CI/CD Series: GitLab CI with testRigor
|
|
testRigor has native integrations with the most popular test management tools, CI/CD systems, and code repositories. This means that there is no more dependency on external plugins or writing heavy custom code for communicating with other applications.
To help you get started quickly, we will show you how to connect testRigor to a GitLab repository in just a few easy steps.
Version Control & Automated Testing with GitLab and testRigor
In GitLab CI pipelines, Git isn’t just a version control system—it’s the heartbeat of automation. When paired with testRigor, Git becomes the trigger, the context, and the audit trail for every test run.
Here’s how testRigor fits into a GitLab-driven testing strategy:
- Centralized test automation: Store your testRigor scripts,
.gitlab-ci.ymlpipeline config, and application code in the same Git repository. This ensures every test run is traceable to a specific commit or merge request. - Trigger tests on merge events: GitLab CI can be configured to run testRigor tests automatically when code is merged into branches, like
mainordevelop. This ensures that no change goes untested. - Branch-aware testing: Use GitLab’s branch filters in
.gitlab-ci.ymlto run different test suites or environments depending on the branch. testRigor’s scripts can adapt based on the branch context. - Scripted integration: testRigor provides ready-to-use Bash scripts that authenticate, trigger test execution, and poll for results. These scripts are versioned in Git and pasted directly into your GitLab pipeline.
- Full visibility: GitLab’s pipeline logs and testRigor’s execution reports together provide a complete picture of what was tested, when, and why—ideal for debugging, audits, and compliance.
With Git as the foundation and testRigor as the testing engine, GitLab CI becomes a powerful, automated quality gate—ensuring every commit is validated before it reaches production.
Integrating testRigor with GitLab Repository
As we can see, on today’s date, every growing company has implemented Continuous Integration and Continuous Development. Whenever any kind of code gets merged into the GitLab code branch, the automation tests need to be triggered and run to make sure there is no failure with the latest code changes. This continuous integration pipeline is straightforward to build in testRigor.
Prerequisite
- You need to have a testRigor account. Also, you need to create a test suite with test cases for execution. If you are new to testRigor and want to learn about creating test scripts for different scenarios, these How-to Articles will help you.
- You need to have a GitLab account with a valid repository.
Steps for testRigor GitLab CI Integration
Step 1: Open the Test Suite in testRigor. On the left side menu, click the CI/CD Integration link. The CI/CD integration page is populated with pre-defined scripts.
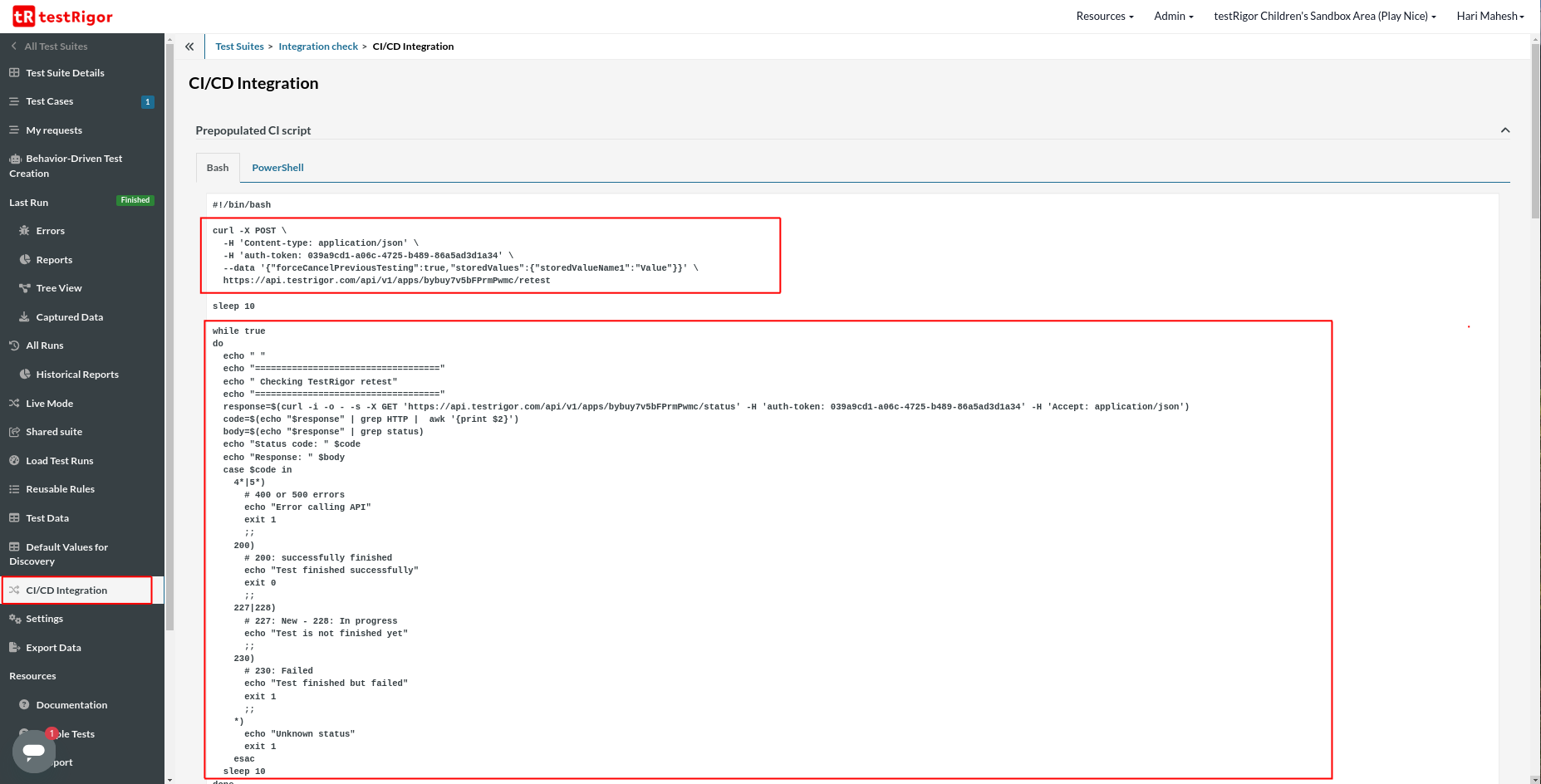
The above test script consists of multiple parts. The first part executes the tests in the test suite. The command contains the test suite authentication token unique to every test suite. Once that command is executed, the test suite will wait for 10 seconds, and then the loop will continue to execute. The script will check the results of the retest. Once the retest is complete, the script will exit.
Step 2: In the GitLab project repository, look for the file “.gitlab-ci.yml” at the root level. If the file doesn’t exist, you can create a new file and ensure the name matches what’s mentioned here. If the file exists, you can edit it.
So, to integrate with testRigor, we need to paste the testRigor script into the test section of the YAML file.
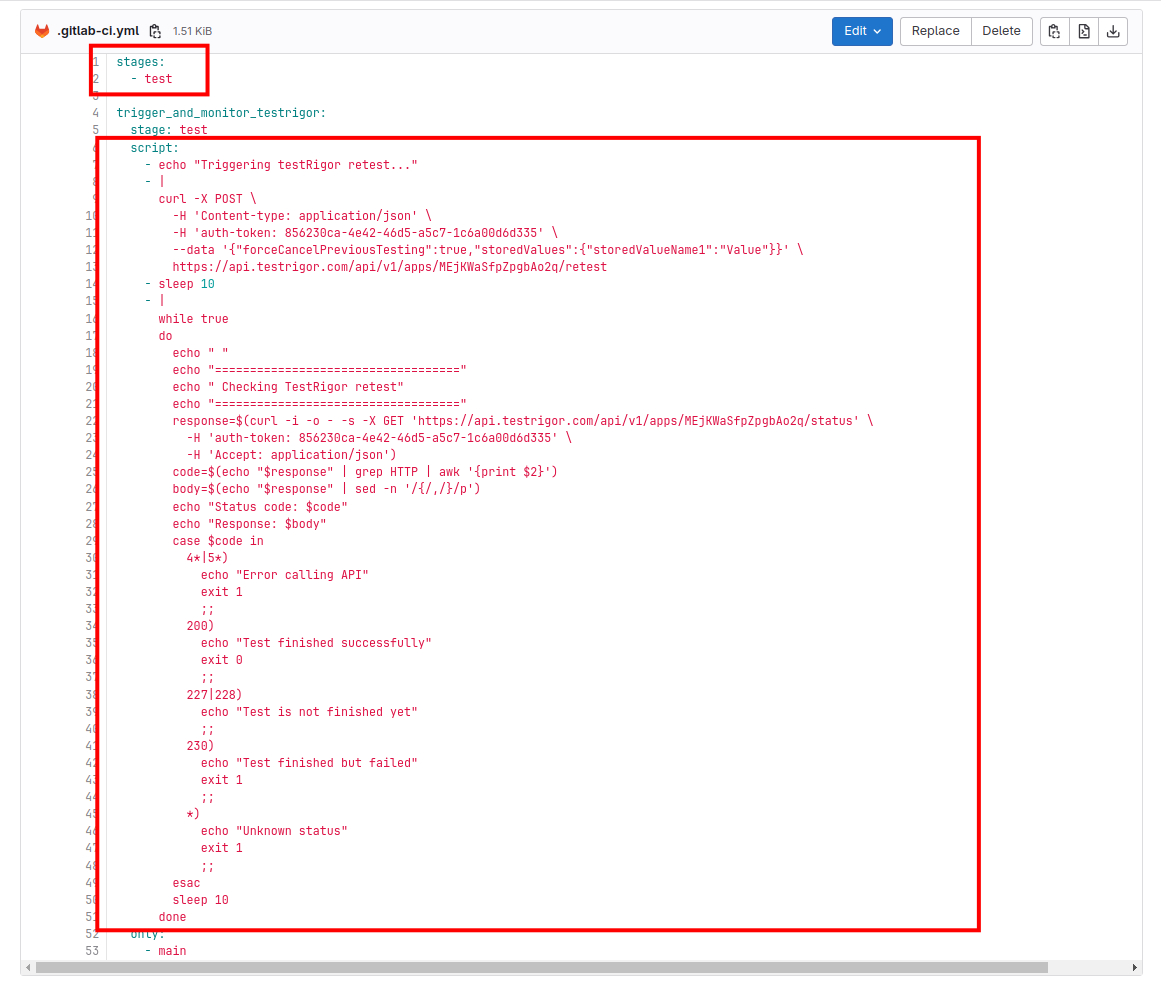
Currently, we are configured to check for any pull request merges in the “Main” branch. If you need to change the branch name, you can mention the branch name under the “Only” option in the yaml file.
Step 3: Once the script is updated, click Commit Changes, which will reflect the changes in the file.
Step 4: To check the integration, let’s create a sample branch and a file. Let’s create a sample Python file named add.py.
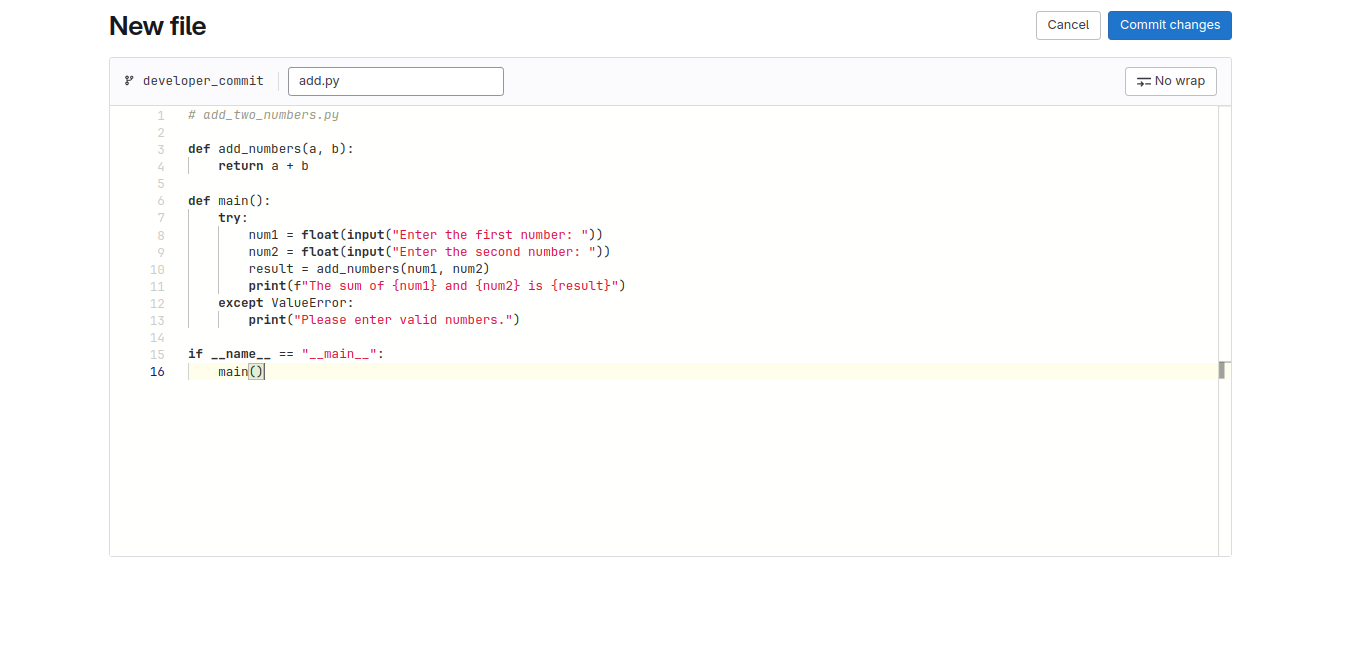
Step 5: Commit the file and then create a Merge request.
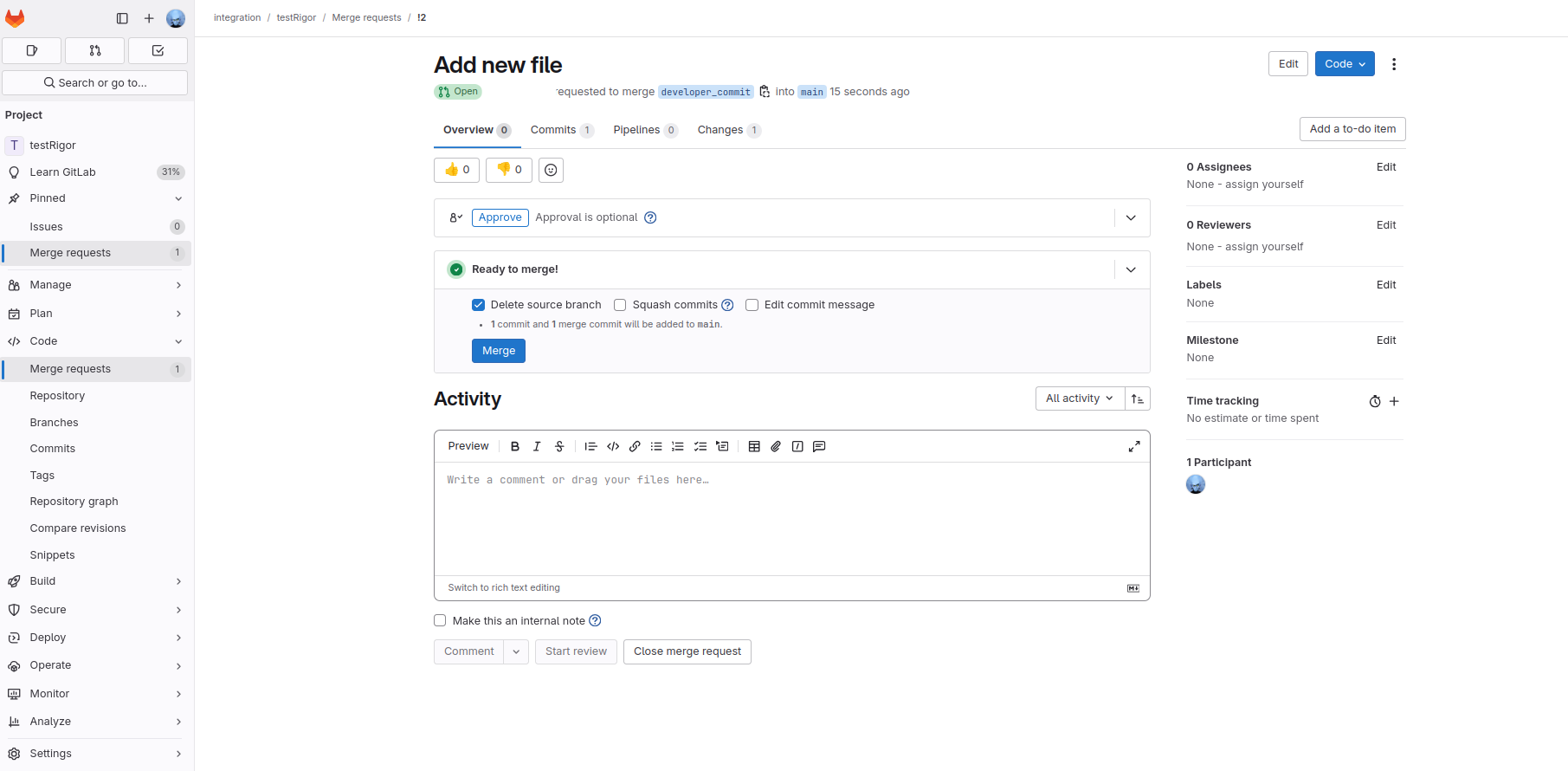
Step 6: Once you merge the pull request, you can see in GitLab that the pipeline has started execution.
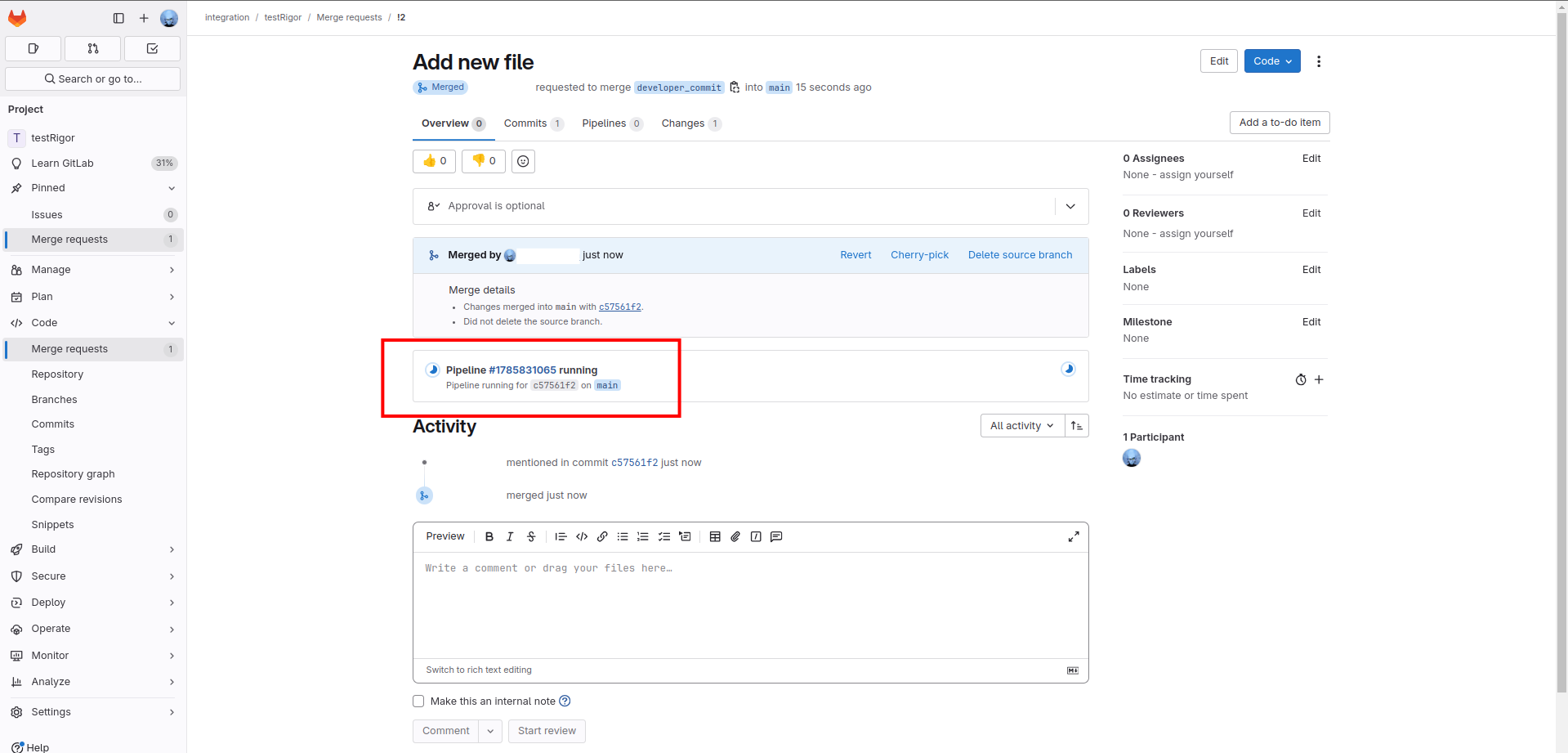
Step 7: You can check the same in testRigor. You can see that the test has triggered and that execution has started.
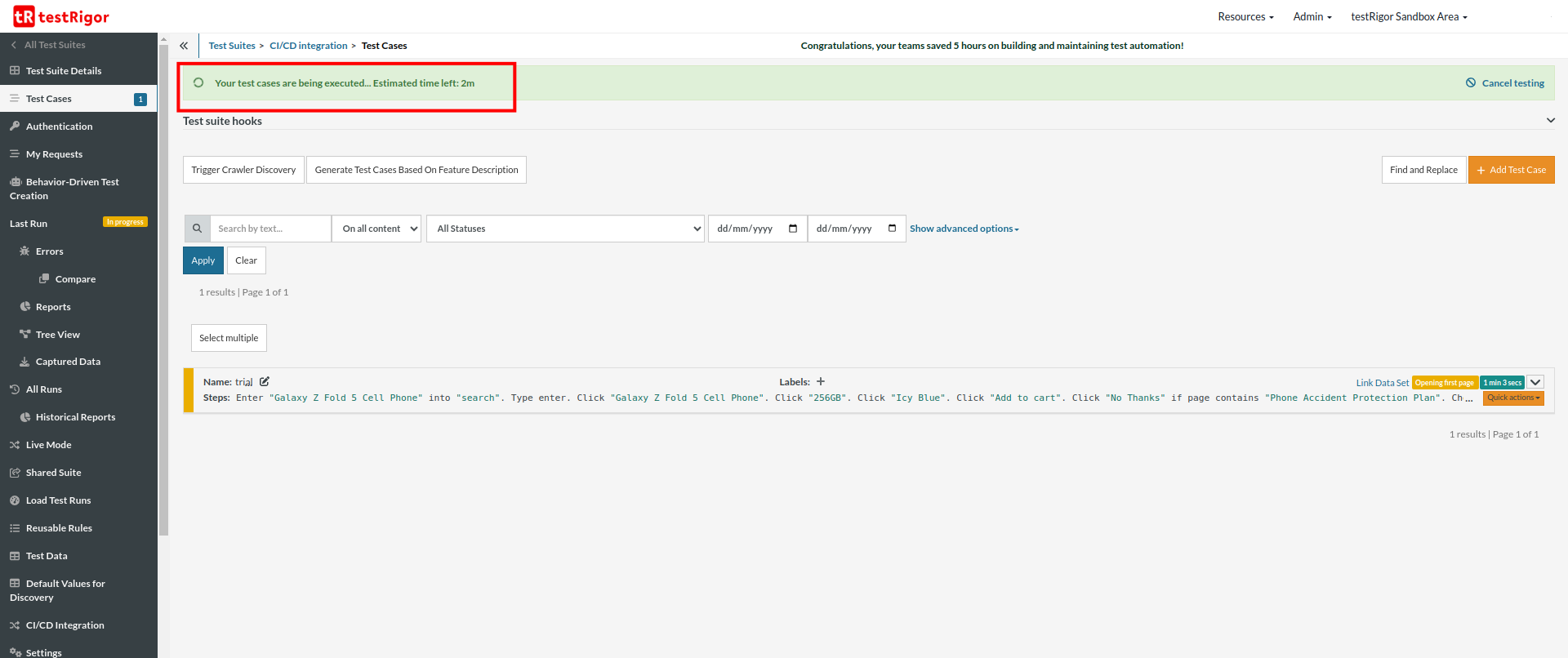
Step 8: Click on the pipeline ID to see the console output of the testRigor execution.
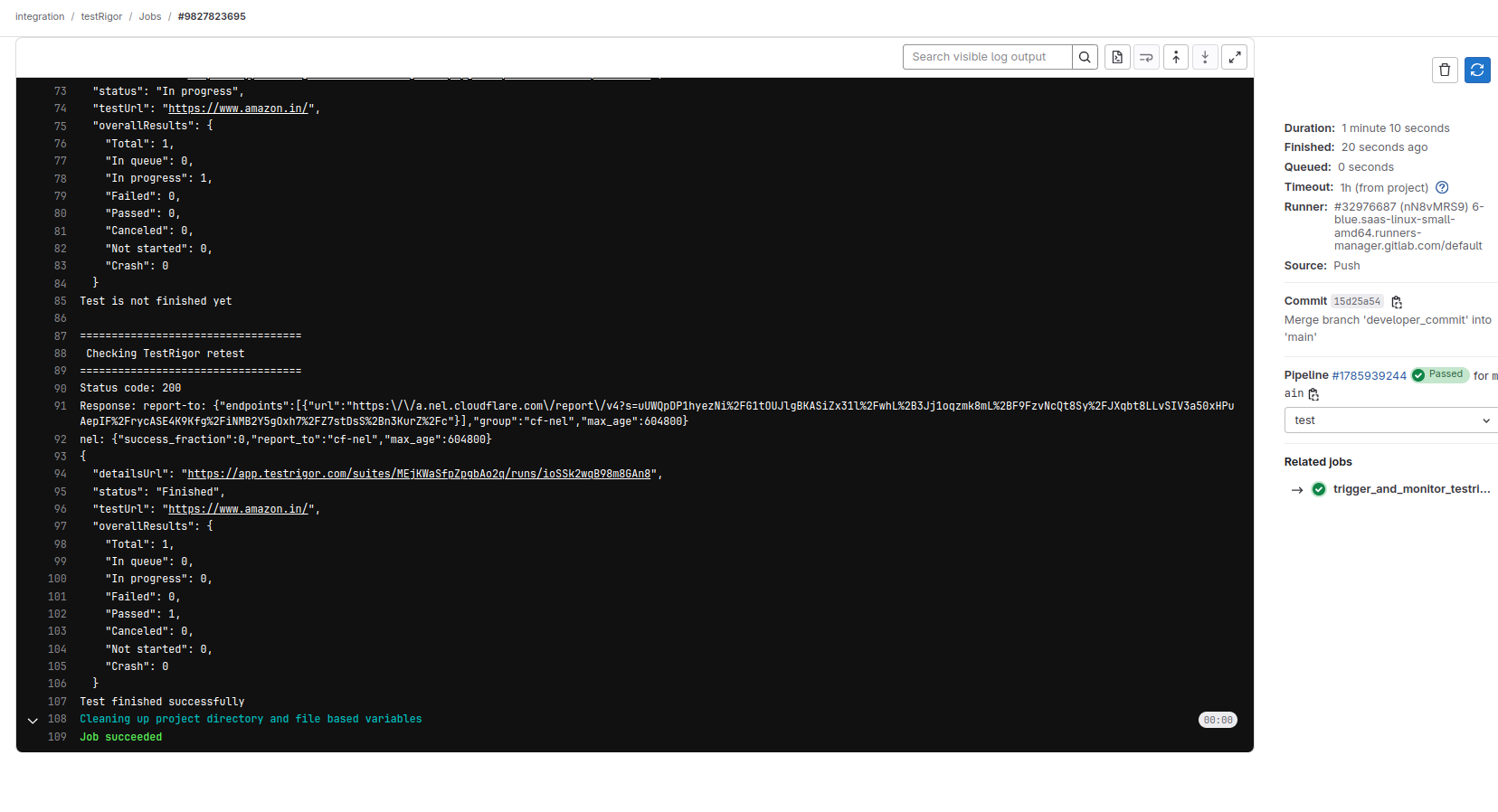
That’s all you need to integrate testRigor with GitLab for continuous integration. As you can imagine, this whole procedure is quick, easy, and hassle-free.
testRigor’s Capabilities
Apart from the simplistic test case design and execution, testRigor’s advanced features help you test your application using simple English commands. testRigor enables you to test native desktop, web, mobile, API, visual, exploratory, AI features, accessibility testing with minimum effort, time, and maintenance, single-handedly.
- Reusable Rules (Subroutines): You can easily create functions for the test steps that you use repeatedly. You can use the Reusable Rules to create such functions and call them in test cases by simply writing their names. See the example of Reusable Rules.
- Global Variables and Data Sets: You can import data from external files or create your own global variables and data sets in testRigor to use them in data-driven testing.
- 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha Resolution: testRigor efficiently manages the 2FA, QR Code, and Captcha resolution through its simple English commands.
- Email, Phone Call, and SMS Testing: Use simple English commands to test the email, phone calls, and SMS. These commands help validate 2FA scenarios, with OTPs and authentication codes being sent via email, phone calls, or via phone text.
- File Upload/ Download Testing: Execute the test steps involving file download or file upload without the requirement of any third-party software. You can also validate the contents of the files using testRigor’s simple English commands.
- Database Testing: Execute database queries and validate the results fetched.
- Test the Untestable: Use testRigor’s other AI-based features that help test the untestable like graphs, images, chatbots, LLMs, Flutter apps, mainframes, form filling, and many more.
Read: All-Inclusive Guide to Test Case Creation in testRigor.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












