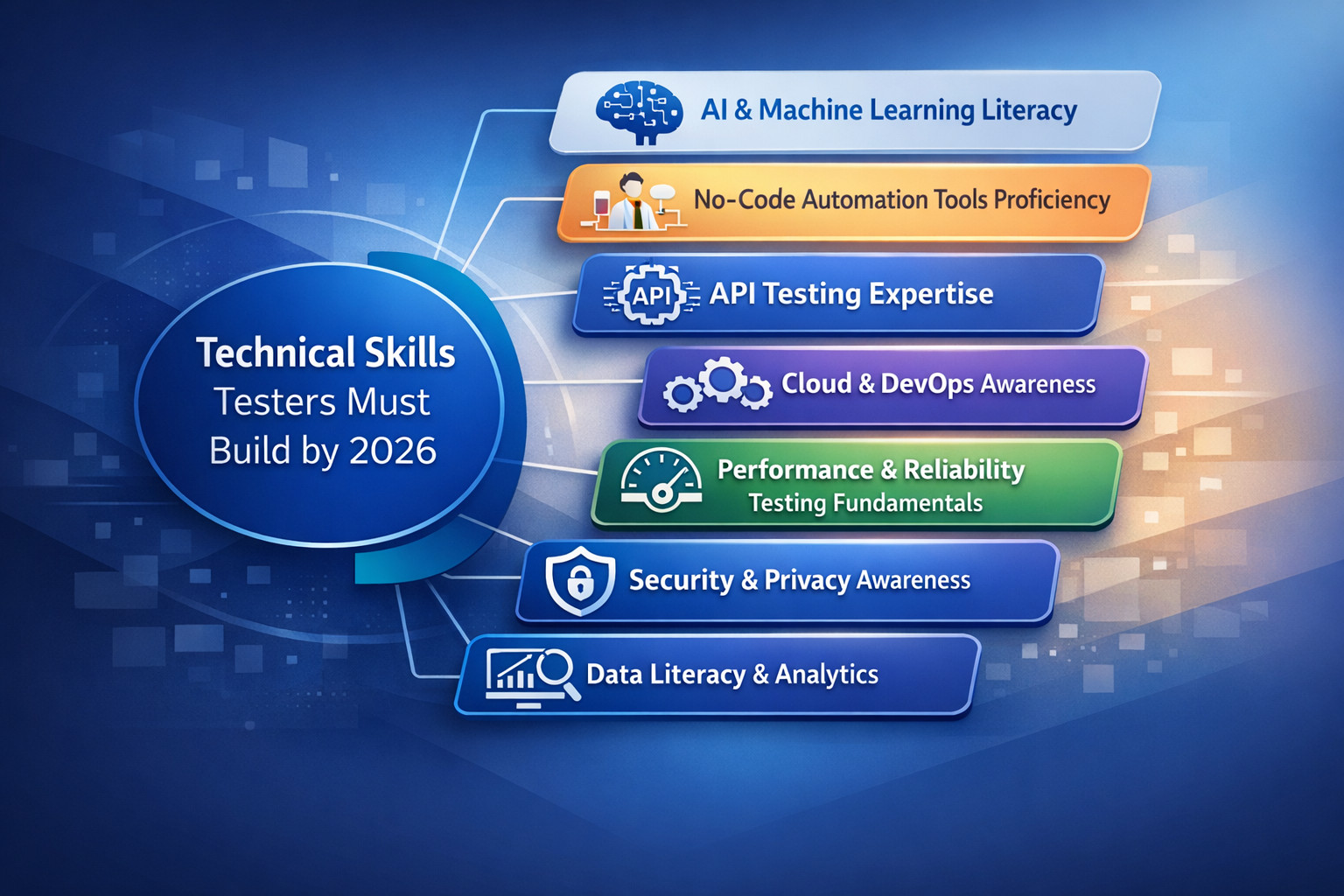
AI and Machine Learning Literacy
Testers don’t need to become data scientists, but they should understand how AI and machine learning work.
Testers need to view AI as a “copilot” for efficiency, rather than a replacement. They can use AI primarily for:
- Prompt engineering to generate test ideas, edge cases, or analyze failures.
- Understand how AI models interpret behavior and how to use AI-assisted tools for tasks like defect clustering and self-healing scripts.
- Apply critical judgment to review AI outputs for errors, biases, or hallucinated requirements.
- Design test scenarios for probabilistic outputs.
- Validate AI performance and drift.
- Work with tools that use AI for test creation.
Organizations expect testers to understand:
- How AI models make decisions.
- How to test AI-driven systems.
- Bias, fairness, and ethical considerations.
- Non-deterministic behavior.
- Data quality issues.
No-Code Automation Tools Proficiency
By 2026, most regression automation will be built by AI and no-code tools like testRigor.
Testers should be able to:
- Write clear, behavior-driven scenarios.
- Design reusable test flows.
- Allow AI to generate tests while maintaining quality control.
Manual scripting won’t be as essential, and the ability to design and verify test logic intelligently will be the most important factor.
API Testing Expertise
Microservices are dominating the architecture landscape, and API testing is no longer optional.
Testers should know:
- Technologies such as REST, GraphQL, and gRPC.
- API testing platforms like Postman, Swagger, and automated API frameworks.
- Contract testing
- API performance and security considerations.
Organizations in 2026 are expected to prioritize testers who can validate systems where UIs are only one small layer.
Cloud and DevOps Awareness
Software runs on distributed cloud platforms, and so must your testing. CI/CD and DevOps integration in QA is now part of the continuous delivery pipeline, rather than a final phase.
Testers should understand:
- CI/CD pipelines with Git workflows and version control.
- Infrastructure-as-Code basics.
- Containers (Docker) and orchestration (Kubernetes).
- Cloud monitoring and observability tools.
- Canary deployments and feature flags.
- Integration of test suites with CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or Azure DevOps.
Performance and Reliability Testing Fundamentals
With systems becoming global and high-traffic, organizations want testers who understand:
- Load testing
- Stress and endurance testing.
- Error budgets and SLOs.
- Monitoring performance in production.
- Tools like JMeter, k6, Gatling, and Locust.
Performance failures are often more costly than functional bugs, and hence, testers should have thorough knowledge of performance testing.
Security and Privacy Awareness
Security testing is becoming a shared responsibility, and testers are expected to act as security gatekeepers, integrating security checks early in SDLC. Testers must understand:
- Common vulnerabilities and familiarity with security testing tools, such as OWASP ZAP or Burp Suite, are required to identify these vulnerabilities.
- How to design security-aware test cases.
- How authentication and authorization flows work.
- Data privacy regulations and testing implications.
- Understanding concepts like data encryption, authentication, and compliance regulations (e.g., GDPR).
Data Literacy and Analytics
Testers need to transition from intuition-based decisions to using empirical data.
- Using programming/scripting languages like Python or SQL for advanced analytics on defect trends and test coverage.
- Proficiency in data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI to translate quality metrics into meaningful business insights.
Soft Skills That Will Matter the Most in 2026
Technology evolves quickly, but what sets testers apart are human skills, those that AI cannot replace. For software testers in 2026, soft skills are as essential as technical expertise, as the role evolves from simple “bug finders” to strategic quality advocates and technology partners within integrated, agile teams. The soft skills that will matter the most for testers are:
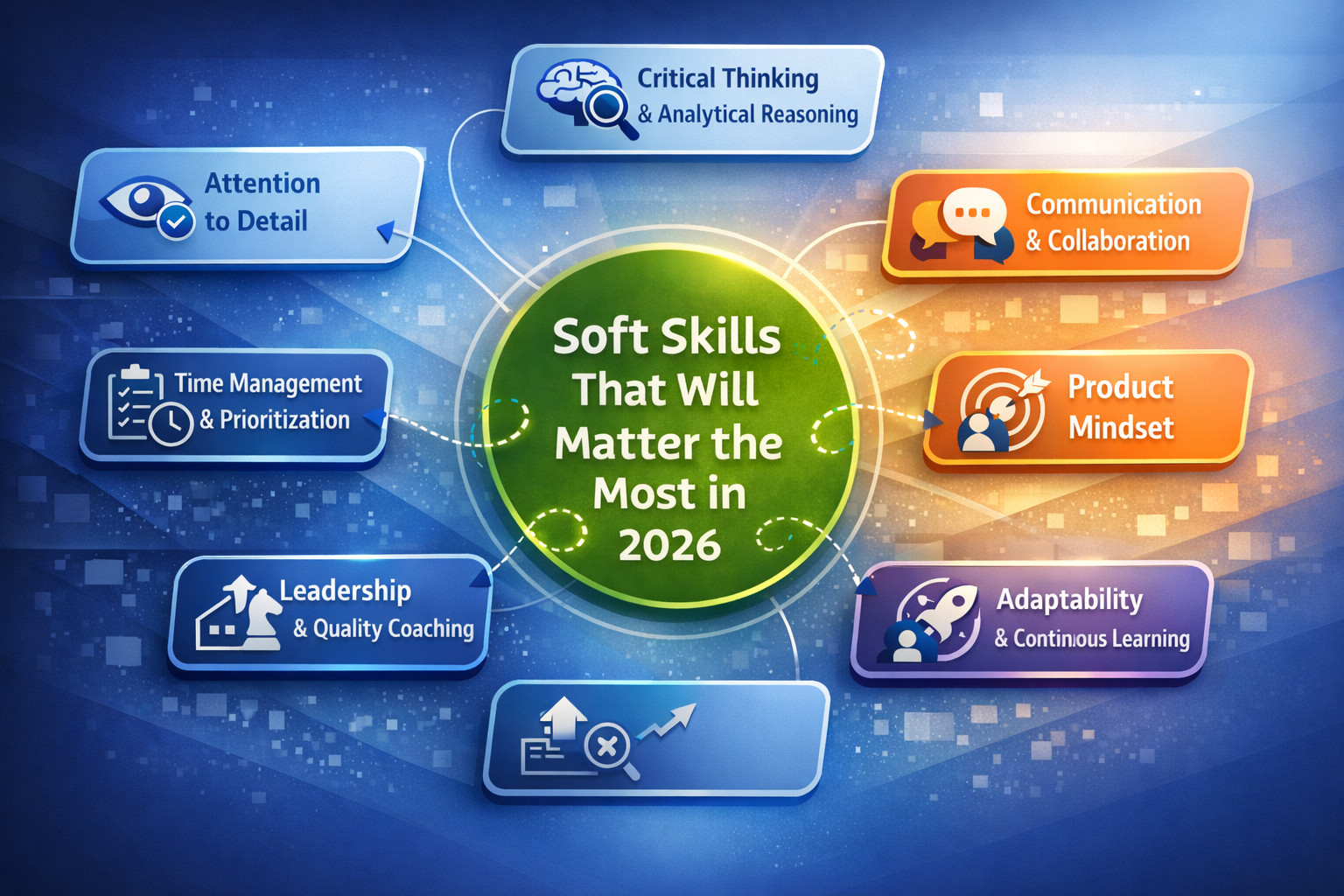
Critical Thinking and Analytical Reasoning
AI tools can automate the routine tasks, but tasks such as analyzing complex issues, thinking beyond obvious scenarios, and identifying potential problems that automation might miss require human critical thinking.
In 2026, testers will spend less time executing tests and more time:
- Evaluating risk.
- Interpreting ambiguous results.
- Asking “What could go wrong?”
- Challenging assumptions.
- Identifying edge cases AI might miss.
Communication and Collaboration
Effective verbal and written communication is essential for documenting bugs clearly, designing test plans, and explaining complex risks to non-technical stakeholders (product owners, managers, clients). Effective communication also involves active listening and knowing how to provide constructive feedback without causing friction within the team.
Testers are increasingly involved in cross-functional Agile and DevOps teams, requiring seamless collaboration with developers, product managers, business analysts, and operations teams.
Product Mindset
Testers should be able to think like an end-user, considering how features will affect the accessibility, user experience, and usability. They should not just test whether the application functions as intended.
Instead of focusing only on defects, testers must understand:
- User behavior
- Business goals
- Market expectations
- Value delivery
This product-centric mindset helps prioritize testing efforts based on business impact and real-world user needs.
Adaptability and Continuous Learning
The technology landscape and testing methodologies are constantly evolving. The tools you use today will not be the ones you use in 2026. Testers must learn quickly and embrace change instead of resisting it. They should be eager to learn new skills and be flexible in their testing approaches to keep up with rapid development cycles.
Leadership and Quality Coaching
Testers are increasingly expected to act as quality advocates with strong negotiation and persuasion skills to influence product decisions. They should ensure that software quality remains a priority amid strict deadlines. Testers should:
- Mentor developers on writing good tests.
- Coach teams on quality practices.
- Facilitate risk discussions.
- Influence architecture decisions.
Time Management and Prioritization
Testing environments are becoming fast-paced with tight deadlines. Testers must be able to prioritize tasks effectively, manage their time efficiently, and make informed decisions about what to test thoroughly versus superficially, using a risk-based approach.
Attention to Detail
This is a critical skill in testing, as it involves the ability to meticulously scrutinize requirements, test cases, and application behavior to spot minute inconsistencies. It is a core competency that prevents minor issues from becoming catastrophic problems later on.
Testing Mindsets That Will Define Success in 2026
A set of forward-looking mindsets that combine human skills with emerging technologies will define success in 2026, emphasizing continuous learning, adaptability, and purpose-driven action.
Key testing mindsets that will define success in 2026 include:
Becoming an AI Supervisor
While AI handles test execution, test generation, and maintenance, testers, just like developers supervising in the DevOps era, must supervise:
- Test coverage
- AI-generated test logic
- Flaky detection
- Data integrity
Prioritizing Risk Over Coverage
It is impractical and unnecessary to aspire for 100% coverage. Instead, testers must:
- Identify highest-risk areas.
- Focus on testing areas where failure affects the most.
- Continuously re-evaluate risk as systems evolve.
Risk-driven testing is the new foundation of a test strategy that enables thorough testing of high-risk areas.
Testing with Production Awareness
With CI/CD pipelines, production is no longer separate from the testing lifecycle. Testers must be knowledgeable of:
- Distributed logs
- Real-time performance
- User analytics
- Feature flag behavior
- Observability dashboards
Quality insights are increasingly derived from the real world, rather than test environments.
Thinking at System Level
With technologies like microservices, distributed systems, and integrations, testers must adopt a systems-thinking mindset and pay more attention to:
- Dependencies
- Failover behavior
- Bottlenecks
- Data propagation
Testers should be aware that UI testing alone cannot ensure reliability in 2026.
Tools Testers Should Learn Before 2026
To remain relevant and in demand by 2026, software testers should prioritize mastering tools and skills related to AI-powered testing, API automation, and DevOps integration. The role of a tester is shifting from manual execution to a more strategic, engineering-focused approach to quality assurance.
The following table provides details of the various tools testers should learn:
| Type of Tool | Examples |
|---|---|
| AI and No-Code Automation |
|
| API and Integration Testing |
|
| Performance Testing |
|
| CI/CD and DevOps Tools |
|
| Version Control |
|
| Cloud Monitoring and Observability |
|
| Security Tools |
|
How Testers Can Prepare for the 2026 Job Market
To thrive in a testing career in 2026, it is not enough to learn new skills. Testers should also prepare themselves for jobs by doing the following:
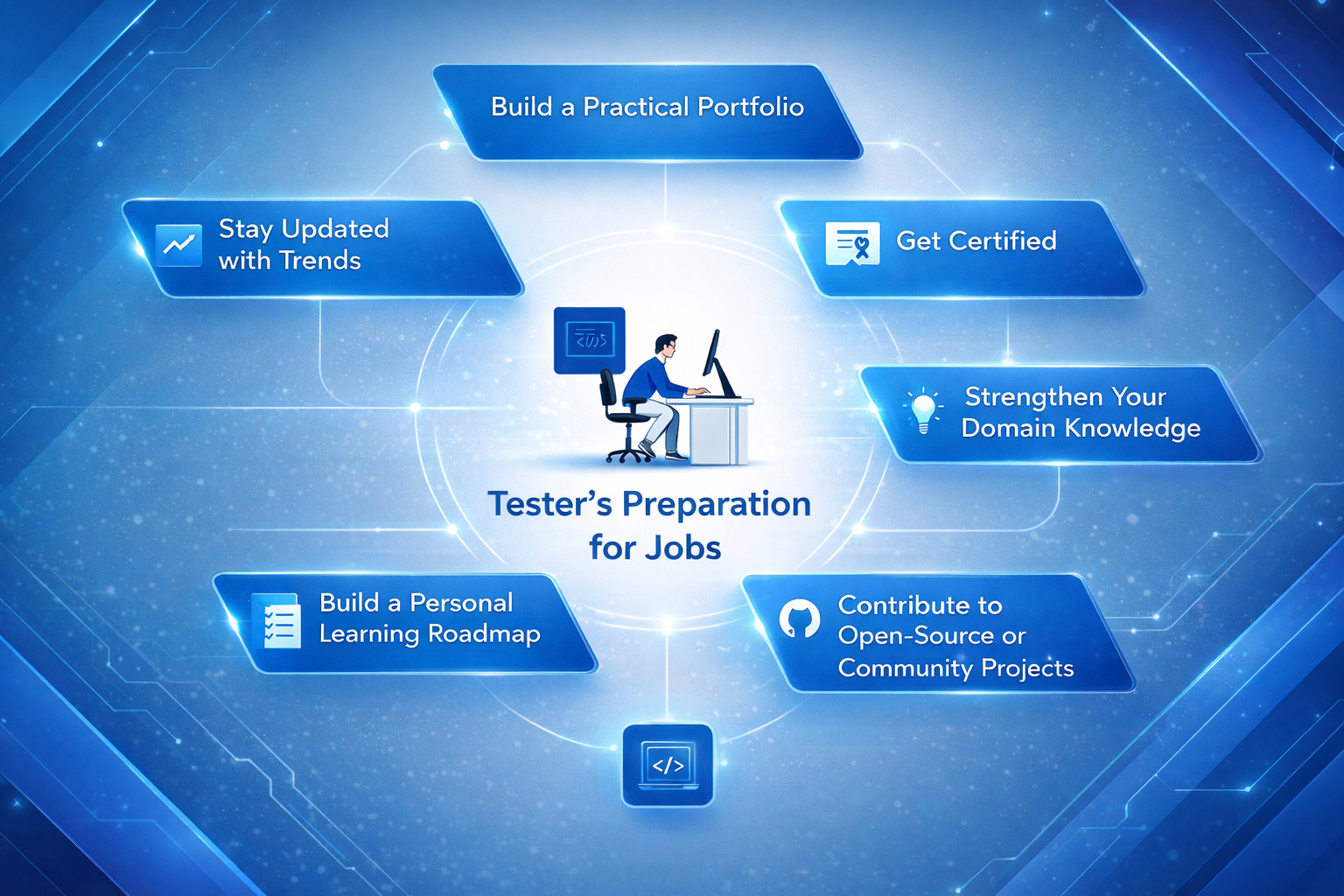
Build a Practical Portfolio
Create samples that highlight the work you have done, such as:
- Test strategies
- API test collections
- AI-generated automation suites
- Performance reports
- Risk assessments
- Data dashboards
Portfolios help candidates to stand out in competitive markets.
Get Certified
Consider applicable certifications, including:
- ISTQB (foundation or advanced, if practical for your region)
- AI testing certifications
- Cloud certifications (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- API testing certifications
- Security certifications (entry level)
Certifications help recruiters quickly validate your skill set.
Strengthen Your Domain Knowledge
In 2026, Industries are looking for testers with domain knowledge of FinTech, healthcare, e-commerce, telecommunications, AI-driven solutions, Robotics, and IoT, among others. Acquire knowledge in various domains to enhance your value in the job market.
Contribute to Open-Source or Community Projects
Working on community or open-source projects demonstrates collaboration, leadership potential, your real-world testing experience, and comfort with distributed systems.
The experience you gain from working on these projects goes a long way in securing your testing career.
Build a Personal Learning Roadmap
Build a personal learning roadmap to include what you want to learn. One such sample roadmap for you may include:
- Learn API testing deeply.
- Get comfortable with AI-assisted automation.
- Master one no-code platform.
- Understand cloud environments.
- Build performance testing fundamentals.
- Improve communication and risk analysis skills.
Note that it is best to progress consistently instead of learning everything at once.
Stay Updated with Trends
Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and innovations in software testing. To stay informed, follow testing conferences, industry newsletters, and the work of AI/tech thought leaders. Join various testing communities and listen to testing-related podcasts/webinars.
The Future Role of Testers in 2026 and Beyond
By 2026, the tester role is expected to evolve into that of a Quality Strategist, AI Supervisor, or Quality Coach, rather than a manual executor of test cases.
Testers will not perform the following tasks anymore:
- Repetitive regression tests.
- Manual test case updates.
- Script-heavy automation maintenance.
- Large, isolated test teams.
Instead, what they will do is:
- Design intelligent, risk-based scenarios.
- Collaborate closely with developers.
- Shape AI-generated automation suites.
- Provide quality insights at every phase.
- Drive continuous improvement.
- Advocate for the customer perspective.
AI is not replacing testers, but is replacing the repetitive work that testers should no longer have to do.
Conclusion
The testing profession is entering a golden era, where testers move from mechanical execution to strategic influence. But success in 2026 requires embracing change, learning continuously, and expanding beyond the traditional boundaries of manual or scripted testing.
To remain competitive, testers must:
- Combine AI knowledge with human intelligence.
- Think at a system and product level.
- Become fluent in no-code automation, API testing, and DevOps concepts.
- Build strong communication and analytical skills.
- Adopt a mindset of continuous learning and adaptability.
The testers who thrive in 2026 will be those who understand that quality is not a phase, a job title, or a checkbox; it is a shared responsibility and a strategic capability. If you prepare today, the opportunities in 2026 will be more exciting, impactful, and rewarding than ever before.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












