Why Gen AI Adoptions are Failing – Stats, Causes, and Solutions
|
|
In a world where AI, generative AI in particular, is so popular, one could be forgiven for thinking of it as the panacea for just about anything. Billions are being invested in Gen AI initiatives by companies vying for a competitive advantage. But behind that hype is a hard truth: Many of these projects are stalling or crumbling. They get stuck in the pilot phase, don’t scale, or just don’t deliver on their promise.
This isn’t a failure of the technology itself. Instead, it’s a failure to properly plan, manage, and execute. In this article, we’ll cut through the noise to explore the key reasons why Gen AI adoption is falling short at so many companies.

AI Adoption Trend – MIT reports 95% of Generative AI Pilots at Companies are Failing
A new report by MIT’s NANDA initiative, “The GenAI Divide: State of AI in Business 2025”, has found that 95% of corporate generative AI pilot projects are failing to deliver measurable financial returns. This study, based on interviews with leaders, employee surveys, and an analysis of over 300 public AI initiatives, highlights a significant gap between the hype surrounding AI and its actual business impact.
Here are the main patterns that were observed during this study:
- Limited Structural Disruption: Despite all the buzz, generative AI isn’t yet a game-changer across the board. The report reveals that only two (tech and media) out of eight major sectors are showing meaningful, structural changes due to AI. This means that for most industries, AI is still more of a tool for individual tasks than a force that’s fundamentally reshaping how businesses operate.
- The Enterprise Paradox: You might think that big companies, with their deep pockets and vast resources, would be leading the charge in AI. The report shows that they are indeed leading in the number of pilot projects they launch. However, they are falling behind smaller, more agile firms when it comes to scaling these projects into full-blown production. This creates a paradox where big firms are exploring AI more but are less effective at making it a core part of their business.
- Investment Bias: Companies are investing in the wrong places. The study points out a clear bias: budgets are favoring AI projects that are visible and customer-facing, like those in sales and marketing. These projects are often aimed at boosting the “top-line” revenue. Meanwhile, the report found that the highest return on investment (ROI) is actually in back-office functions like procurement and finance, which can deliver significant cost savings and efficiency gains. This focus on flash over substance is a major reason for the low overall ROI.
- The Implementation Advantage: Trying to build an AI solution from scratch is a risky business. The report found that companies that partner with an external vendor have a success rate that is twice as high as those that try to build everything internally. This suggests that the real advantage in AI implementation isn’t in developing your own models but in strategically partnering with experts who can customize and integrate solutions effectively.
The report further highlights that the 5% of companies that are succeeding focus on a single pain point, execute well, and partner smartly with companies that provide tools that can be customized to their processes.
Let’s debunk the causes of this failure to launch gen AI projects and the ways to be successful.
The Root Causes of Gen AI Adoption Failure
While the potential of generative AI is immense, its implementation is proving to be a minefield. The reason for these failures isn’t a lack of technological prowess; it’s a series of common, and often avoidable, mistakes. Here’s what’s really happening behind the scenes.
A Flawed Approach
The problem isn’t about the AI itself but how companies are approaching it. The biggest mistake is treating a complex, strategic deployment like an off-the-shelf purchase. They either try to build a generic tool that doesn’t fit their unique needs or rush to adopt a solution without a clear use case. The most successful companies take a deliberate, strategic approach, customizing and adapting the technology to their specific business problems.
The Learning Gap
When you use a consumer-facing tool like ChatGPT, it feels like a flexible, ever-improving assistant. It adapts to your style and gets better the more you use it. However, in the corporate world, many enterprise AI systems are far more rigid. They’re built and then essentially left to be. They don’t learn from new data, they don’t adapt to the way your team actually works, and they certainly don’t get smarter over time. This lack of continuous learning makes them static and quickly outdated, so they can’t keep up with the dynamic needs of a business.
Poor Integration
A great AI tool is useless if it can’t talk to the rest of your systems. Many pilot projects are built as standalone solutions. They might be amazing at one specific task, but they don’t integrate with your existing CRM, enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, or other critical software. This creates more friction than it solves, limiting the benefits to a single user or a small team instead of making a meaningful impact across the entire organization.
Unrealistic Expectations and Vague Goals
The biggest mistake companies make is treating Gen AI as a magic wand. They hear about the technology’s capabilities and decide they need it without first defining a specific, measurable business problem to solve. They’ll launch a project to “improve efficiency” or “boost innovation” without a clear path or way to measure success. This often leads to a solution that looks impressive in a demo but doesn’t actually solve a real-world problem or provide any tangible business value. Without a clear goal from the start, it’s impossible to know if the project is a success.
Misaligned Investment
Where a company puts its money says a lot about its priorities. Right now, most businesses are spending a lot on customer-facing AI applications for sales and marketing. But the report shows that the real value lies elsewhere. The highest returns come from automating “boring” back-office functions like finance, procurement, and operations. By chasing the flashy front-end applications, companies are missing out on the biggest opportunities to drive real savings and efficiency.
The “Pilot-to-Production” Gap
Many companies successfully run small, contained pilot projects only to find that they can’t scale them. This is a classic problem in software development, and it’s even more pronounced with AI. A Gen AI model that works in a controlled environment often fails when it needs to be integrated into an organization’s complex existing IT infrastructure. The model might not be able to handle the volume of requests, or it might not connect seamlessly with other business systems. The result? A great idea that never makes it to the finish line because it was never designed for the real world.
Organizational and Cultural Hurdles
Finally, it’s not just about the tech; it’s about the people.
The introduction of AI can create fear and skepticism among employees who worry about job displacement. If leadership doesn’t communicate transparently, involve employees in the process, and provide proper training, resistance will build. Without a solid change management strategy, employees may be reluctant to adopt the new tool, leading to a perfectly functional AI system that nobody uses. This lack of buy-in and a general reluctance to adapt to new workflows can be the final nail in the coffin for an AI project.
How to Make Your Generative AI Initiative a Success
Companies that are winning with AI aren’t just buying better technology; they’re adopting a smarter strategy.
Build a Learning-Focused System
Opt for AI systems that are designed to learn. The most successful solutions are those that retain feedback, adapt to workflows, and continuously improve. This ensures your AI investment grows in value alongside your business.
Integrate Deeply
Your AI tools must be built to work seamlessly with your existing technology stack. Instead of a general-purpose tool, look for a solution that can be deeply embedded into a specific, high-value workflow. This reduces friction, drives adoption, and ensures the benefits are shared across the entire team.
Start Small, Scale Smart
The most effective approach is to start with a narrow, high-value problem. Launch a small pilot project with a clear, measurable goal. Once you prove its value and establish a smooth workflow, you can confidently scale it across the organization.
Invest Strategically
Shift your focus from “cool” to “profitable.” While customer-facing AI is important, the biggest returns are in back-office automation. By strategically automating tasks in finance and operations, you can unlock significant cost savings and free up your employees to focus on higher-value work.
Partner with Experts
You don’t have to do it alone. The report highlights that companies that partner with external AI vendors are twice as likely to succeed as those that try to build everything in-house. These vendors are experts at customizing and integrating solutions, helping you avoid common pitfalls.
Example of a Successful Generative AI Adoption
testRigor is an example of a generative AI tool that allows you to customize and scale your test automation. Here’s a success story.
IDT Corporation had a goal of automating 90%+ of its test cases. They started working with Selenium and quickly climbed up to 33-34%. But then, after about a year, as the software started changing, engineers started spending all of their time maintaining the Selenium test cases instead of writing new ones. Results didn’t improve for about 3 years as test maintenance kept wearing them down.
After a lot of research, the company decided to go with testRigor. A big push for them to work with testRigor was when they saw that some of their interns, who had no prior coding background, were able to automate test cases using testRigor. Once they moved to testRigor, they went from 34% automation to 91% automation in 9 months.
Read the full story over here – How IDT Corporation went from 34% automation to 91% automation in 9 months.
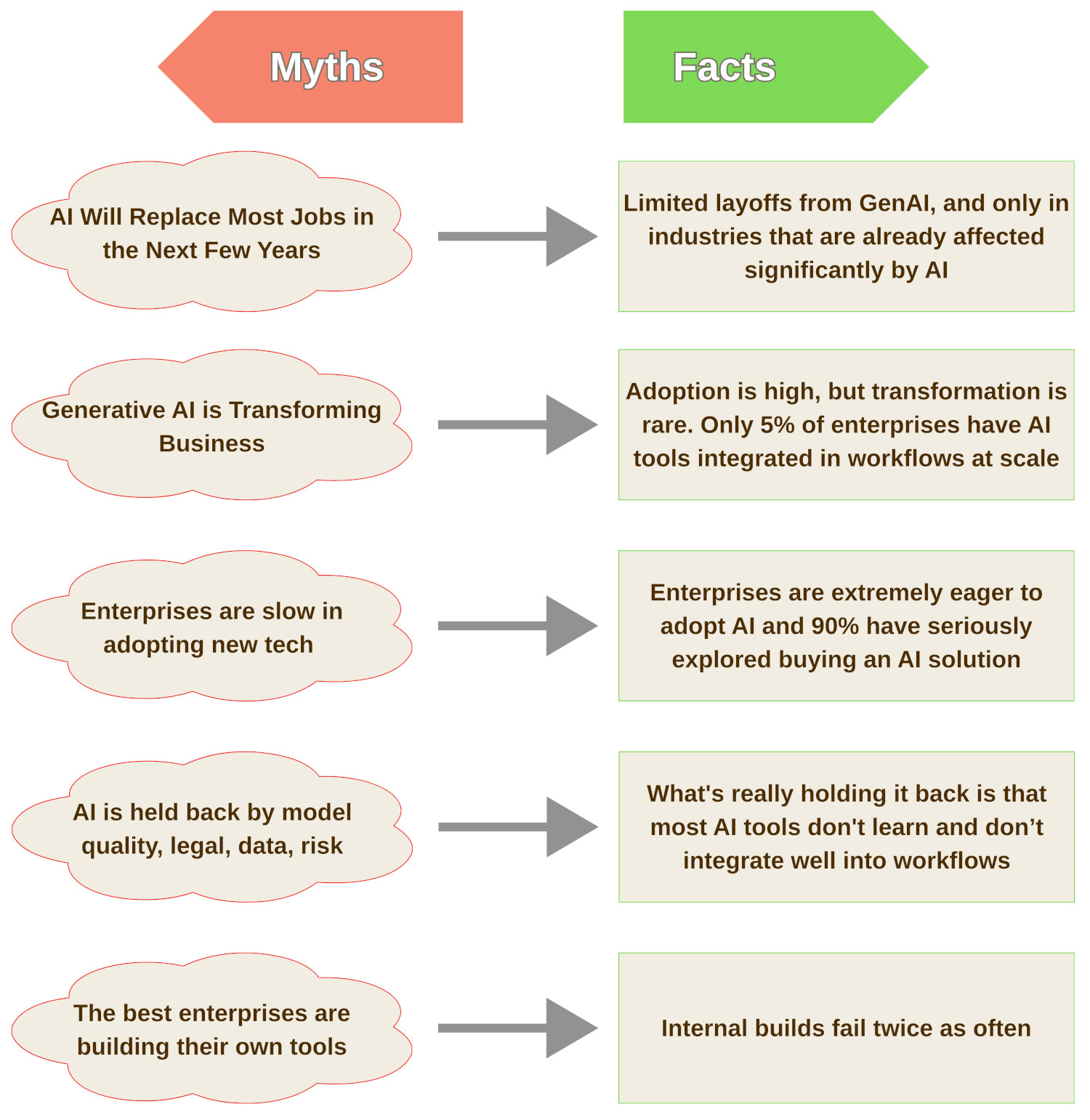
Facts and Myths About Gen AI (According to the Report)
Conclusion
To successfully adopt generative AI within organizations, one needs to partner with the right vendors, constantly customize the AI solutions to fit their ecosystem, and select tools that can integrate well and scale over time.
As AI keeps growing, we can expect to see the next evolution beyond individual AI agents is an agentic web. This is where autonomous systems can discover, negotiate, and coordinate across the entire internet infrastructure, fundamentally changing how business processes operate. The infrastructure foundations for this transformation are already emerging through protocols like the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
Additional Resources
- AI and ML Top Agenda for APAC CIOs
- Is AI Slowing Down Test Automation? – Here’s How to Fix It
- What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) vs. AI Agents
- Weak AI vs. Strong AI
- AI in Engineering – Ethical Implications
- What is Multimodal AI?
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












