The 9 Leading Android Emulators for PCs in 2025
|
|
You can find over 3 million apps on the Google Play Store as of 2025, with a selection of Android apps offering different services like games, social media, news and magazines, productivity, health and fitness, finance, sports, and more. This clearly shows us the unbeatable popularity of Android and, by extension, of mobile devices. In many cases, however, operating Android apps on a mobile device may not suffice, or the device itself may not be accessible. This is mostly seen among gamers or app developers and testers who want the Android experience but with the flexibility and comfort of PCs. This has given rise to the need for emulators in the market to mimic the Android environment on a PC.
Before we carry on with emulators, let’s take a small detour and see how Android rose to popularity and Google’s role in propelling it to its current stardom.
Origins of the Android OS
In August 2005, Google acquired Android Inc., which was founded by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears, and Chris White. Then, in November 2007, Google, along with several other companies in the tech industry, including HTC, Samsung, and Motorola, formed the Open Handset Alliance (OHA) that aimed to develop open standards for mobile devices and promote Android as an open-source OS. Android was released as an open-source operating system under the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) in October 2008. This allowed anyone to use, modify, and distribute Android’s source code freely.
Google introduced the Android Market, now known as Google Play, in October 2008, providing a centralized platform for users to download and install Android apps. Over the years, Google has continued to develop and improve Android, releasing numerous versions with new features and enhancements.
While Android is open source and freely available, Google requires device manufacturers to comply with specific licensing agreements and compatibility requirements to use Google Play services and the Google Play Store. This ensures a consistent Android experience on most devices.
What is an Android Emulator?
Simply put, an emulator lets you mimic one system on another. Android emulators create a virtual Android environment on your computer, complete with an Android OS and access to the Google Play Store, so you can install and use Android apps just as you would on an actual Android device.
Top Android Emulators to Choose From
Most of the Android emulators these days come packed with customization capabilities, built-in screen recording capabilities, support for multiple instances simultaneously, pre-installed Google Play Store, and good performance. If you intend to use an emulator for developing and testing mobile apps, then opting for tools that are compatible with your tech stack and project requirements is essential. With this in mind, let’s take a look at some of the most popular Android emulators available in the market.
Android Studio
Android Studio is the official integrated development environment (IDE) for Android app development and testing. It is a powerful and feature-rich software tool provided by Google, designed specifically for creating Android applications. Android Studio offers a comprehensive set of development tools, a code editor, debugging capabilities, and various resources to streamline the app development process. It also includes an Android emulator that allows developers to run and test their apps on virtual Android devices with various screen sizes, Android versions, and hardware configurations. This open-source emulator is best suited for Android app development and testing rather than gaming. It is compatible with Windows, Linux, and Mac OS.
NOX Player
NOX Player is a popular open-source Android emulator for Windows and Mac. NOX Player is primarily used for gaming, and it offers several features and benefits, like keyboard mapping, controller support, and the ability to run multiple instances simultaneously. However, it is known to strain the system and hence cause lag when too many windows are open simultaneously.
BlueStacks
A long-time market contender, BlueStacks is one of the most popular Android emulators for running apps or playing games on Windows and Mac. While BlueStacks can run any Android app, it is particularly popular among gamers. It offers features like keyboard mapping, gamepad support, and the ability to run multiple instances of the emulator for multitasking or playing multiple games simultaneously. It is known for its stability, performance, and lightweight implementation. BlueStacks offers both a free version and a premium version (BlueStacks Premium) with additional features, such as priority technical support and ad removal.
MEmu
MEmu is another popular Android emulator, similar to BlueStacks and NoxPlayer, that allows users to run Android apps and games on their Windows PC. MEmu is known for its performance, compatibility, and user-friendly interface. One of its popular features is its support for AMD and NVidia graphic cards and different versions of Android like Jelly Bean, Kit Kat, and Lollipop. MEmu supports cloud synchronization, allowing users to sync app data and game progress across different MEmu instances or devices. It is available in both a free version and a premium version with additional features, including priority customer support.
Genymotion
Genymotion is an advanced Android emulator known for its flexibility, powerful features, and performance, making it a popular choice for testing and developing Android applications. It stands out for its focus on providing a virtualized Android environment for various testing scenarios. Genymotion seamlessly integrates with Android Studio and supports a wide range of Android versions, allowing users to create and manage virtual Android devices with different configurations, including various Android versions, screen sizes, and hardware characteristics. It is also compatible with many testing frameworks like Espresso, Appium, and Robotium. They offer various paid plans that include different features.
LDPlayer
LDPlayer is an open-source Android emulator that allows users to run Android games and apps on Windows computers, offering features and optimizations geared towards gaming performance. Most of the high-performing emulators are better suited for high-end devices. However, LDPlayer is able to offer flexibility even to low-end devices. Like the other emulators, LDPlayer also includes a multi-instance sync feature that enables users to create and manage multiple virtual Android devices. It is compatible with various Windows OS versions and is regularly updated to support the latest Android versions.
Bliss OS
This is not your traditional emulator. Bliss OS is an open-source OS based on the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) that is designed to run on personal computers. In essence, Bliss OS allows users to transform their computers into Android-based systems. Bliss OS supports multi-boot setups, meaning you can install it alongside other operating systems like Windows or Linux on the same computer. This allows users to choose which OS to run at startup. Bliss OS offers a high degree of customization, allowing users to tailor the Android experience to their preferences. Users can install and remove apps, customize the user interface, and adjust settings just like on a regular Android device.
GameLoop
GameLoop is a free, Windows-based Android emulator developed by Tencent, one of the largest gaming companies in the world. It was initially known as Tencent Gaming Buddy and was specifically developed for playing Tencent’s popular battle royale game, PUBG Mobile, on PCs. It is primarily designed for gaming and allows users to play Android games on their Windows computers. Over time, it evolved into a more general-purpose Android emulator for gaming. It offers high performance, customizable keyboard and mouse controls, multi-instance support, multi-language support, and regular updates.
Prime OS
Like Bliss OS, this is another open-source option for those who prefer booting the Android OS on their PCs. It aims to provide users with a desktop-like Android experience, making it possible to use Android apps and games on larger screens with traditional input methods like keyboard and mouse. You can open multiple Android apps in resizable windows, similar to how Windows operates on traditional desktop operating systems. There are various customization options, including the ability to change wallpapers, themes, and system settings. It can be installed on a PC in various ways, including as a standalone operating system, alongside existing operating systems in a multi-boot setup, or even as a live USB system for temporary usage.
Built-in Android Emulator Support for App Testing
The above list gives you many options to choose from if you simply want to run Android apps and games on your PC. However, if you are more inclined to do thorough testing of your Android apps, then relying on manual testing through these emulators will not suffice.
You can optimize your testing endeavors by opting for an intelligent testing tool that supports mobile testing.
testRigor for Mobile Testing
testRigor is a holistic solution to mobile testing (Android and iOS apps). It will not only give you the Android emulator environment to test in but also let you automate a variety of test scenarios and cases. Along with desktop testing, you can easily automate the testing of web-based, hybrid, and native mobile apps.
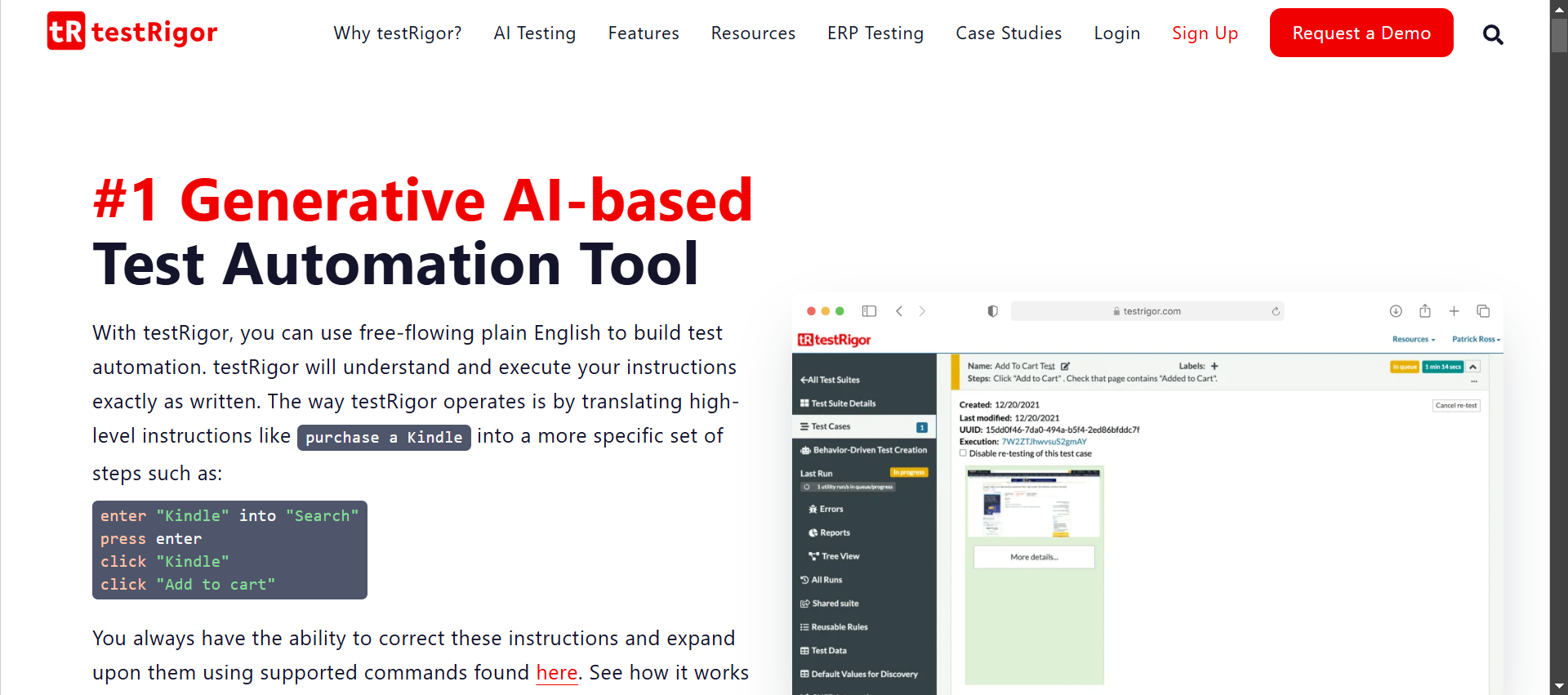
Let’s see how testRigor makes this process easy.
- Does not depend on installations/configurations: testRigor does not bother you with complex setups and configurations to be compatible with underlying code. It is cloud-based and supports end-to-end, functional, system, and UI-based testing. You can get started directly by registering for your account.
- Easy test generation for everyone: Writing tests and interacting with UI elements through test cases is straightforward, thanks to testRigor’s use of generative AI. Use plain English commands, making it ideal for everyone to understand and collaborate on. Moreover, there is no need to find implementation details of complex UI elements visible on the screen because testRigor does not ask you to mention XPaths or CSS tags. All you need to do is mention how the element appears to you on the screen and leave it to testRigor to use AI and ML to find what you are looking for. Read: All-Inclusive Guide to Test Case Creation in testRigor.
- Fast and stable test execution: testRigor uses AI to improve test stability and scalability further to ensure that you get the most stable and accurate test results.
- Easy to use and clean UI: Most often you will find testers and even developers struggling to learn the finer points like scripting language, commands, and system capabilities of an automation framework. With testRigor, this learning is effortless. It has a simplistic UI and elaborate documentation to assist with this.
- All-in-one with testRigor’s supported integrations: You can expand your testing activities by integrating with frameworks and tools that provide device farms, offer CI/CD capabilities, and perform issue and requirement tracking.
- Negligible test maintenance: Due to testRigor’s use of AI to make test creation and execution as painless as possible, test maintenance, which sticks out like a sore thumb for automation testers, is reduced drastically. Read: Decrease Test Maintenance Time by 99.5% with testRigor.
Take a look at this guide on How to automate Android testing with testRigor?
Conclusion
Android emulators are the way ahead for anyone who wants to use Android apps on a larger screen, either for development, testing, gaming, or general day-to-day activities. They offer a great way to get that Android device experience on a PC in a cost-effective manner. In fact, Windows 11 has started supporting installation and running Android apps natively, eliminating the need to install a separate emulator for this task.
Manually testing a mobile app, that too across various devices may not be feasible, even with an Android emulator. This is when you should employ automation testing by using powerful test automation tools like testRigor to get that testing efficiency and not rely solely on manual testing.
Additional Resources
- How to compile for Android Emulator
- Viewing Desktop Websites on an Android Device: How To
- Using Free Android Emulator to Test Apps and Websites
- A guide to using APK files on iOS devices
- Choosing the Best Mobile Testing Option: Real Devices vs. Emulators
| Achieve More Than 90% Test Automation | |
| Step by Step Walkthroughs and Help | |
| 14 Day Free Trial, Cancel Anytime |












