Wealth Management Testing: Ensuring Financial Systems and Client Data Integrity
|
|
If you’ve heard the term “wealth management”, you might think it’s just a fancy way of saying “investing”. While investing is a big part of it, true wealth management is much broader – it’s like having a dedicated financial quarterback for your entire economic life.
In the finance sector, wealth management is a high-level professional service that combines financial planning, investment portfolio management, and a number of aggregated financial services to meet the needs of affluent clients. Many of these wealth management services are now possible through various software. While this eases the process and automates many aspects of wealth management, it also introduces the challenge of ensuring its quality.
In this article, we’ll be looking at how testing is carried out for wealth management services and products available through digital platforms.

| Key Takeaways: |
|---|
|
Why is Wealth Management Testing Critical?
Software systems that manage people’s assets are the core engine of a financial institution. When these engines fail, the consequences aren’t just technical; they are immediate, disastrous, and often public. Here’s why rigorous testing of wealth management systems is absolutely critical.
- Financial Accuracy: Imagine a system that handles millions of transactions daily, from buying bonds to calculating annual fees. A tiny, overlooked bug in the code for portfolio valuation or performance calculation can lead to massive financial misstatements. Testing ensures financial accuracy is 100% reliable. It prevents small technical glitches from becoming huge financial liabilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Wealth management systems must constantly comply with rules covering everything from how trades are executed (MiFID II) to how client identities are verified (KYC) and how data is protected (GDPR). Testing is the evidence you need to prove compliance and avoid crushing fines.
- Data Integrity and Security: A data breach in this sector can destroy a firm’s reputation overnight. Testing includes rigorous security and penetration testing to find vulnerabilities before hackers do. If clients feel their most private financial information is vulnerable, they will take their money elsewhere immediately. In wealth management, reputation is everything, and a breach can wipe it out instantly.
Read: Automated Testing in the Financial Sector: Challenges and Solutions
Wealth Management System Testing: Most Suited Testing Types
Wealth management systems are too critical to be checked with simple, casual tests. To guarantee the accuracy and safety of client funds and data, testing needs to be strategic and cover every angle – from simple calculations to massive regulatory compliance checks. Here are the most effective methods and testing types used to ensure the integrity of wealth management platforms.
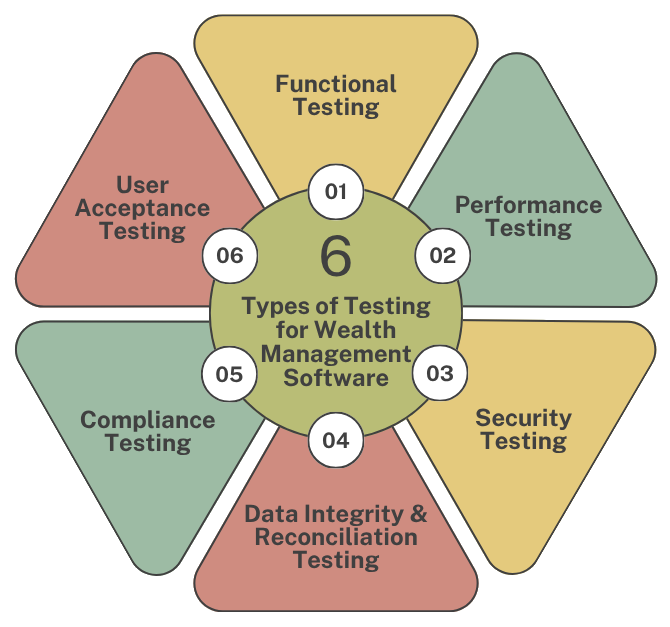
Essential Software Testing Types for Wealth Management Systems
These are the testing types that are vital for wealth management systems.
Functional Testing (Does It Work?)
This is the baseline. It ensures every feature works exactly as the user (the wealth manager or the client) expects it to.
- Key Scenarios: Can a manager successfully set up a new client account? Does the system correctly apply the client’s preferred investment model? Does the “Generate Report” button actually produce a usable PDF?
Read: Functional Testing Types: An In-Depth Look
Regulatory Compliance Testing (The Rule Keeper)
This is arguably the most critical type of testing in the financial sector. It ensures the system’s logic adheres to all government and industry rules.
- Key Scenarios:
- KYC (Know Your Client): Does the system prevent an account from being opened if mandatory identification details are missing?
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering): Does the system correctly flag a rapid series of large deposits from unusual sources?
- Suitability Rules: Does the system record and justify that an investment recommendation is suitable for a client’s stated risk profile and financial goals?
Read: Top Mistakes in Software Standards Compliance
Performance and Load Testing (Can It Handle the Stress?)
When the market is volatile, everyone logs in at once. This testing ensures the system won’t crash when faced with high demand or a huge data spike.
- Performance: Checks the speed of the system (e.g., can a trade be executed in less than one second?).
- Load: Simulates thousands of users logging in, running reports, and executing trades simultaneously to ensure the system scales without slowing down or making errors.
Read: What is Performance Testing: Types and Examples
Security Testing (The Burglar Test)
This is the intentional attempt to break the system’s security defenses, often called Penetration Testing (Pen Testing).
- What it does: Security experts try to hack the application to find weaknesses – like trying to access another client’s portfolio details or injecting malicious code into the system. This is done to secure client data against real-world threats.
Read: Security Testing
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) (The Final Sign-Off)
Before the system goes live, the actual end-users (the wealth managers, advisors, and maybe a few trusted clients) test the final product.
- Purpose: To confirm that the system is not only technically correct but also easy to use and meets the real-world needs of the business. It’s the last chance for the business owner to say, “Yes, I approve this for public use”.
Read: User Acceptance Testing: Manual vs. Automated Approaches
Key Software Testing Methods for Wealth Management Systems
These methods describe how the tests are performed, focusing on efficiency and coverage.
Test Automation
This is the most critical method. Instead of having a human manually click through the system every day (which is slow and error-prone), we write automated scripts that run the same complex tests perfectly, thousands of times.
- Why it’s essential: Wealth management platforms have frequent updates. Automation ensures that a new feature doesn’t accidentally break an old, critical function (like portfolio rebalancing). It’s the backbone of fast, continuous quality.
Read: How to Start with Test Automation Right Now?
Risk-Based Testing
You can’t test everything equally. This method means the testing team works with the business to identify the highest-risk areas and tests those most intensely.
- Examples of High Risk: The calculation of client fees, the logic for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) flags, or the transfer of large sums of money. If a function is legally sensitive or involves high dollars, it gets the most testing.
Read: Risk-based Testing: A Strategic Approach to QA
Data Integrity and Reconciliation
Since these systems are all about numbers and data, this method focuses heavily on whether the data is correct, complete, and consistent across different parts of the bank.
- What it does: Testers compare data from the source system (where a trade originated) with the target system (where it’s stored for reporting). They run SQL queries (database checks) to ensure that the balance in one place exactly matches the balance in another place, down to the last penny.
Read: Database Testing Best Practices
The Path to Continuous Compliance and Quality
For wealth management firms, the goal is to transform testing from a bottleneck to a business enabler.
- Continuous Testing (CT): Integrate automated tests into the development pipeline. Every code check-in should trigger a set of tests, including smoke, regression, and critical compliance checks. This continuous feedback loop ensures issues are found and fixed immediately.
- AI/ML in Testing: Modern testing is being enhanced with Artificial Intelligence (AI) to improve efficiency. AI can prioritize tests based on the risk associated with recent code changes (Predictive Defect Analysis) and automatically detect and adapt to changes in the User Interface (Self-Healing Automation), significantly reducing test maintenance costs.
- Cross-System Integration Testing: Wealth management often involves complex integrations with external systems (custodian banks, market data feeds, FinTech partners). Rigorous API and integration testing must confirm that data exchange is seamless, secure, and preserves data integrity across all boundaries.
- Continuous Compliance: Ensure that every deployed system update adheres to rules (like AML, KYC, GDPR) by design. Specific, automated compliance tests are written directly into the continuous testing process.
Choosing Test Automation for Wealth Management
You need tools that can handle massive complexity, guarantee financial accuracy, and satisfy strict regulators. Here’s a look at the types of test automation tools best suited for the job, and why a new breed of AI-powered platforms like testRigor is changing the game.
The Traditional Toolkit for Financial Software Testing
These tools are powerful but require deep programming skills (usually Java, Python, or JavaScript).
- Examples: Selenium and Cypress
- The Pro: They offer ultimate flexibility. If your wealth platform uses custom, cutting-edge technology, a skilled developer can program a test for almost anything.
- The Con:
- The “Maintenance Trap”: These scripts are extremely brittle. If a designer simply moves a button or changes the layout on the client portal, the code breaks. Your team then spends most of its time fixing broken tests rather than writing new ones, a fatal flaw in a fast-moving financial environment.
- Time-Consuming: In order to write test cases in code, engineers end up spending days trying to get it right.
- Technical Proficiency Needed: Quite often, this translation of a test case into code leads to a less-effective test case since it is quite difficult to code most of those regulatory clauses that need to be checked. Thus, you need experts who can code well.
The Modern Alternative for Financial Software Testing
Wealth management firms need a solution that can be run by the people who know the business best – the manual QA teams and business analysts – without needing programming. This is where tools like testRigor come in, representing the next generation of AI-powered, codeless testing.
1. Plain English Test Creation
Instead of writing lines of code, you write test steps in simple, plain English – just like a manual tester would write a test case.
- Example (Selenium Code):
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='login-button']")).click(); - Example (testRigor Plain English):
click "Login button"
This means your non-technical experts (the ones who truly understand the compliance rules and financial logic) can write and maintain the automated tests, scaling your automation coverage rapidly. This is also suitable for testing end-to-end workflows and compliance regulations.
Unmatched Test Stability (“Self-Healing”)
The biggest problem in financial testing is the “maintenance trap” mentioned above. testRigor uses generative AI and advanced smart logic to interact with elements the way a human would, relying on the visual text or image on the screen, not hidden code details (like XPath).
Thus, if a developer moves a button or changes its color, the test doesn’t break. The AI sees the button is still there and clicks it. This eliminates up to 99% of the maintenance overhead that plagues traditional tools, freeing up your technical staff to focus on complex performance or API testing.
True End-to-End Testing (Across All Platforms)
Wealth management involves many channels: web portals, mobile apps, desktop apps, emails for two-factor authentication (2FA), and even SMS confirmations. testRigor allows you to write one single test script that flows seamlessly across all of these channels.
For example: "Log in on the web portal. Then, check the received SMS for the 2FA code. Enter the code. Finally, verify the portfolio value on the mobile app." This is extremely hard or impossible with traditional, single-channel tools.
login click “Mutual Funds” type “ELSS Tax Saver” into “Search a fund” enter enter click “One Time” enter “500000” into “Amount” click “Place Order” check that page contains "Your Mutual Fund Order Has Been Placed."
You can even test all those dynamic UI elements and AI features like chatbots and LLMs with plain English testRigor test cases.
Conclusion
Wealth management testing isn’t just a technical requirement for the IT department; it’s a core business function. It’s the mechanism that guarantees accuracy, compliance, and security. In an industry where trust is the primary commodity, testing is what allows firms to confidently say: “Your money is safe, your data is secure, and your financial future is in reliable hands”.
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












